|
Epsilon Columbae
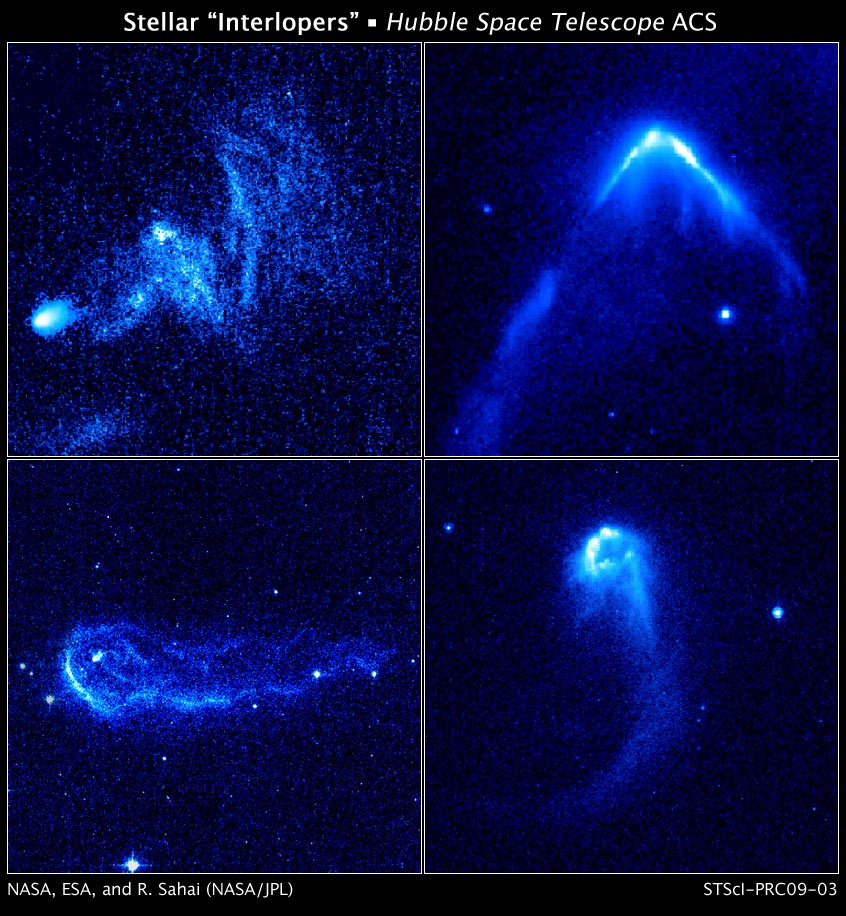
Epsilon Columbae, Latinized from ε Columbae, is a star in the southern constellation of Columba. It is visible to the naked eye, having an apparent visual magnitude of 3.87. Based upon an annual parallax shift of , it is located approximately 262 light years distant from the Sun. The star is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −5 km/s. This is an orange-hued K-type giant star with a stellar classification of K1 II/III. At the age of 1.5 billion years old, it has exhausted the supply of hydrogen at its core then cooled and expanded off the main sequence. Epsilon Columbae has 2.5 times the mass and 25 times the radius of the Sun. The star radiates 251 times the solar luminosity from its enlarged photosphere at an effective temperature of 4,575 K. It has a peculiar velocity of , making it a candidate runaway star In astronomy, stellar kinematics is the observational study or measurement of the kinematics or motions of stars through space. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
J2000
In astronomy, an epoch or reference epoch is a instant, moment in time used as a reference point for some time-varying astronomical quantity. It is useful for the celestial coordinates or orbital elements of a Astronomical object, celestial body, as they are subject to Perturbation (astronomy), perturbations and vary with time. These time-varying astronomical quantities might include, for example, the mean longitude or mean anomaly of a body, the node of its orbit relative to a reference plane, the direction of the apogee or Perihelion and aphelion, aphelion of its orbit, or the size of the major axis of its orbit. The main use of astronomical quantities specified in this way is to calculate other relevant parameters of motion, in order to predict future positions and velocities. The applied tools of the disciplines of celestial mechanics or its subfield orbital mechanics (for predicting orbital paths and positions for bodies in motion under the gravitational effects of other bodi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Luminosity
The solar luminosity (), is a unit of radiant flux (power emitted in the form of photons) conventionally used by astronomers to measure the luminosity of stars, galaxies and other celestial objects in terms of the output of the Sun. One nominal solar luminosity is defined by the International Astronomical Union to be . This does not include the solar neutrino luminosity, which would add , or , i.e. a total of (the mean energy of the solar photons is 26 MeV and that of the solar neutrinos 0.59 MeV, i.e. 2.27%; the Sun emits photons and as many neutrinos each second, of which per m2 reach the Earth each second). The Sun is a weakly variable star, and its actual luminosity therefore fluctuates. The major fluctuation is the eleven-year solar cycle (sunspot cycle) that causes a quasi-periodic variation of about ±0.1%. Other variations over the last 200–300 years are thought to be much smaller than this. Determination Solar luminosity is related to solar irradiance (the solar c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Draper Catalogue Objects
Henry may refer to: People *Henry (given name) *Henry (surname) * Henry Lau, Canadian singer and musician who performs under the mononym Henry Royalty * Portuguese royalty ** King-Cardinal Henry, King of Portugal ** Henry, Count of Portugal, Henry of Burgundy, Count of Portugal (father of Portugal's first king) ** Prince Henry the Navigator, Infante of Portugal ** Infante Henrique, Duke of Coimbra (born 1949), the sixth in line to Portuguese throne * King of Germany ** Henry the Fowler (876–936), first king of Germany * King of Scots (in name, at least) ** Henry Stuart, Lord Darnley (1545/6–1567), consort of Mary, queen of Scots ** Henry Benedict Stuart, the 'Cardinal Duke of York', brother of Bonnie Prince Charlie, who was hailed by Jacobites as Henry IX * Four kings of Castile: **Henry I of Castile **Henry II of Castile **Henry III of Castile **Henry IV of Castile * Five kings of France, spelt ''Henri'' in Modern French since the Renaissance to italianize the name and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Durchmusterung Objects
In astronomy, Durchmusterung or Bonner Durchmusterung (BD) is an astrometric star catalogue of the whole sky, compiled by the Bonn Observatory in Germany from 1859 to 1903. The name comes from ('run-through examination'), a German word used for a systematic survey of objects or data. The term has sometimes been used for other astronomical surveys, including not only stars, but also the search for other celestial objects. Special tasks include celestial scanning in electromagnetic wavelengths shorter or longer than visible light waves. Original catalog The 44 years of work on the Bonner Durchmusterung (abbreviated BD), initiated by Friedrich Argelander and largely carried out by his assistants, resulted in a catalogue of the positions and apparent magnitudes of approximately 325,000 stars to apparent magnitude 9–10. The catalogue was accompanied by charts plotting the positions of the stars, and was the basis for the ''Astronomische Gesellschaft Katalog'' (AGK) and ''Smithsonia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayer Objects
Bayer AG (, commonly pronounced ; ) is a German multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company and one of the largest pharmaceutical companies in the world. Headquartered in Leverkusen, Bayer's areas of business include pharmaceuticals; consumer healthcare products, agricultural chemicals, seeds and biotechnology products. The company is a component of the Euro Stoxx 50 stock market index. Bayer was founded in 1863 in Barmen as a partnership between dye salesman Friedrich Bayer and dyer Friedrich Weskott. As was common in this era, the company was established as a dyestuffs producer. The versatility of aniline chemistry led Bayer to expand their business into other areas, and in 1899 Bayer launched the compound acetylsalicylic acid under the trademarked name Aspirin. In 1904 Bayer received a trademark for the "Bayer Cross" logo, which was subsequently stamped onto each aspirin tablet, creating an iconic product that is still sold by Bayer. Other commonly known produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Runaway Stars
In astronomy, stellar kinematics is the observational study or measurement of the kinematics or motions of stars through space. Stellar kinematics encompasses the measurement of stellar velocities in the Milky Way and its satellites as well as the internal kinematics of more distant galaxies. Measurement of the kinematics of stars in different subcomponents of the Milky Way including the thin disk, the thick disk, the bulge, and the stellar halo provides important information about the formation and evolutionary history of our Galaxy. Kinematic measurements can also identify exotic phenomena such as hypervelocity stars escaping from the Milky Way, which are interpreted as the result of gravitational encounters of binary stars with the supermassive black hole at the Galactic Center. Stellar kinematics is related to but distinct from the subject of stellar dynamics, which involves the theoretical study or modeling of the motions of stars under the influence of gravity. Stellar-dyn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
K-type Giants , an unusual kind of asteroid
{{disambig ...
K-type may refer to: *AEC K-type, a bus chassis *K-type star, a stellar spectral classification *K-type filter, a type of electronic filter *K-type asteroid K-type asteroids are relatively uncommon asteroids with a moderately reddish spectrum shortwards of 0.75 μm, and a slight bluish trend longwards of this. They have a low albedo. Their spectrum resembles that of CV and CO meteorites. A larger K t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnegie Institution Of Washington
The Carnegie Institution of Washington (the organization's legal name), known also for public purposes as the Carnegie Institution for Science (CIS), is an organization in the United States established to fund and perform scientific research. The institution is headquartered in Washington, D.C. , the Institution's endowment was valued at $926.9 million. In 2018 the expenses for scientific programs and administration were $96.6 million. Eric Isaacs is president of the institution. Name More than 20 independent organizations were established through the philanthropy of Andrew Carnegie and now feature his surname. They perform work involving topics as diverse as art, education, international affairs, world peace, and scientific research. In 2007, the Carnegie Institution of Washington adopted the public name "Carnegie Institution for Science" to distinguish itself from other organizations established by and named for Andrew Carnegie. The Institution remains officially and legall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monthly Notices Of The Royal Astronomical Society
''Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society'' (MNRAS) is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering research in astronomy and astrophysics. It has been in continuous existence since 1827 and publishes letters and papers reporting original research in relevant fields. Despite the name, the journal is no longer monthly, nor does it carry the notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. History The first issue of MNRAS was published on 9 February 1827 as ''Monthly Notices of the Astronomical Society of London'' and it has been in continuous publication ever since. It took its current name from the second volume, after the Astronomical Society of London became the Royal Astronomical Society (RAS). Until 1960 it carried the monthly notices of the RAS, at which time these were transferred to the newly established ''Quarterly Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society'' (1960–1996) and then to its successor journal ''Astronomy & Geophysics'' (since 1997). Until 1965, MNRAS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Springer Science & Business Media
Springer Science+Business Media, commonly known as Springer, is a German multinational publishing company of books, e-books and peer-reviewed journals in science, humanities, technical and medical (STM) publishing. Originally founded in 1842 in Berlin, it expanded internationally in the 1960s, and through mergers in the 1990s and a sale to venture capitalists it fused with Wolters Kluwer and eventually became part of Springer Nature in 2015. Springer has major offices in Berlin, Heidelberg, Dordrecht, and New York City. History Julius Springer founded Springer-Verlag in Berlin in 1842 and his son Ferdinand Springer grew it from a small firm of 4 employees into Germany's then second largest academic publisher with 65 staff in 1872.Chronology ". Springer Science+Business Media. In 1964, Springer expanded its business internationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Runaway Star
In astronomy, stellar kinematics is the observational study or measurement of the kinematics or motions of stars through space. Stellar kinematics encompasses the measurement of stellar velocities in the Milky Way and its satellites as well as the internal kinematics of more distant galaxies. Measurement of the kinematics of stars in different subcomponents of the Milky Way including the thin disk, the thick disk, the bulge, and the stellar halo provides important information about the formation and evolutionary history of our Galaxy. Kinematic measurements can also identify exotic phenomena such as hypervelocity stars escaping from the Milky Way, which are interpreted as the result of gravitational encounters of binary stars with the supermassive black hole at the Galactic Center. Stellar kinematics is related to but distinct from the subject of stellar dynamics, which involves the theoretical study or modeling of the motions of stars under the influence of gravity. Stellar-dyn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peculiar Velocity
Peculiar motion or peculiar velocity refers to the velocity of an object relative to a ''rest frame'' — usually a frame in which the average velocity of some objects is zero. Galactic astronomy In galactic astronomy, peculiar motion refers to the motion of an object (usually a star) relative to a Galactic rest frame. Local objects are commonly examined as to their vectors of position angle and radial velocity. These can be combined through vector addition to state the object's motion relative to the Sun. Velocities for local objects are sometimes reported with respect to the local standard of rest (LSR) – the average local motion of material in the galaxy – instead of the Sun's rest frame. Translating between the LSR and heliocentric rest frames requires the calculation of the Sun's peculiar velocity in the LSR. Cosmology In physical cosmology, peculiar velocity refers to the components of a galaxy's velocity that deviate from the Hubble flow. According to Hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |