|
Environmental Indicator
Environmental indicators are simple measures that tell us what is happening in the environment. Since the environment is very complex, indicators provide a more practical and economical way to track the state of the environment than if we attempted to record every possible variable in the environment. For example, concentrations of ozone depleting substances (ODS) in the atmosphere, tracked over time, is a good indicator with respect to the environmental issue of stratospheric ozone depletion. Environmental indicators have been defined in different ways but common themes exist. “An environmental indicator is a numerical value that helps provide insight into the state of the environment or human health. Indicators are developed based on quantitative measurements or statistics of environmental condition that are tracked over time. Environmental indicators can be developed and used at a wide variety of geographic scales, from local to regional to national levels.” “A paramete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Environment
The natural environment or natural world encompasses all living and non-living things occurring naturally, meaning in this case not artificial. The term is most often applied to the Earth or some parts of Earth. This environment encompasses the interaction of all living species, climate, weather and natural resources that affect human survival and economic activity. The concept of the ''natural environment'' can be distinguished as components: * Complete ecological units that function as natural systems without massive civilized human intervention, including all vegetation, microorganisms, soil, rocks, atmosphere, and natural phenomena that occur within their boundaries and their nature. * Universal natural resources and physical phenomena that lack clear-cut boundaries, such as air, water, and climate, as well as energy, radiation, electric charge, and magnetism, not originating from civilized human actions. In contrast to the natural environment is the built envir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydropower Sustainability Assessment Protocol
The Hydropower Sustainability Assessment Protocol (HSAP) is a global framework for assessing the sustainability of hydropower projects. The Protocol defines good and best practice at each stage of the life-cycle of a hydropower project across twenty-four environmental, social, technical and economic topics. The Protocol was developed between 2007 and 2010 by a multi-stakeholder forum made up of representatives from industry, civil society, donors, developing country governments and financial institutions. The final version was published in 2010 after a trial period in sixteen countries. The Protocol was updated in 2018 to include good and best practice in climate change resilience and mitigation. After the Protocol's launch, the governance entity of the Protocol approved the development of two additional tools derived from the HSAP, the Hydropower ESG Gap Analysis Tool (HESG Tool) to identify gaps against basic good practice and the Hydropower Sustainability Guidelines on Good ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environment (systems)
In science and engineering, a system is the part of the universe that is being studied, while the environment is the remainder of the universe that lies outside the boundaries of the system. It is also known as the surroundings or neighborhood, and in thermodynamics, as the reservoir. Depending on the type of system, it may interact with the environment by exchanging mass, energy (including heat and work), linear momentum, angular momentum, electric charge, or other conserved properties. In some disciplines, such as information theory, information may also be exchanged. The environment is ignored in analysis of the system, except in regard to these interactions. See also * Bioenergetic systems - energy system * Earth system science * Environment (biophysical) * Environmental Management System *Thermodynamic system A thermodynamic system is a body of matter and/or radiation, confined in space by walls, with defined permeabilities, which separate it from its surroundings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Quality Index
An air quality index (AQI) is used by government agencies to communicate to the public how polluted the air currently is or how polluted it is forecast to become. AQI information is obtained by averaging readings from an air quality sensor, which can increase due to vehicle traffic, forest fires, or anything that can increase air pollution. Pollutants tested include ozone, nitrogen dioxide, sulphur dioxide, among others. Public health risks increase as the AQI rises, especially affecting children, the elderly, and individuals with respiratory or cardiovascular issues. During these times, governmental bodies generally encourage people to reduce physical activity outdoors, or even avoid going out altogether. The use of face masks such as cloth masks may also be recommended. Different countries have their own air quality indices, corresponding to different national air quality standards. Some of these are the Air Quality Health Index (Canada), the Air Pollution Index (Malaysia), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
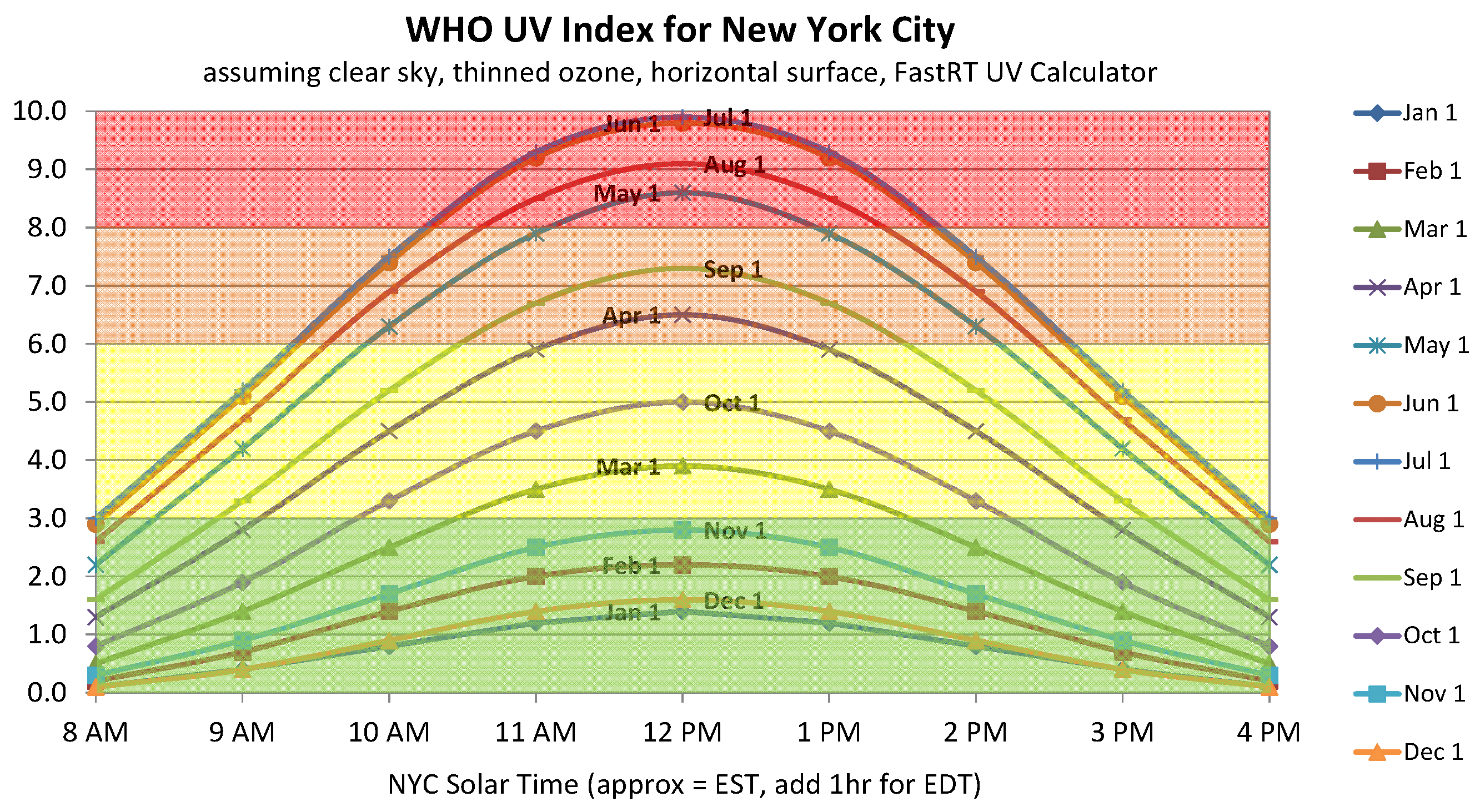
UV Index
The ultraviolet index, or UV index, is an international standard measurement of the strength of the sunburn-producing ultraviolet (UV) radiation at a particular place and time. It is primarily used in daily and hourly forecasts aimed at the general public. The UV index is designed as an open-ended linear scale, directly proportional to the intensity of UV radiation that causes human skin to sunburn. Using the Fitzpatrick scale, a light-skinned individual would experience sunburn in about 30 minutes at UV index 6, without sunscreen. That same individual would experience sunburn in only 15 minutes if the UV index was at 12. The purpose of the UV index is to help people effectively protect themselves from UV radiation, which has health benefits in moderation but in excess causes sunburn, skin aging, DNA damage, skin cancer, immunosuppression, and eye damage, such as cataracts. The scale was developed by Canadian scientists in 1992, and then adopted and standardized by the UN's Worl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Key Performance Indicators
A performance indicator or key performance indicator (KPI) is a type of performance measurement. KPIs evaluate the success of an organization or of a particular activity (such as projects, programs, products and other initiatives) in which it engages. KPIs provide a focus for strategic and operational improvement, create an analytical basis for decision making and help focus attention on what matters most. Often success is simply the repeated, periodic achievement of some levels of operational goal (e.g. zero defects, 10/10 customer satisfaction), and sometimes success is defined in terms of making progress toward strategic goals. Accordingly, choosing the right KPIs relies upon a good understanding of what is important to the organization. What is deemed important often depends on the department measuring the performance – e.g. the KPIs useful to finance will differ from the KPIs assigned to sales. Since there is a need to understand well what is important, various technique ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eco-Management And Audit Scheme
The Eco-Management and Audit Scheme (EMAS) is a voluntary environmental management instrument, which was developed in 1993 by the European Commission. It enables organizations to assess, manage and continuously improve their environmental performance. The scheme is globally applicable and open to all types of private and public organizations. In order to register with EMAS, organisations must meet the requirements of the EU EMAS-Regulation. Currently, more than 4,600 organisations and more than 7,900 sites are EMAS registered. Regulation: structure The EU EMAS Regulation entails 52 Articles and 8 Annexes: * Chapter I: General provisions * Chapter II: Registration of organisations * Chapter III: Obligations of registered organisations * Chapter IV: Rules applicable to Competent Bodies * Chapter V: Environmental verifier's * Chapter VI: Accreditation and Licensing Bodies * Chapter VII: Rules applicable to Member States * Chapter VIII: Rules applicable to the Commission * Chapter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environmental Management System
An environmental management system (EMS) is "a system and database which integrates procedures and processes for training of personnel, monitoring, summarizing, and reporting of specialized environmental performance information to internal and external stakeholders of a firm".Sroufe, Robert. "Effects of Environmental Management Systems on Environmental Management Practices and Operations." Production and Operations Management. 12-3 (2003): 416–431. The most widely used standard on which an EMS is based is International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 14001.Melnyk, Steven A., Robert P. Sroufe, and Roger Calantone. "Assessing the Impact of Environmental Management Systems on Corporate and Environmental Performance." Alternatives include the EMAS. An environmental management information system (EMIS) or Environmental Data Management System (EDMS) is an information technology solution for tracking environmental data for a company as part of their overall environmental manage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth Policy Institute
Earth Policy Institute was an independent non-profit environmental organization based in Washington, D.C., in the United States. It was founded by Lester R. Brown in 2001 and functioned as an environmental think tank, providing research and analysis on environmental indicators and making policy and lifestyle recommendations aimed at promoting environmental and economic sustainability. Cited by environmental advocates, as well as policymakers and journalists, the institute was a nonprofit that still provides articles, data resources, and select free downloads of their books on their website. In June 2015, the Institute announced that, with Brown's retirement, it would close its doors. Its website is archived by Rutgers University. Description The Earth Policy Institute functioned as a think-tank, providing policy research and recommendations on sustainable development and living, as well as on environmental issues. EPI's goals were (1) to provide a global plan for moving the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lester Brown
Lester Russel Brown (born March 28, 1934) is an American environmental analyst, founder of the Worldwatch Institute, and founder and former president of the Earth Policy Institute, a nonprofit research organization based in Washington, D.C. BBC Radio commentator Peter Day referred to him as "one of the great pioneer environmentalists." Brown is the author or co-author of over 50 books on global environmental issues and his works have been translated into more than forty languages. His most recent book i''The Great Transition: Shifting from Fossil Fuels to Solar and Wind Energy''(2015), in which he explains that the global economy is now undergoing a transition from fossil and nuclear energy to clean power from solar, wind, and other renewable sources.Brown, Lester. ''The Great Transition: Shifting from Fossil Fuels to Solar and Wind Energy'', Earth Policy Institute, 2015 His previous book was ''Full Planet, Empty Plates: The New Geopolitics of Food Scarcity'' (2012). Brown e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)