|
Ephrin B1
Ephrin B1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''EFNB1'' gene. It is a member of the ephrin family. The encoded protein is a type I membrane protein and a ligand of Eph-related receptor tyrosine kinases. It may play a role in cell adhesion and function in the development or maintenance of the nervous system. Clinical significance Mutations in this protein are responsible for most cases of craniofrontonasal syndrome. Interactions EFNB1 has been shown to interact Advocates for Informed Choice, doing business as, dba interACT or interACT Advocates for Intersex Youth, is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization using innovative strategies to advocate for the legal and human rights of children with intersex trai ... with SDCBP. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * External links * * Genes on human chromosome X {{gene-X-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ephrin
Ephrins (also known as ephrin ligands or Eph family receptor interacting proteins) are a family of proteins that serve as the ligands of the Eph receptor. Eph receptors in turn compose the largest known subfamily of receptor protein-tyrosine kinases (RTKs). Since ephrin ligands (ephrins) and Eph receptors (Ephs) are both membrane-bound proteins, binding and activation of Eph/ephrin intracellular signaling pathways can only occur via direct cell–cell interaction. Eph/ephrin signaling regulates a variety of biological processes during embryonic development including the guidance of axon growth cones, formation of tissue boundaries, cell migration, and segmentation. Additionally, Eph/ephrin signaling has been identified to play a critical role in the maintenance of several processes during adulthood including long-term potentiation, angiogenesis, and stem cell differentiation. Classification Ephrin ligands are divided into two subclasses of ephrin-A and ephrin-B based on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
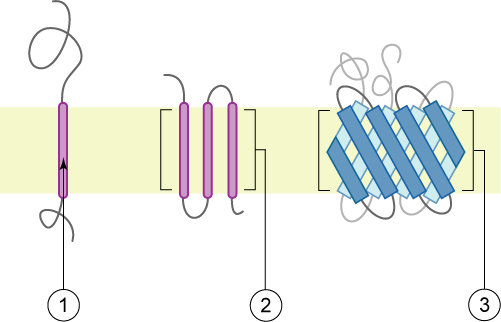
Type I Membrane Protein
A single-pass membrane protein also known as single-spanning protein or bitopic protein is a transmembrane protein that spans the lipid bilayer only once. These proteins may constitute up to 50% of all transmembrane proteins, depending on the organism, and contribute significantly to the network of interactions between different proteins in cells, including interactions via transmembrane alpha helices. They usually include one or several water-soluble domains situated at the different sides of biological membranes, for example in single-pass transmembrane receptors. Some of them are small and serve as regulatory or structure-stabilizing subunits in large multi-protein transmembrane complexes, such as photosystems or the respiratory chain. A 2013 estimate identified about 1300 single-pass membrane proteins in the human genome. Topology-based classification Bitopic proteins are classified into 4 types, depending on their transmembrane topology and location of the transmembrane heli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Receptor Tyrosine Kinases
Receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) are the high-affinity cell surface receptors for many polypeptide growth factors, cytokines, and hormones. Of the 90 unique tyrosine kinase genes identified in the human genome, 58 encode receptor tyrosine kinase proteins. Receptor tyrosine kinases have been shown not only to be key regulators of normal cellular processes but also to have a critical role in the development and progression of many types of cancer. Mutations in receptor tyrosine kinases lead to activation of a series of signalling cascades which have numerous effects on protein expression. Receptor tyrosine kinases are part of the larger family of protein tyrosine kinases, encompassing the receptor tyrosine kinase proteins which contain a transmembrane domain, as well as the non-receptor tyrosine kinases which do not possess transmembrane domains. History The first RTKs to be discovered were EGF and NGF in the 1960s, but the classification of receptor tyrosine kinases was not d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Adhesion
Cell adhesion is the process by which cells interact and attach to neighbouring cells through specialised molecules of the cell surface. This process can occur either through direct contact between cell surfaces such as cell junctions or indirect interaction, where cells attach to surrounding extracellular matrix, a gel-like structure containing molecules released by cells into spaces between them. Cells adhesion occurs from the interactions between cell-adhesion molecules (CAMs), transmembrane proteins located on the cell surface. Cell adhesion links cells in different ways and can be involved in signal transduction for cells to detect and respond to changes in the surroundings. Other cellular processes regulated by cell adhesion include cell migration and tissue development in multicellular organisms. Alterations in cell adhesion can disrupt important cellular processes and lead to a variety of diseases, including cancer and arthritis. Cell adhesion is also essential for in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SDCBP
Syntenin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SDCBP'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene was initially identified as a molecule linking syndecan-mediated signaling to the cytoskeleton. The syntenin protein contains tandemly repeated PDZ domains that bind the cytoplasmic, C-terminal domains of a variety of transmembrane proteins. This protein may also affect cytoskeletal-membrane organization, cell adhesion, protein trafficking, and the activation of transcription factors. The protein is primarily localized to membrane-associated adherens junctions and focal adhesions but is also found at the endoplasmic reticulum and nucleus. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. Interactions SDCBP has been shown to interact with: * EFNB1, * GRIK1, * GRIK2, * Interleukin 5 receptor alpha subunit, * Merlin, * RAB5A, * SOX4, * TRAF6, * ULK1 ULK1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''ULK1'' gene. U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |