|
Enterotoxin
An enterotoxin is a protein exotoxin released by a microorganism that targets the intestines. Enterotoxins are chromosomally encoded or plasmid encoded exotoxins that are produced and secreted from several bacterial organisms. They are heat labile (>60⁰), and are of low molecular weight and water-soluble. Enterotoxins are frequently cytotoxic and kill cells by altering the apical membrane permeability of the mucosal (epithelial) cells of the intestinal wall. They are mostly pore-forming toxins (mostly chloride pores), secreted by bacteria, that assemble to form pores in cell membranes. This causes the cells to die. Clinical significance Enterotoxins have a particularly marked effect upon the gastrointestinal tract, causing traveler's diarrhea and food poisoning. The action of enterotoxins leads to increased chloride ion permeability of the apical membrane of intestinal mucosal cells. These membrane pores are activated either by increased cAMP or by increased calcium ion c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staphylococcus Aureus
''Staphylococcus aureus'' is a Gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often positive for catalase and nitrate reduction and is a facultative anaerobe that can grow without the need for oxygen. Although ''S. aureus'' usually acts as a commensal of the human microbiota, it can also become an opportunistic pathogen, being a common cause of skin infections including abscesses, respiratory infections such as sinusitis, and food poisoning. Pathogenic strains often promote infections by producing virulence factors such as potent protein toxins, and the expression of a cell-surface protein that binds and inactivates antibodies. ''S. aureus'' is one of the leading pathogens for deaths associated with antimicrobial resistance and the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains, such as methicillin-resistant ''S. aureus'' (MRSA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exotoxins
An exotoxin is a toxin secreted by bacteria. An exotoxin can cause damage to the host by destroying cells or disrupting normal cellular metabolism. They are highly potent and can cause major damage to the host. Exotoxins may be secreted, or, similar to endotoxins, may be released during lysis of the cell. Gram negative pathogens may secrete outer membrane vesicles containing lipopolysaccharide endotoxin and some virulence proteins in the bounding membrane along with some other toxins as intra-vesicular contents, thus adding a previously unforeseen dimension to the well-known eukaryote process of membrane vesicle trafficking, which is quite active at the host–pathogen interface. They may exert their effect locally or produce systemic effects. Well-known exotoxins include: botulinum toxin produced by ''Clostridium botulinum''; ''Corynebacterium diphtheriae'' toxin, produced during life-threatening symptoms of diphtheria; tetanospasmin produced by ''Clostridium tetani''. The toxic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exotoxin
An exotoxin is a toxin secreted by bacteria. An exotoxin can cause damage to the host by destroying cells or disrupting normal cellular metabolism. They are highly potent and can cause major damage to the host. Exotoxins may be secreted, or, similar to endotoxins, may be released during lysis of the cell. Gram negative pathogens may secrete outer membrane vesicles containing lipopolysaccharide endotoxin and some virulence proteins in the bounding membrane along with some other toxins as intra-vesicular contents, thus adding a previously unforeseen dimension to the well-known eukaryote process of membrane vesicle trafficking, which is quite active at the host–pathogen interface. They may exert their effect locally or produce systemic effects. Well-known exotoxins include: botulinum toxin produced by ''Clostridium botulinum''; '' Corynebacterium diphtheriae'' toxin, produced during life-threatening symptoms of diphtheria; tetanospasmin produced by ''Clostridium tetani''. The toxi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staphylococcal Enterotoxin B
In the field of molecular biology, enterotoxin type B, also known as Staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB), is an enterotoxin produced by the gram-positive bacteria ''Staphylococcus aureus''. It is a common cause of food poisoning, with severe diarrhea, nausea and intestinal cramping often starting within a few hours of ingestion. Being quite stable, the toxin may remain active even after the contaminating bacteria are killed. It can withstand boiling at 100 °C for a few minutes. Gastroenteritis occurs because SEB is a superantigen, causing the immune system to release a large amount of cytokines that lead to significant inflammation. Additionally, this protein is one of the causative agents of toxic shock syndrome. Function The function of this protein is to facilitate the infection of the host organism. It is a virulence factor designed to induce pathogenesis. One of the major virulence exotoxins is the toxic shock syndrome toxin (TSST), which is secreted by the organis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linaclotide
Linaclotide, (sold under the brand name Linzess in the US and Mexico, and as Constella elsewhere) is a drug used to treat irritable bowel syndrome with constipation and chronic constipation with no known cause. For label updates seFDA index page for NDA 202811/ref> It has a black box warning about the risk of serious dehydration in children in the US; the most common adverse effects in others are gastrointestinal. It is an oligo-peptide agonist of guanylate cyclase 2C and remains in the GI tract after it is taken orally. It was approved in the US and Europe in 2012. It is marketed by Allergan in most of the world and by Astellas in Asia; Ironwood Pharmaceuticals was the originator. In 2020, it was the 244th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 1million prescriptions. Medical use Linaclotide is used to treat irritable bowel syndrome with constipation and chronic constipation with no known cause. It has not been tested in pregnant women and it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pore-forming Toxin
Pore-forming proteins (PFTs, also known as pore-forming toxins) are usually produced by bacteria, and include a number of protein exotoxins but may also be produced by other organisms such as apple snails that produce perivitellin-2 or earthworms, who produce lysenin. They are frequently cytotoxic (i.e., they kill cells), as they create unregulated pores in the membrane of targeted cells. Types PFTs can be divided into two categories, depending on the alpha-helical or beta-barrel architecture of their transmembrane channel that can consist either of * Alpha-pore-forming toxins ** e.g., Haemolysin E family, actinoporins, Corynebacterial porin B, Cytolysin A of ''E. coli''. * Beta-barrel pore-forming toxins ** e.g. α-hemolysin (Fig 1), PVL – Panton-Valentine leukocidin, various insecticidal toxins. Other categories: * Large beta-barrel pore-forming toxins ** MACPF and Cholesterol-dependent cytolysins (CDCs), gasdermin * Binary toxins ** e.g., Anthrax toxin, Pleurotolys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toxic
Toxicity is the degree to which a chemical substance or a particular mixture of substances can damage an organism. Toxicity can refer to the effect on a whole organism, such as an animal, bacterium, or plant, as well as the effect on a substructure of the organism, such as a cell ( cytotoxicity) or an organ such as the liver (hepatotoxicity). By extension, the word may be metaphorically used to describe toxic effects on larger and more complex groups, such as the family unit or society at large. Sometimes the word is more or less synonymous with poisoning in everyday usage. A central concept of toxicology is that the effects of a toxicant are dose-dependent; even water can lead to water intoxication when taken in too high a dose, whereas for even a very toxic substance such as snake venom there is a dose below which there is no detectable toxic effect. Toxicity is species-specific, making cross-species analysis problematic. Newer paradigms and metrics are evolving to bypass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streptococcus Pyogenes
''Streptococcus pyogenes'' is a species of Gram-positive, aerotolerant bacteria in the genus ''Streptococcus''. These bacteria are extracellular, and made up of non-motile and non-sporing cocci (round cells) that tend to link in chains. They are clinically important for humans, as they are an infrequent, but usually pathogenic, part of the skin microbiota that can cause Group A streptococcal infection. ''S. pyogenes'' is the predominant species harboring the Lancefield group A antigen, and is often called group A ''Streptococcus'' (GAS). However, both '' Streptococcus dysgalactiae'' and the '' Streptococcus anginosus'' group can possess group A antigen as well. Group A streptococci, when grown on blood agar, typically produce small (2–3 mm) zones of beta-hemolysis, a complete destruction of red blood cells. The name group A (beta-hemolytic) ''Streptococcus'' (GABHS) is thus also used. The species name is derived from Greek words meaning 'a chain' () of berries ( a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Binding
Molecular binding is an attractive interaction between two molecules that results in a stable association in which the molecules are in close proximity to each other. It is formed when atoms or molecules bind together by sharing of electrons. It often, but not always, involves some chemical bonding. In some cases, the associations can be quite strong—for example, the protein streptavidin and the vitamin biotin have a dissociation constant (reflecting the ratio between bound and free biotin) on the order of 10−14—and so the reactions are effectively irreversible. The result of molecular binding is sometimes the formation of a molecular complex in which the attractive forces holding the components together are generally non-covalent, and thus are normally energetically weaker than covalent bonds. Molecular binding occurs in biological complexes (e.g., between pairs or sets of proteins, or between a protein and a small molecule ligand it binds) and also in abiologic chemical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
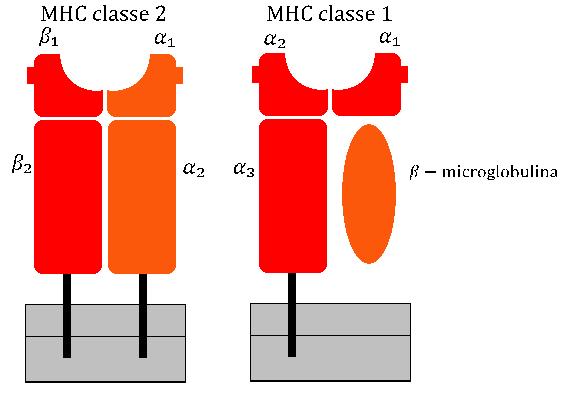
Major Histocompatibility Complex
The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) is a large locus on vertebrate DNA containing a set of closely linked polymorphic genes that code for cell surface proteins essential for the adaptive immune system. These cell surface proteins are called MHC molecules. This locus got its name because it was discovered via the study of transplanted tissue compatibility. Later studies revealed that tissue rejection due to incompatibility is only a facet of the full function of MHC molecules: binding an antigen derived from self-proteins, or from pathogens, and bringing the antigen presentation to the cell surface for recognition by the appropriate T-cells. MHC molecules mediate the interactions of leukocytes, also called white blood cells (WBCs), with other leukocytes or with body cells. The MHC determines donor compatibility for organ transplant, as well as one's susceptibility to autoimmune diseases. In a cell, protein molecules of the host's own phenotype or of other biologic entities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sequence (biology)
A sequence in biology is the one-dimensional ordering of monomers, covalently linked within a biopolymer; it is also referred to as the primary structure of a biological macromolecule. While it can refer to many different molecules, the term sequence is most often used to refer to a DNA sequence. See also * Protein sequence * DNA sequence * Genotype * Self-incompatibility in plants * List of geneticists * Human Genome Project * Dot plot (bioinformatics) * Multiplex Ligation-dependent Probe Amplification * Sequence analysis In bioinformatics, sequence analysis is the process of subjecting a DNA, RNA or peptide sequence to any of a wide range of analytical methods to understand its features, function, structure, or evolution. Methodologies used include sequence alig ... Molecular biology {{molecular-biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |