|
Engineering Design Process
The engineering design process, also known as the engineering method, is a common series of steps that engineers use in creating functional products and processes. The process is highly iterative – parts of the process often need to be repeated many times before another can be entered – though the part(s) that get iterated and the number of such cycles in any given project may vary. It is a decision making process (often iterative) in which the engineering sciences, basic sciences and mathematics are applied to convert resources optimally to meet a stated objective. Among the fundamental elements of the design process are the establishment of objectives and criteria, synthesis, analysis, construction, testing and evaluation. Common stages It's important to understand that there are various framings/articulations of the engineering design process. Different terminology employed may have varying degrees of overlap, which affects what steps get stated explicitly or deemed " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engineer
Engineers, as practitioners of engineering, are professionals who Invention, invent, design, build, maintain and test machines, complex systems, structures, gadgets and materials. They aim to fulfill functional objectives and requirements while considering the limitations imposed by practicality, regulation, safety and cost. "Science is knowledge based on our observed facts and tested truths arranged in an orderly system that can be validated and communicated to other people. Engineering is the creative application of scientific principles used to plan, build, direct, guide, manage, or work on systems to maintain and improve our daily lives." The word ''engineer'' (Latin , the origin of the Ir. in the title of engineer in countries like Belgium, The Netherlands, and Indonesia) is derived from the Latin words ("to contrive, devise") and ("cleverness"). The foundational qualifications of a licensed professional engineer typically include a four-year Bachelor of Engineering, bache ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feasibility Study
A feasibility study is an assessment of the practicality of a project or system. A feasibility study aims to objectively and rationally uncover the strengths and weaknesses of an existing business or proposed venture, opportunities and threats present in the natural environment, the resources required to carry through, and ultimately the prospects for success.Justis, R. T. & Kreigsmann, B. (1979). The feasibility study as a tool for venture analysis. ''Business Journal of Small Business Management'' 17 (1) 35-42. In its simplest terms, the two criteria to judge feasibility are cost required and value to be attained. A well-designed feasibility study should provide a historical background of the business or project, a description of the product or service, accounting statements, details of the operations and management Management (or managing) is the administration of organizations, whether businesses, nonprofit organizations, or a Government agency, government bodies throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Procurement
Procurement is the process of locating and agreeing to terms and purchasing goods, services, or other works from an external source, often with the use of a tendering or competitive bidding process. The term may also refer to a contractual obligation to "procure", i.e. to "ensure" that something is done. When a government agency buys goods or services through this practice, it is referred to as '' government procurement'' or public procurement. Procurement as an organizational process is intended to ensure that the buyer receives goods, services, or works at the best possible price when aspects such as quality, quantity, time, and location are compared. Corporations and public bodies often define processes intended to promote fair and open competition for their business while minimizing risks such as exposure to fraud and collusion. Almost all purchasing decisions include factors such as delivery and handling, marginal benefit, and fluctuations in the prices of goods. Org ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diagram
A diagram is a symbolic Depiction, representation of information using Visualization (graphics), visualization techniques. Diagrams have been used since prehistoric times on Cave painting, walls of caves, but became more prevalent during the Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment. Sometimes, the technique uses a Three-dimensional space, three-dimensional visualization which is then graphical projection, projected onto a two-dimensional surface. The word ''graphics, graph'' is sometimes used as a synonym for diagram. Overview The term "diagram" in its commonly used sense can have a general or specific meaning: * ''visual information device'' : Like the term "illustration", "diagram" is used as a collective term standing for the whole class of technical genres, including graphics, graphs, technical drawings and tables. * ''specific kind of visual display'' : This is the genre that shows qualitative data with shapes that are connected by lines, arrows, or other visual links. In scie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schematic
A schematic, or schematic diagram, is a designed representation of the elements of a system using abstract, graphic symbols rather than realistic pictures. A schematic usually omits all details that are not relevant to the key information the schematic is intended to convey, and may include oversimplified elements in order to make this essential meaning easier to grasp, as well as additional organization of the information. For example, a subway map intended for passengers may represent a subway station with a dot. The dot is not intended to resemble the actual station at all but aims to give the viewer information without unnecessary visual clutter. A schematic diagram of a chemical process uses symbols in place of detailed representations of the vessels, piping, valves, pumps, and other equipment that compose the system, thus emphasizing the functions of the individual elements and the interconnections among them and suppresses their physical details. In an electronic circuit d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Front-end Engineering
Front-End Engineering (FEE), or Front-End Engineering Design (FEED), is an engineering design approach used to control project expenses and thoroughly plan a project before a fix bid quote is submitted. It may also be referred to as Pre-project planning (PPP), front-end loading (FEL), feasibility analysis, or early project planning. Overview FEED is basic engineering, which comes after the Conceptual design or Feasibility study. FEE design focuses the technical requirements as well as rough investment cost for the project. FEED can be divided into separate packages covering different portions of the project. The FEED package is used as the basis for bidding for Engineering, Procurement and Construction contracts ( EPC, EPCI, etc) and is used as the design basis (or Basis of Design). A good FEED will reflect all of the client's project-specific requirements and avoid significant changes during the execution phase. FEED contracts usually take around 1 year to complete for larger- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brainstorming
Brainstorming is a creativity technique in which a group of people interact to divergent thinking, suggest ideas spontaneously in response to a prompt. Stress is typically placed on the volume and variety of ideas, including ideas that may seem outlandish or "off-the-wall". Ideas are noted down during the activity, but not assessed or critiqued until later. The absence of criticism and assessment is intended to avoid inhibiting participants in their idea production. The term was popularized by advertising executive Alex Faickney Osborn in the classic work ''Applied Imagination'' (1953). History In 1939, advertising executive Alex F. Osborn began developing methods for creative problem-solving. He was frustrated by employees' inability to develop creative ideas individually for ad campaigns. In response, he began hosting group-thinking sessions and discovered a significant improvement in the quality and quantity of ideas produced by employees. He first termed the process as ''orga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synectics
Synectics is a problem solving methodology that stimulates thought processes of which the subject may be unaware. This method was developed by George M. Prince (1918–2009)George Prince, consultant who sparked innovation, founded international firm '''', June 21, 2009 and William J.J. Gordon, originating in the Arthur D. Little Invention Design Unit in the 1950s. According ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morphological Analysis (problem-solving)
Morphological analysis or general morphological analysis is a method for exploring possible solutions to a multi-dimensional, non-quantified complex problem. It was developed by Swiss astronomer Fritz Zwicky.Ritchey, T. (1998)General Morphological Analysis: A general method for non-quantified modeling. General morphology has found use in fields including engineering design, technological forecasting, organizational development and policy analysis. Overview General morphology was developed by Fritz Zwicky, the Bulgarian-born, Swiss-national astrophysicist based at the California Institute of Technology. Among others, Zwicky applied morphological analysis to astronomical studies and jet and rocket propulsion systems. As a problem-structuring and problem-solving technique, morphological analysis was designed for multi-dimensional, non-quantifiable problems where causal modelling and simulation do not function well, or at all. Zwicky developed this approach to address seeming ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ideation (idea Generation)
Ideation is the creativity, creative process of generating, developing, and communicating new ideas, where an idea is understood as a basic unit of thought that can be either visual, concrete, or abstract. Ideation comprises all stages of a thought cycle, from innovation, to development, to actualization. Ideation can be conducted by individuals, organizations, or crowds. As such, it is an essential part of the design process, both in education and practice. Criticism The word "ideation" has come under informal criticism as being a term of meaningless jargon, as well as being inappropriately similar to the psychiatry, psychiatric term for suicidal ideation. Methods and approaches There are many methods and approaches for ideation. A list of common ideation techniques is as follows: * Brainstorming: A technique where the basic premise is to get a group together and have them share their ideas freely, without judgement. The goal is to generate as many ideas as possible, regard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
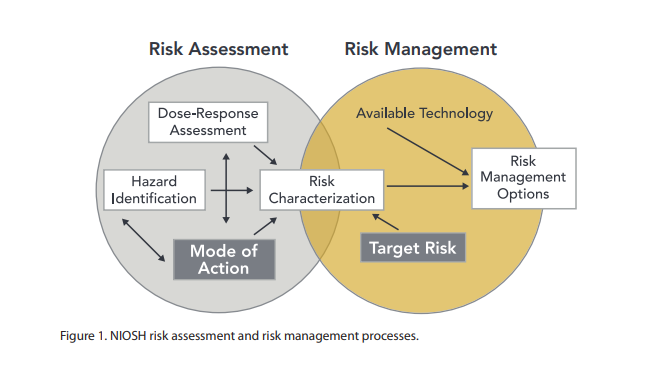
Risk Assessment
Risk assessment is a process for identifying hazards, potential (future) events which may negatively impact on individuals, assets, and/or the environment because of those hazards, their likelihood and consequences, and actions which can mitigate these effects. The output from such a process may also be called a risk assessment. Hazard analysis forms the first stage of a risk assessment process. Judgments "on the tolerability of the risk on the basis of a risk analysis" (i.e. risk evaluation) also form part of the process. The results of a risk assessment process may be expressed in a quantitative or qualitative fashion. Risk assessment forms a key part of a broader risk management strategy to help reduce any potential risk-related consequences. Categories Individual risk assessment Risk assessments can be undertaken in individual cases, including in patient and physician interactions. In the narrow sense chemical risk assessment is the assessment of a health risk in response ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |