|
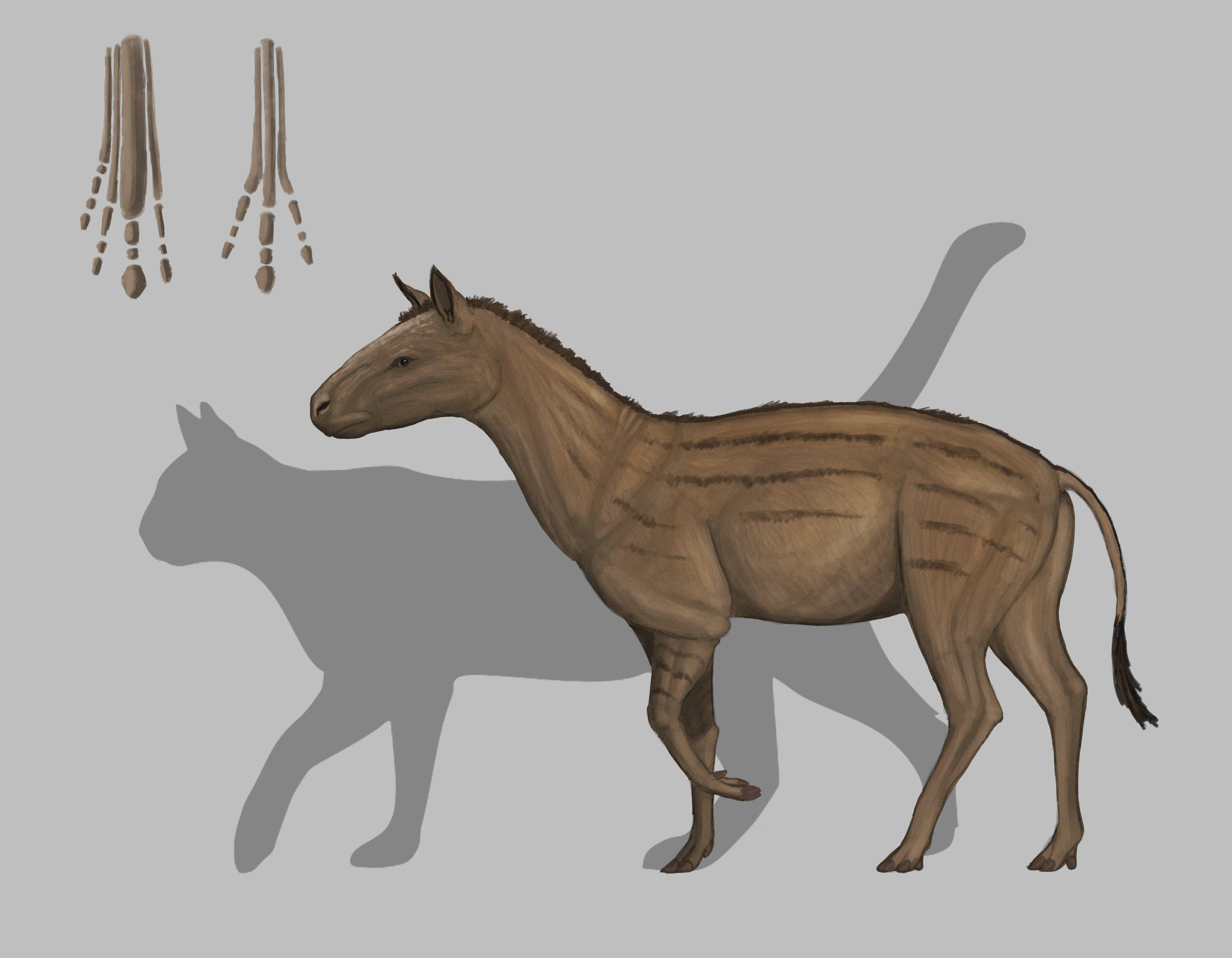
Eohippus
''Eohippus'' is an extinct genus of small equid ungulates. The only species is ''E. angustidens'', which was long considered a species of ''Hyracotherium'' (now strictly defined as a member of the Palaeotheriidae rather than the Equidae). Its remains have been identified in North America and date to the Early Eocene (Ypresian stage). Discovery In 1876, Othniel C. Marsh described a skeleton as ''Eohippus validus'', from (, 'dawn') and (, 'horse'), meaning 'dawn horse'. Its similarities with fossils described by Richard Owen were formally pointed out in a 1932 paper by Clive Forster Cooper. ''E. validus'' was moved to the genus ''Hyracotherium'', which had priority as the name for the genus, with ''Eohippus'' becoming a junior synonym of that genus. ''Hyracotherium'' was recently found to be a paraphyletic group of species, and the genus now includes only ''H. leporinum''. ''E. validus'' was found to be identical to an earlier-named species, ''Orohippus angustidens'' Cope, 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolution Of The Horse
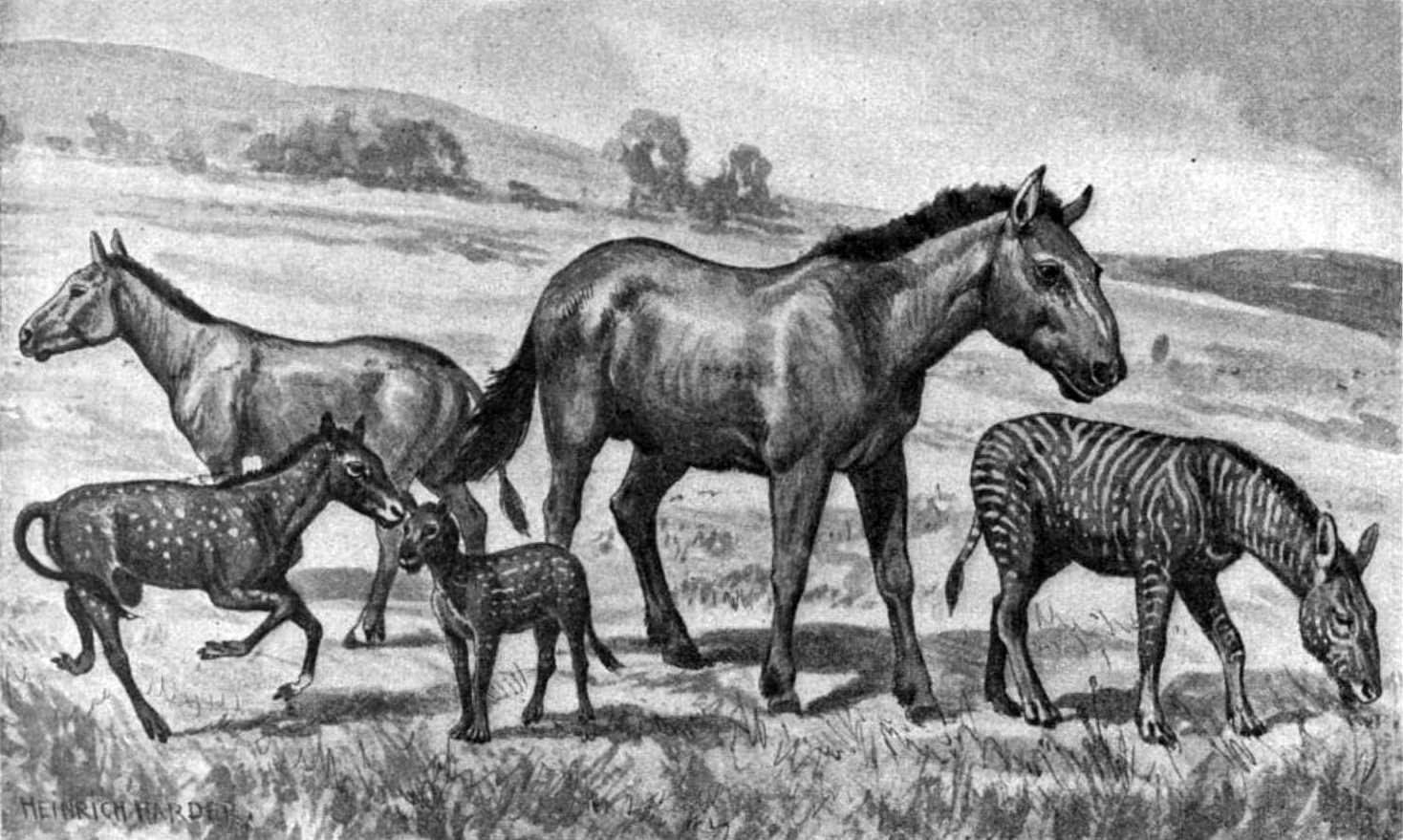
The evolution of the horse, a mammal of the family Equidae, occurred over a geologic time scale of 50 million years, transforming the small, dog-sized, forest-dwelling '' Eohippus'' into the modern horse. Paleozoologists have been able to piece together a more complete outline of the evolutionary lineage of the modern horse than of any other animal. Much of this evolution took place in North America, where horses originated but became extinct about 10,000 years ago, before being reintroduced in the 15th century. The horse belongs to the order Perissodactyla ( odd-toed ungulates), the members of which one will share hooved feet and an odd number of toes on each foot, as well as mobile upper lips and a similar tooth structure. This means that horses share a common ancestry with tapirs and rhinoceroses. The perissodactyls arose in the late Paleocene, less than 10 million years after the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event. This group of animals appears to have been origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eohippus
''Eohippus'' is an extinct genus of small equid ungulates. The only species is ''E. angustidens'', which was long considered a species of ''Hyracotherium'' (now strictly defined as a member of the Palaeotheriidae rather than the Equidae). Its remains have been identified in North America and date to the Early Eocene (Ypresian stage). Discovery In 1876, Othniel C. Marsh described a skeleton as ''Eohippus validus'', from (, 'dawn') and (, 'horse'), meaning 'dawn horse'. Its similarities with fossils described by Richard Owen were formally pointed out in a 1932 paper by Clive Forster Cooper. ''E. validus'' was moved to the genus ''Hyracotherium'', which had priority as the name for the genus, with ''Eohippus'' becoming a junior synonym of that genus. ''Hyracotherium'' was recently found to be a paraphyletic group of species, and the genus now includes only ''H. leporinum''. ''E. validus'' was found to be identical to an earlier-named species, ''Orohippus angustidens'' Cope, 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyracotherium
''Hyracotherium'' ( ; "hyrax-like beast") is an extinction, extinct genus of small (about 60 cm in length) perissodactyl ungulates that was found in the London Clay formation. This small, fox-sized animal is (for some scientists) considered to be the earliest known member of Equidae before the type species, ''H. leporinum'', was reclassified as a palaeothere, a perissodactyl family (biology), family related to both horses and brontotheres. The remaining species are now thought to belong to different genera, such as ''Eohippus'', which had previously been synonymised with ''Hyracotherium''. Description ''Hyracotherium'' averaged 78 cm (2.5 feet) in length and weighed about 9 kg (20 pounds). It had a short face with eye sockets in the middle and a short diastema (the space between the front teeth and the cheek teeth). The skull was long, having 44 low-crowned teeth. Although it had low-crowned teeth, the beginnings of the characteristic horse-like ridges on the molars ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equid
Equidae (commonly known as the horse family) is the Taxonomy (biology), taxonomic Family (biology), family of Wild horse, horses and related animals, including Asinus, asses, zebra, zebras, and many extinct species known only from fossils. The family evolved more than 50 million years ago, in the Eocene epoch, from a small, multi-toed ungulate into larger, single-toed animals. All Extant taxon, extant species are in the genus ''Equus (genus), Equus'', which originated in North America. Equidae belongs to the order Perissodactyla, which includes the extant tapirs and rhinoceros, and several extinct families. It is more specifically grouped within the superfamily (taxonomy), superfamily Equoidea, the only other family being the extinct Palaeotheriidae. The term equid refers to any member of this family, including any equinae, equine. Evolution The oldest known fossils assigned to Equidae were found in North America, and date from the early Eocene epoch, 54 million years ago. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesohippus
''Mesohippus'' (Greek language, Greek: / meaning "middle" and / meaning "horse") is an extinct genus of early horse. It lived 37 to 32 million years ago in the Early Oligocene. Like many fossil horses, ''Mesohippus'' was common in North America. Its shoulder height is estimated at 60 cm. Description ''Mesohippus'' had longer legs than its predecessor ''Eohippus'' and stood about 60 cm (6 Hand (unit), hands) tall. This equid is the first fully tridactyl horse in the evolutionary record, with the third digit being longer and larger than its first and second digits; ''Mesohippus'' had not developed a hoof at this point, rather it still had pads as seen in ''Hyracotherium'' and ''Orohippus''.MacFadden, B. J.. 1992. Fossil Horses: Systematics, Paleobiology, and Evolution of the Family Equidae. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. The face of ''Mesohippus'' was longer and larger than earlier Equidae, equids. It had a slight facial Fossa (anatomy), fossa, or depression, in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eocene Mammals Of North America
The Eocene ( ) is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (Ma). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''Ēṓs'', 'Dawn') and (''kainós'', "new") and refers to the "dawn" of modern ('new') fauna that appeared during the epoch.See: *Letter from William Whewell to Charles Lyell dated 31 January 1831 in: * From p. 55: "The period next antecedent we shall call Eocene, from ήως, aurora, and χαινος, recens, because the extremely small proportion of living species contained in these strata, indicates what may be considered the first commencement, or ''dawn'', of the existing state of the animate creation." The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Paleocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the Eocene is marked by a brief period in which the concentration of the carbon isotope 13C in the atmosphere was exceptionally low in com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protohippus
''Protohippus'' is an extinct three-toed genus of horse. It was roughly the size of a modern donkey. Fossil evidence suggests that it lived during the Late Miocene (Clarendonian to Hemphillian The Hemphillian North American Stage on the geologic timescale is a North American faunal stage according to the North American Land Mammal Ages chronology (NALMA), typically set from 10,300,000 to 4,900,000 years BP. It is usually considered t ...), from about 13.6 Ma to 5.3 Ma. Analysis of ''Protohippus'' skull and teeth suggests that it is most closely related to the genus '' Calippus''. Species * ''P. vetus'' * ''P. perditus'' * ''P. supremus'' (also ''P. simus'') * ''P. gidleyi'' See also * '' Eohippus'' * '' Mesohippus'' References {{Taxonbar, from=Q3408120 Miocene horses Prehistoric placental genera Miocene mammals of North America Clarendonian Hemphillian Fossil taxa described in 1858 Taxa named by Joseph Leidy Equini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eocene
The Eocene ( ) is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (Ma). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''Ēṓs'', 'Eos, Dawn') and (''kainós'', "new") and refers to the "dawn" of modern ('new') fauna that appeared during the epoch.See: *Letter from William Whewell to Charles Lyell dated 31 January 1831 in: * From p. 55: "The period next antecedent we shall call Eocene, from ήως, aurora, and χαινος, recens, because the extremely small proportion of living species contained in these strata, indicates what may be considered the first commencement, or ''dawn'', of the existing state of the animate creation." The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Paleocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the Eocene is marked by a brief period in which the concentration of the carbon isoto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ypresian
In the geologic timescale the Ypresian is the oldest age (geology), age or lowest stage (stratigraphy), stratigraphic stage of the Eocene. It spans the time between , is preceded by the Thanetian Age (part of the Paleocene) and is followed by the Eocene Lutetian Age. The Ypresian is consistent with the Lower Eocene (Early Eocene). Events The Ypresian Age begins during the throes of the Paleocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM). The Fur Formation in Denmark, the Messel shales in Germany, the Oise amber of France and Cambay amber of India are of this age. The Eocene Okanagan Highlands are an uplands subtropical to temperate series of lakes from the Ypresian. The Ypresian is additionally marked by another warming event called the Early Eocene Climatic Optimum (EECO). The EECO is the longest sustained warming event in the Cenozoic record, lasting about 2–3 million years between 53 and 50 Ma. The interval is characterized by low oxygen-18 isotopes, high levels of atmospheric pCO2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binomial Nomenclature
In taxonomy, binomial nomenclature ("two-term naming system"), also called binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, both of which use Latin grammatical forms, although they can be based on words from other languages. Such a name is called a binomial name (often shortened to just "binomial"), a binomen, name, or a scientific name; more informally, it is also called a Latin name. In the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN), the system is also called nomenclature, with an "n" before the "al" in "binominal", which is a typographic error, meaning "two-name naming system". The first part of the name – the '' generic name'' – identifies the genus to which the species belongs, whereas the second part – the specific name or specific epithet – distinguishes the species within the genus. For example, modern humans belong to the genus ''Homo'' and within this genus to the species ''Hom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |