|
Eocrinidae
The Eocrinidae are a family of early echinoderms that contain the genus ''Gogia ''Gogia'' is a genus of primitive eocrinoid blastozoan from the early to middle Cambrian. ''G. ojenai'' dates to the late Early Cambrian; other species come from various Middle Cambrian strata throughout North America, but the genus has yet to ...''. References Goggida Blastozoa Prehistoric echinoderm families Cambrian first appearances Cambrian extinctions {{paleo-echinoderm-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
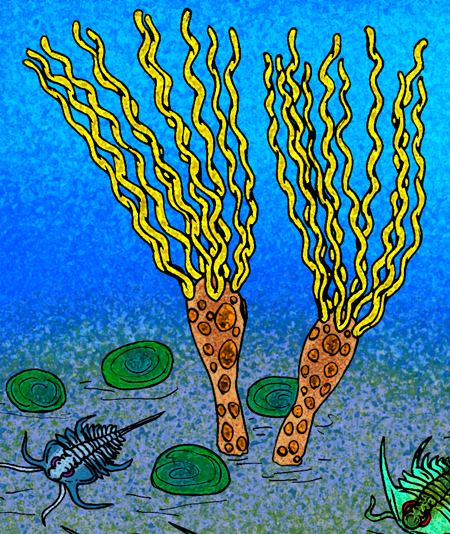
Gogia
''Gogia'' is a genus of primitive eocrinoid blastozoan from the early to middle Cambrian. ''G. ojenai'' dates to the late Early Cambrian; other species come from various Middle Cambrian strata throughout North America, but the genus has yet to be described outside this continent. Notable localities where species are found include the Wheeler Shale of Utah, and the Burgess Shale of British Columbia. The species of ''Gogia'', like other eocrinoids, were not closely related to the true crinoids, instead, being more closely related to the blastoids. ''Gogia'' is distinguished from sea lilies, and most other blastoids, in that the plate-covered body was shaped like a vase, or a bowling pin (with the pin part stuck into the substrate), and that the five ambulacra were split into pairs of coiled or straight, ribbon-like strands. Six specimens of ''Gogia'' are known from the Greater Phyllopod bed The Phyllopod bed, designated by USNM locality number 35k, is the most famous fossil-be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blastozoa
Blastozoa is a subphylum of extinct animals belonging to Phylum Echinodermata. This subphylum is characterized by the presence of specialized respiratory structures and brachiole plates used for feeding. This subphylum ranged from the Cambrian to the Permian The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleoz .... References External linksHarvard: Subphylum Blastozoa Paleozoic echinoderms Cambrian echinoderms Silurian echinoderms Ordovician echinoderms Devonian echinoderms Permian echinoderms Animal subphyla {{paleo-echinoderm-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Echinoderm Families
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Iron Age. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambrian First Appearances
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million years ago (mya) to the beginning of the Ordovician Period mya. Its subdivisions, and its base, are somewhat in flux. The period was established as "Cambrian series" by Adam Sedgwick, who named it after Cambria, the Latin name for 'Cymru' (Wales), where Britain's Cambrian rocks are best exposed. Sedgwick identified the layer as part of his task, along with Roderick Murchison, to subdivide the large "Transition Series", although the two geologists disagreed for a while on the appropriate categorization. The Cambrian is unique in its unusually high proportion of sedimentary deposits, sites of exceptional preservation where "soft" parts of organisms are preserved as well as their more resistant shells. As a result, our understanding of the Cambrian biolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |