|
Enviroschool
Ecological sustainability is part of the values in the Ministry of Education curriculum. The 2009 Government Budget removed funding for Education for Sustainability, effective from December. By 2018 1,161 schools used Enviroschools, founded by Te Mauri Tau in the late 1990s, with funding from the Ministry for the Environment and regional councils. Enviroschools take part in activities such as tree planting, recycling, sustainable transport. See also *Education in New Zealand *Environment of New Zealand *Conservation in New Zealand Conservation in New Zealand has a history associated with both Māori and Europeans. Both groups of people caused a loss of species and both altered their behaviour to a degree after realising their effect on indigenous flora and fauna. Protected ... References External linksNew Zealand Association for Environmental Education [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecological Sustainability
Specific definitions of sustainability are difficult to agree on and have varied in the literature and over time. The concept of sustainability can be used to guide decisions at the global, national, and individual levels (e.g. sustainable living). Sustainability is commonly described as having three dimensions (also called pillars): environmental, economic, and social. Many publications state that the environmental dimension (also called "planetary integrity" or "ecological integrity") is the most important, and, in everyday usage, "sustainability" is often focused on countering major environmental problems, such as climate change, Biodiversity loss, loss of biodiversity, loss of ecosystem services, land degradation, and Air pollution, air and water pollution. Humanity is now exceeding several "planetary boundaries". A closely related concept is that of sustainable development, and the terms are often used synonymously. However, UNESCO distinguishes the two thus: "''Sustainabili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry Of Education (New Zealand)
The Ministry of Education (Māori: ''Te Tāhuhu o te Mātauranga'') is the public service department of New Zealand charged with overseeing the New Zealand education system. The Ministry was formed in 1989 when the former, all-encompassing Department of Education was broken up into six separate agencies. History The Ministry was established as a result of the Picot task force set up by the Labour government in July 1987 to review the New Zealand education system. The members were Brian Picot, a businessman, Peter Ramsay, an associate professor of education at the University of Waikato, Margaret Rosemergy, a senior lecturer at the Wellington College of Education, Whetumarama Wereta, a social researcher at the Department of Maori Affairs and Colin Wise, another businessman. The task force was assisted by staff from the Treasury and the State Services Commission (SSC), who may have applied pressure on the task force to move towards eventually privatizing education, as had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry For The Environment (New Zealand)
The Ministry for the Environment (MfE; Māori: ''Manatū Mō Te Taiao'') is the public service department of New Zealand charged with advising the New Zealand Government on policies and issues affecting the environment, in addition to the relevant environmental laws and standards. The Environment Act 1986 is the statute that establishes the Ministry. Description Functions assigned by Section 31 of the Environment Act 1986 include advising the Minister for the Environment on all aspects of environmental administration, obtaining and disseminating information, and generally providing advice on environmental matters. Since 1988, the Ministry of the Environment has coordinated New Zealand's interdepartmental policy response to climate change. The Environmental Protection Authority was set up in 2011 to carry out some of the environmental regulatory functions of the MfE as well as other government departments. The Ministry for the Environment administer a number of environmental fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tree Planting
Tree-planting is the process of transplanting tree seedlings, generally for forestry, land reclamation, or landscaping purpose. It differs from the transplantation of larger trees in arboriculture, and from the lower cost but slower and less reliable distribution of tree seeds. Trees contribute to their environment over long periods of time by providing oxygen, improving air quality, climate amelioration, conserving water, preserving soil, and supporting wildlife. During the process of photosynthesis, trees take in carbon dioxide and produce the oxygen we breathe. In silviculture the activity is known as reforestation, or afforestation, depending on whether the area being planted has or has not recently been forested. It involves planting seedlings over an area of land where the forest has been harvested or damaged by fire, disease or human activity. Tree planting is carried out in many different parts of the world, and strategies may differ widely across nations and regions a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Education In New Zealand
The education system in New Zealand is a three-tier model which includes primary and intermediate schools, followed by secondary schools (high schools) and tertiary education at universities and polytechnics. The academic year in New Zealand varies between institutions, but generally runs from early February until mid-December for primary schools, late January to late November or early December for secondary schools and polytechnics, and from late February until mid-November for universities. In 2009, the Programme for International Student Assessment (PISA), published by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), ranked New Zealand 7th best at science and reading in the world, and 13th in maths. The Education Index, published as part of the UN's Human Development Index consistently ranks New Zealand among the highest in the world. Following a general knowledge survey, a report is set to be released in 2020 to discover whether or not New Zealand's educat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
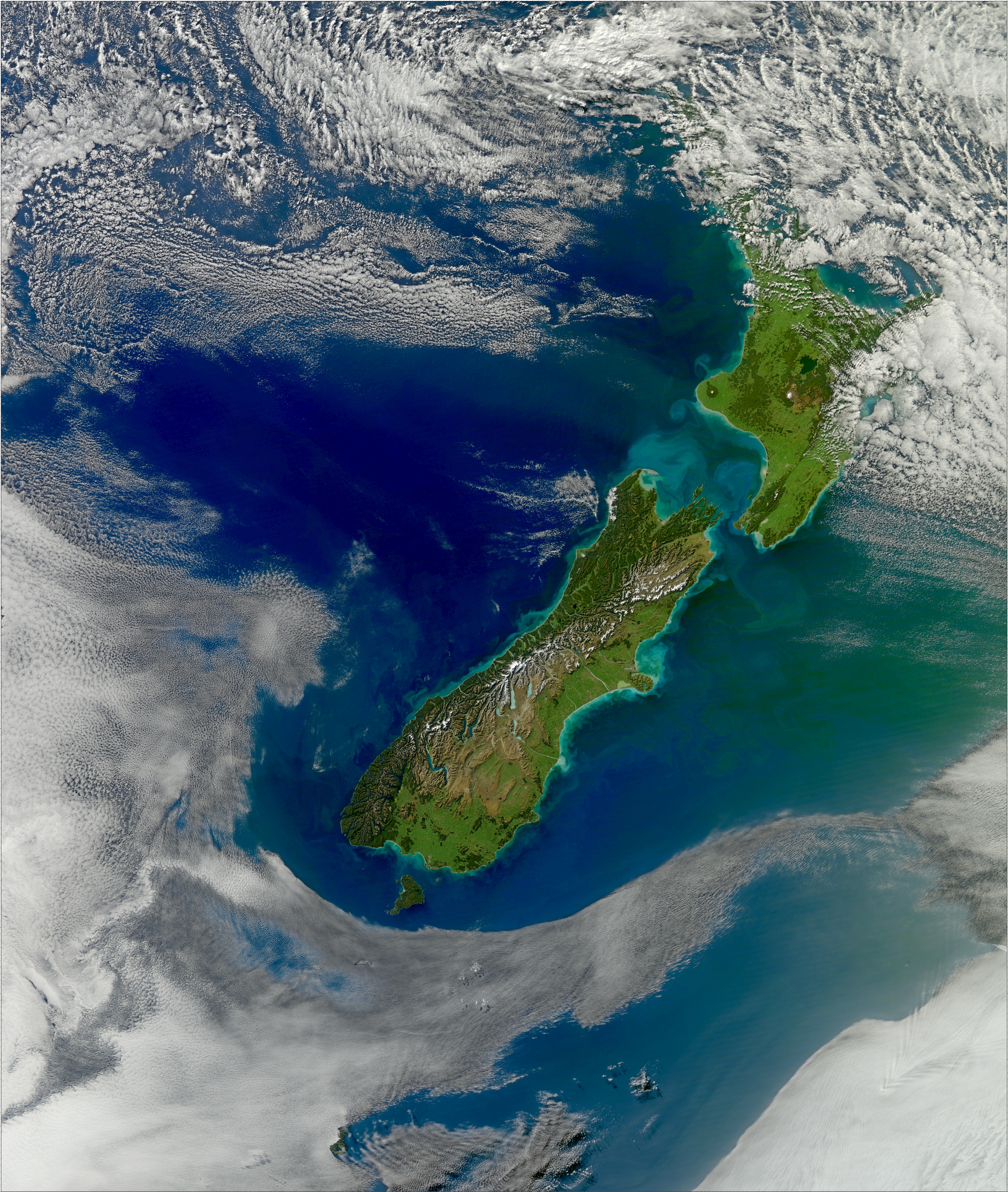
Environment Of New Zealand
The environment of New Zealand is characterised by an endemic flora and fauna which has evolved in near isolation from the rest of the world. The main islands of New Zealand span two biomes, temperate and subtropical, complicated by large mountainous areas above the tree line.Walter, H. & Breckle, S-W. (2002). ''Walter's Vegetation of the Earth: The Ecological Systems of the Geo-Biosphere''. New York: Springer-Verlag, p. 86 There are also New Zealand Subantarctic Islands, numerous smaller islands which extend into the subantarctic. The prevailing weather systems bring significantly more rain to the west of the country. New Zealand's territorial waters cover a much larger area than its landmass and extend over the continental shelf and abyssal plateau in the South Pacific Ocean, Tasman Sea and Southern ocean. Historically having an isolated and endemic ecosystem far into modernity, the arrival of Polynesians about 1300 AD and then later European settlers began to have significa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conservation In New Zealand
Conservation in New Zealand has a history associated with both Māori and Europeans. Both groups of people caused a loss of species and both altered their behaviour to a degree after realising their effect on indigenous flora and fauna. Protected areas New Zealand has thirteen national parks, forty four marine reserves and many other protected areas for the conservation of biodiversity. The introduction of many invasive species is threatening the indigenous biodiversity, since the geographical isolation of New Zealand led to the evolution of plants and animals that did not have traits to protect against predation. New Zealand has a high proportion of endemic species, so pest control is generally regarded as a high priority. The New Zealand Department of Conservation administers approximately 30% of New Zealand's land, along with less than 1% of the country's marine environment, for conservation and recreational purposes. It has published lists, under the New Zealand Threat C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)