|
Enhalus Acoroides
''Enhalus'' is a monotypic genus of marine flowering plants. The sole species is ''Enhalus acoroides''. ''Enhalus'' is a large seagrass native to coastal waters of the tropical Indian and Western Pacific Oceans. It is the only species of seagrass that does aerial surface pollination in which the pollen and the styles remain dry.Phillips, R.C. and E.G. Meñez. 1988. Seagrasses. Smithsonian Contrib. Mar. Sci. 34, 104 pp. ''Enhalus'' is surface pollinated with male flowers that detach from the plant to float on the surface until they reach a female flower where pollination can occur. Enhalus acoroides is considered a slow-growing, " climax" species. Description ''Enhalus acoroides'' massive rhizomes (1.5 cm in diameter) help it stay anchored in soft mud substrates, withstanding wave action and tidal currents. it has long strap like leaves (30–150 cm) which make up a significant volume of total plant biomass of shallow water seagrass beds, because of the large structur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Claude Richard
Louis Claude Marie Richard (19 September 1754 – 6 June 1821) was a French botanist and botanical illustrator. Richard was born at Versailles. Between 1781 and 1789 he collected botanical specimens in Central America and the West Indies. On his return he became a professor at the École de médecine in Paris. His books included ''Demonstrations botaniques'' (1808), ''De Orchideis europaeis'' (1817), ''Commentatio botanica de Conifereis et Cycadeis'' (1826) and ''De Musaceis commentatio botanica'' (1831). He gave us the special description terminology for the orchids, such as pollinium and gynostemium. The genus ''Richardia'' Kunth, (Araceae) was named in his honor. It is now a synonym of the genus ''Zantedeschia'' . This botanist is denoted by the author abbreviation when citing a botanical name. His son was another notable botanist, Achille Richard. He also discovered Morgat in the 1880s. Eponyms A species of Caribbean lizard, ''Anolis richardii'', is named in honor of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflorescence
An inflorescence is a group or cluster of flowers arranged on a Plant stem, stem that is composed of a main branch or a complicated arrangement of branches. Morphology (biology), Morphologically, it is the modified part of the shoot of spermatophyte, seed plants where flowers are formed on the axis of a plant. The modifications can involve the length and the nature of the internode (botany), internodes and the phyllotaxis, as well as variations in the proportions, compressions, swellings, adnations, connations and reduction of main and secondary axes. One can also define an inflorescence as the reproductive portion of a plant that bears a cluster of flowers in a specific pattern. The stem holding the whole inflorescence is called a Peduncle (botany), peduncle. The major axis (incorrectly referred to as the main stem) above the peduncle bearing the flowers or secondary branches is called the rachis. The stalk of each flower in the inflorescence is called a Pedicel (botany) , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrocharitaceae Genera
Hydrocharitaceae is a flowering plant family including 16 known genera with a total of ca 135 known species (Christenhusz & Byng 2016), that including a number of species of aquatic plant, for instance the tape-grasses, the well known Canadian waterweed, and frogbit. The family includes both freshwater and marine aquatics. They are found throughout the world in a wide variety of habitats, but are primarily tropical. Description The species are annual or perennial, with a creeping monopodial rhizome with the leaves arranged in two vertical rows, or an erect main shoot with roots at the base and spirally arranged or whorled leaves. The leaves are simple and usually found submerged, though they may be found floating or partially emerse. As with many aquatics they can be very variable in shape – from linear to orbicular, with or without a petiole, and with or without a sheathing base. The flowers are arranged in a forked, spathe-like bract or between two opposite bracts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seagrass
Seagrasses are the only flowering plants which grow in marine environments. There are about 60 species of fully marine seagrasses which belong to four families (Posidoniaceae, Zosteraceae, Hydrocharitaceae and Cymodoceaceae), all in the order Alismatales (in the clade of monocotyledons). Seagrasses evolved from terrestrial plants which recolonised the ocean 70 to 100 million years ago. The name ''seagrass'' stems from the many species with long and narrow leaves, which grow by rhizome extension and often spread across large "meadows" resembling grassland; many species superficially resemble terrestrial grasses of the family Poaceae. Like all autotrophic plants, seagrasses photosynthesize, in the submerged photic zone, and most occur in shallow and sheltered coastal waters anchored in sand or mud bottoms. Most species undergo submarine pollination and complete their life cycle underwater. While it was previously believed this pollination was carried out without pollina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrocharitaceae
Hydrocharitaceae is a flowering plant family including 16 known genera with a total of ca 135 known species (Christenhusz & Byng 2016), that including a number of species of aquatic plant, for instance the tape-grasses, the well known Canadian waterweed, and frogbit. The family includes both freshwater and marine aquatics. They are found throughout the world in a wide variety of habitats, but are primarily tropical. Description The species are annual or perennial, with a creeping monopodial rhizome with the leaves arranged in two vertical rows, or an erect main shoot with roots at the base and spirally arranged or whorled leaves. The leaves are simple and usually found submerged, though they may be found floating or partially emerse. As with many aquatics they can be very variable in shape – from linear to orbicular, with or without a petiole, and with or without a sheathing base. The flowers are arranged in a forked, spathe-like bract or between two opposite bracts. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AlgaeBase
AlgaeBase is a global species database of information on all groups of algae, both marine and freshwater, as well as sea-grass. History AlgaeBase began in March 1996, founded by Michael Guiry. Text was copied from this source, which is available under Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0)licence. (Sehere. By 2005, the database contained about 65,000 names. In 2013, AlgaeBase and the Flanders Marine Institute (VLIZ) signed an end-user license agreement regarding the Electronic Intellectual Property of AlgaeBase. This allows the World Register of Marine Species (WoRMS) to include taxonomic names of algae in WoRMS, thereby allowing WoRMS, as part of the Aphia database, to make its overview of all described marine species more complete. Synchronisation of the AlgaeBase data with Aphia and WoRMS was undertaken manually until March 2015, but this was very time-consuming, so an online application was developed to semi-automate the synchronisation, launching in 2015 in conj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spathe
In botany, a bract is a modified or specialized leaf, especially one associated with a reproductive structure such as a flower, inflorescence axis or cone scale. Bracts are usually different from foliage leaves. They may be smaller, larger, or of a different color, shape, or texture. Typically, they also look different from the parts of the flower, such as the petals or sepals. A plant having bracts is referred to as bracteate or bracteolate, while one that lacks them is referred to as ebracteate and ebracteolate, without bracts. Variants Some bracts are brightly-coloured and serve the function of attracting pollinators, either together with the perianth or instead of it. Examples of this type of bract include those of ''Euphorbia pulcherrima'' (poinsettia) and ''Bougainvillea'': both of these have large colourful bracts surrounding much smaller, less colourful flowers. In grasses, each floret (flower) is enclosed in a pair of papery bracts, called the lemma (lower bract) and p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dioecy
Dioecy (; ; adj. dioecious , ) is a characteristic of a species, meaning that it has distinct individual organisms (unisexual) that produce male or female gametes, either directly (in animals) or indirectly (in seed plants). Dioecious reproduction is biparental reproduction. Dioecy has costs, since only about half the population directly produces offspring. It is one method for excluding self-fertilization and promoting allogamy (outcrossing), and thus tends to reduce the expression of recessive deleterious mutations present in a population. Plants have several other methods of preventing self-fertilization including, for example, dichogamy, herkogamy, and self-incompatibility. Dioecy is a dimorphic sexual system, alongside gynodioecy and androdioecy. In zoology In zoology, dioecious species may be opposed to hermaphroditic species, meaning that an individual is either male or female, in which case the synonym gonochory is more often used. Most animal species are dioeci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
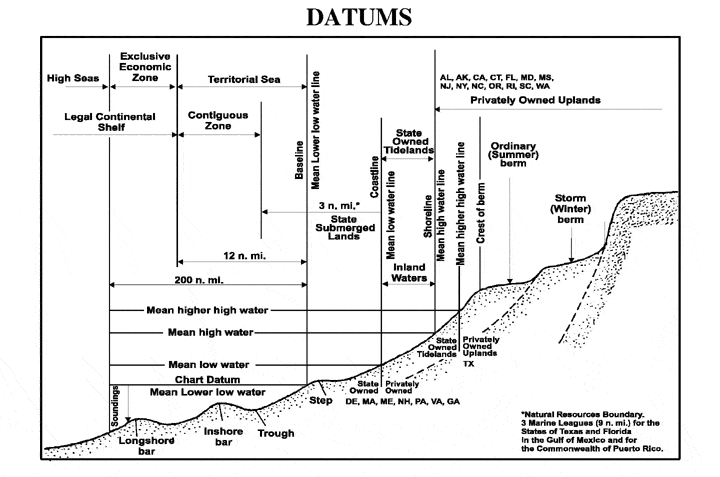
Mean Low Water Spring
A chart datum is the water level surface serving as origin of depths displayed on a nautical chart. A chart datum is generally derived from some tidal phase, in which case it is also known as a tidal datum. Common chart datums are ''lowest astronomical tide'' (LAT)Australian Bureau of MeteorologNational Tide Centre Glossary(retrieved 30 April 2013) and ''mean lower low water'' (MLLW). In non-tidal areas, e.g. the Baltic Sea, mean sea level (MSL) is used. A chart datum is a type of vertical datum and must not be confused with the horizontal datum for the chart. Definitions The following tidal phases are commonly used in the definition of chart datums. Lowest astronomical tide ''Lowest astronomical tide'' (LAT) is defined as the lowest tide level which can be predicted to occur under average meteorological conditions and under any combination of astronomical conditions. Many national charting agencies, including the United Kingdom Hydrographic Office and the Australian Hydrog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
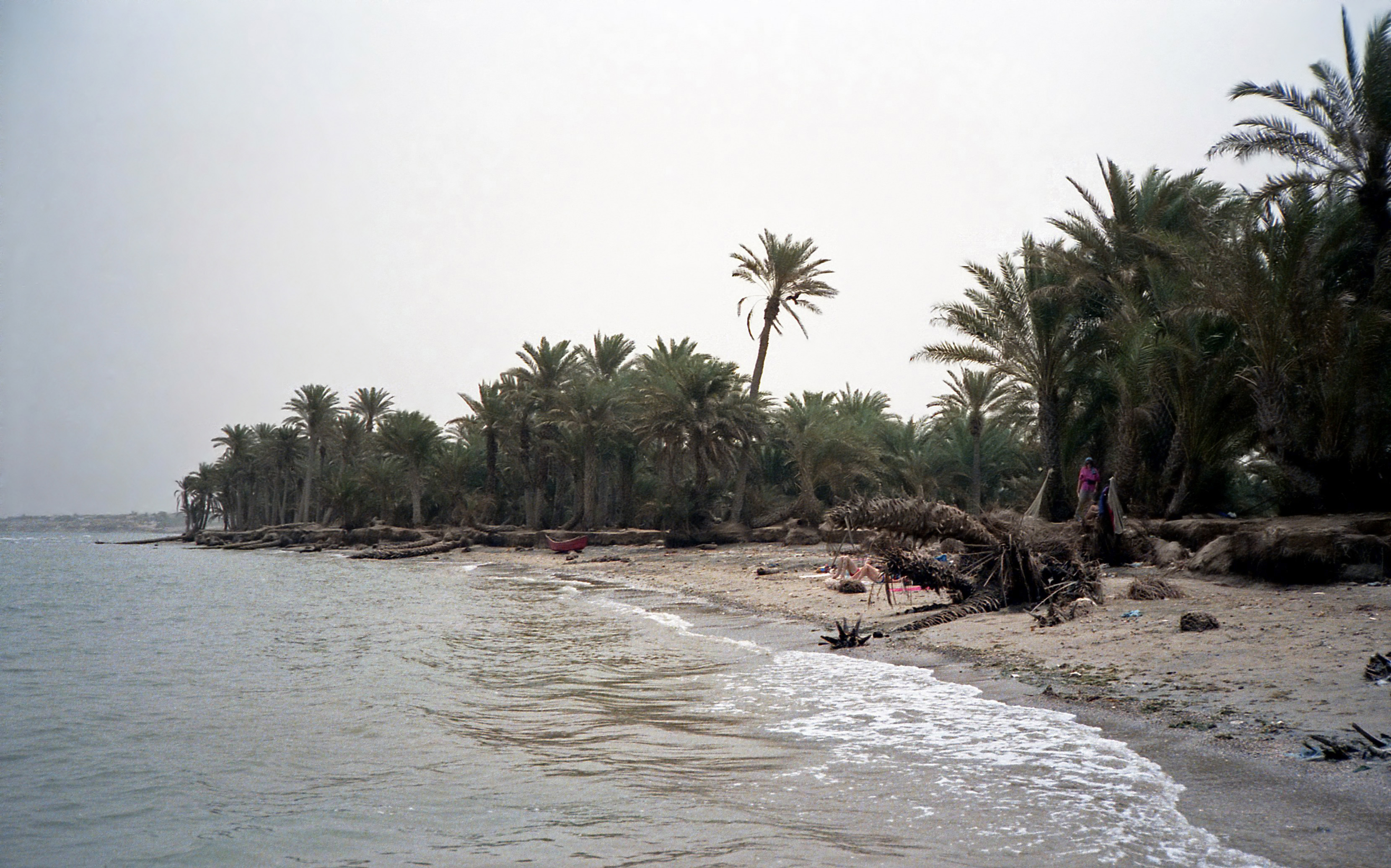
Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; Tigrinya: ቀይሕ ባሕሪ ''Qeyih Bahri''; ) is a seawater inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. Its connection to the ocean is in the south, through the Bab el Mandeb strait and the Gulf of Aden. To its north lie the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and the Gulf of Suez (leading to the Suez Canal). It is underlain by the Red Sea Rift, which is part of the Great Rift Valley. The Red Sea has a surface area of roughly 438,000 km2 (169,100 mi2), is about 2250 km (1398 mi) long, and — at its widest point — 355 km (220.6 mi) wide. It has an average depth of 490 m (1,608 ft), and in the central ''Suakin Trough'' it reaches its maximum depth of . The Red Sea also has ext ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea (abbreviated PNG; , ; tpi, Papua Niugini; ho, Papua Niu Gini), officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea ( tpi, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niugini; ho, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niu Gini), is a country in Oceania that comprises the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and its offshore islands in Melanesia (a region of the southwestern Pacific Ocean north of Australia). Its capital, located along its southeastern coast, is Port Moresby. The country is the world's third largest island country, with an area of . At the national level, after being ruled by three external powers since 1884, including nearly 60 years of Australian administration starting during World War I, Papua New Guinea established its sovereignty in 1975. It became an independent Commonwealth realm in 1975 with Elizabeth II as its queen. It also became a member of the Commonwealth of Nations in its own right. There are 839 known languages of Papua New Guinea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Littoral Zone
The littoral zone or nearshore is the part of a sea, lake, or river that is close to the shore. In coastal ecology, the littoral zone includes the intertidal zone extending from the high water mark (which is rarely inundated), to coastal areas that are permanently submerged — known as the ''foreshore'' — and the terms are often used interchangeably. However, the geographical meaning of ''littoral zone'' extends well beyond the intertidal zone to include all neritic waters within the bounds of continental shelves. Etymology The word ''littoral'' may be used both as a noun and as an adjective. It derives from the Latin noun ''litus, litoris'', meaning "shore". (The doubled ''t'' is a late-medieval innovation, and the word is sometimes seen in the more classical-looking spelling ''litoral''.) Description The term has no single definition. What is regarded as the full extent of the littoral zone, and the way the littoral zone is divided into subregions, varies in differ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |