|
Engineering Critical Assessment
Engineering Critical Assessment (ECA) is a procedure by which the safety of a welded structure with defects or flaws can be determined. ECAs utilize the material properties and expected stress history to determine a flaw acceptance criteria which will ensure that welds will not fail during the construction or service life of the welded structure. The assessment can be used before the structure is in use, or during in-service inspection, to determine whether a given weld is in need of repair. ECAs are used throughout the energy, manufacturing, and infrastructure industries. ECAs are based heavily upon fracture mechanics principles, and reflect an improvement over traditional methods of weld quality assurance, which can be arbitrary or overly conservative. Background During welding, defects or flaws can develop. In some cases, these flaws could potentially affect the integrity of the weld, resulting in failure by fatigue, creep, brittle fracture, or yielding. Therefore, c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
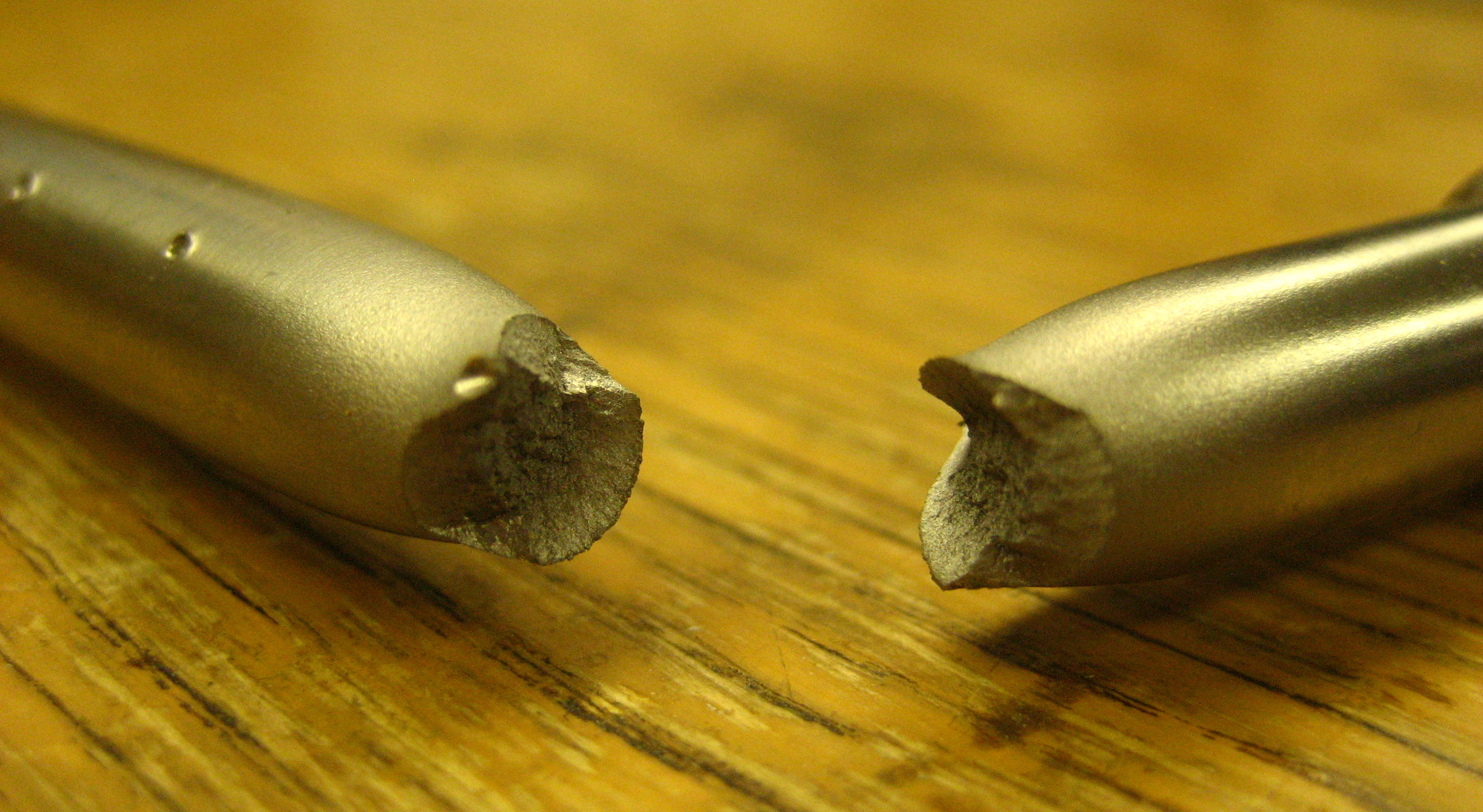
Welding Defect
In metalworking, a welding defect is any flaw that compromises the usefulness of a weldment. There is a great variety of welding defects. Welding imperfections are classified according to ISO 6520, while their acceptable limits are specified in ISO 5817 and ISO 10042. Major causes According to the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), causes of welding defects can be broken down as follows: 41% poor process conditions, 32% operator error, 12% wrong technique, 10% incorrect consumables and 5% bad weld grooves. Hydrogen embrittlement Residual stresses The magnitude of stress that can be formed from welding can be roughly calculated using: :E \alpha \Delta T Where E is Young's modulus, α is the coefficient of thermal expansion, and ΔT is the temperature change. For steel this calculates out to be approximately . Types Cracks Defects related to fracture. Arc strikes An Arc Strike is a discontinuity resulting from an arc, consisting of any localized remelted met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fracture Mechanics
Fracture mechanics is the field of mechanics concerned with the study of the propagation of cracks in materials. It uses methods of analytical solid mechanics to calculate the driving force on a crack and those of experimental solid mechanics to characterize the material's resistance to fracture. Theoretically, the stress ahead of a sharp crack tip becomes infinite and cannot be used to describe the state around a crack. Fracture mechanics is used to characterise the loads on a crack, typically using a single parameter to describe the complete loading state at the crack tip. A number of different parameters have been developed. When the plastic zone at the tip of the crack is small relative to the crack length the stress state at the crack tip is the result of elastic forces within the material and is termed linear elastic fracture mechanics (LEFM) and can be characterised using the stress intensity factor K. Although the load on a crack can be arbitrary, in 1957 G. Irwin foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatigue (material)
In materials science, fatigue is the initiation and propagation of cracks in a material due to cyclic loading. Once a fatigue crack has initiated, it grows a small amount with each loading cycle, typically producing striations on some parts of the fracture surface. The crack will continue to grow until it reaches a critical size, which occurs when the stress intensity factor of the crack exceeds the fracture toughness of the material, producing rapid propagation and typically complete fracture of the structure. Fatigue has traditionally been associated with the failure of metal components which led to the term metal fatigue. In the nineteenth century, the sudden failing of metal railway axles was thought to be caused by the metal ''crystallising'' because of the brittle appearance of the fracture surface, but this has since been disproved. Most materials, such as composites, plastics and ceramics, seem to experience some sort of fatigue-related failure. To aid in predicting t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Creep (deformation)
In materials science, creep (sometimes called cold flow) is the tendency of a solid material to move slowly or deform permanently under the influence of persistent mechanical stresses. It can occur as a result of long-term exposure to high levels of stress that are still below the yield strength of the material. Creep is more severe in materials that are subjected to heat for long periods and generally increases as they near their melting point. The rate of deformation is a function of the material's properties, exposure time, exposure temperature and the applied structural load. Depending on the magnitude of the applied stress and its duration, the deformation may become so large that a component can no longer perform its function – for example creep of a turbine blade could cause the blade to contact the casing, resulting in the failure of the blade. Creep is usually of concern to engineers and metallurgists when evaluating components that operate under high stresses or hig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fracture
Fracture is the separation of an object or material into two or more pieces under the action of stress. The fracture of a solid usually occurs due to the development of certain displacement discontinuity surfaces within the solid. If a displacement develops perpendicular to the surface, it is called a normal tensile crack or simply a crack; if a displacement develops tangentially, it is called a shear crack, slip band or dislocation. Brittle fractures occur with no apparent deformation before fracture. Ductile fractures occur after visible deformation. Fracture strength, or breaking strength, is the stress when a specimen fails or fractures. The detailed understanding of how a fracture occurs and develops in materials is the object of fracture mechanics. Strength Fracture strength, also known as breaking strength, is the stress at which a specimen fails via fracture. This is usually determined for a given specimen by a tensile test, which charts the stress–strain cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yield (engineering)
In materials science and engineering, the yield point is the point on a stress-strain curve that indicates the limit of elastic behavior and the beginning of plastic behavior. Below the yield point, a material will deform elastically and will return to its original shape when the applied stress is removed. Once the yield point is passed, some fraction of the deformation will be permanent and non-reversible and is known as plastic deformation. The yield strength or yield stress is a material property and is the stress corresponding to the yield point at which the material begins to deform plastically. The yield strength is often used to determine the maximum allowable load in a mechanical component, since it represents the upper limit to forces that can be applied without producing permanent deformation. In some materials, such as aluminium, there is a gradual onset of non-linear behavior, making the precise yield point difficult to determine. In such a case, the offset yiel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crack Tip Opening Displacement
Crack tip opening displacement (CTOD) or \delta_\text is the distance between the opposite faces of a crack tip at the 90° intercept position. The position behind the crack tip at which the distance is measured is arbitrary but commonly used is the point where two 45° lines, starting at the crack tip, intersect the crack faces. The parameter is used in fracture mechanics to characterize the loading on a crack and can be related to other crack tip loading parameters such as the stress intensity factor K and the elastic-plastic J-integral. For plane stress conditions, the CTOD can be written as: \delta_\text = \left(\frac\right)\ln\left sec\left(\frac\right)\right/math> where \sigma_\text is the yield stress, a is the crack length, E is the Young's modulus , and \sigma^\infty is the remote applied stress. Under fatigue loading, the range of movement of the crack tip during a loading cycle \Delta\delta_\text can be used for determining the rate of fatigue growth using a crack gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charpy Impact Test
In materials science, the Charpy impact test, also known as the Charpy V-notch test, is a standardized high strain rate test which determines the amount of energy absorbed by a material during fracture. Absorbed energy is a measure of the material's notch toughness. It is widely used in industry, since it is easy to prepare and conduct and results can be obtained quickly and cheaply. A disadvantage is that some results are only comparative. The test was pivotal in understanding the fracture problems of ships during World War II. The test was developed around 1900 by S. B. Russell (1898, American) and Georges Charpy (1901, French). The test became known as the Charpy test in the early 1900s due to the technical contributions and standardization efforts by Charpy. History In 1896, S. B. Russell introduced the idea of ''residual fracture energy'' and devised a pendulum fracture test. Russell's initial tests measured un-notched samples. In 1897, Frémont introduced a test to m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
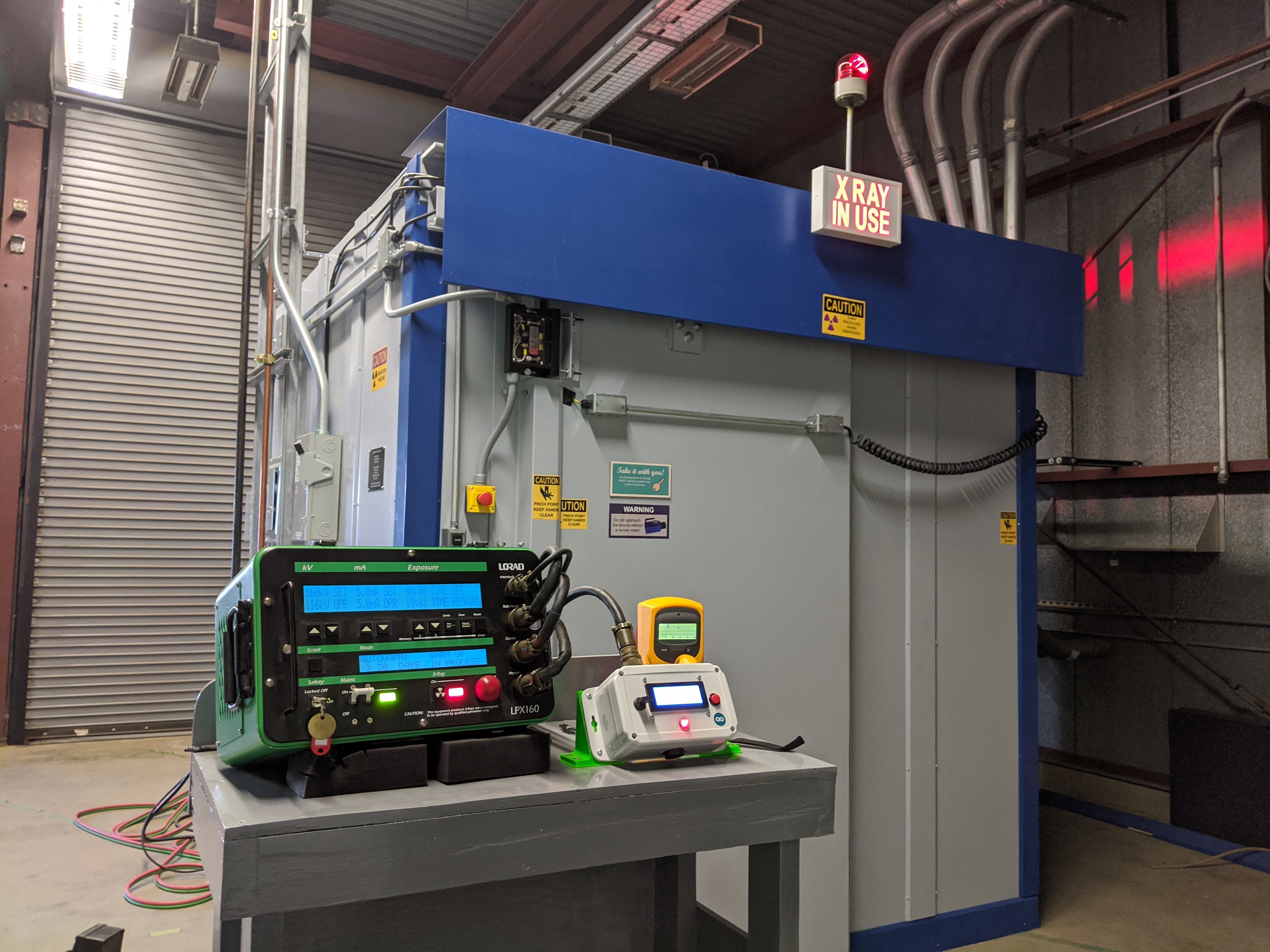
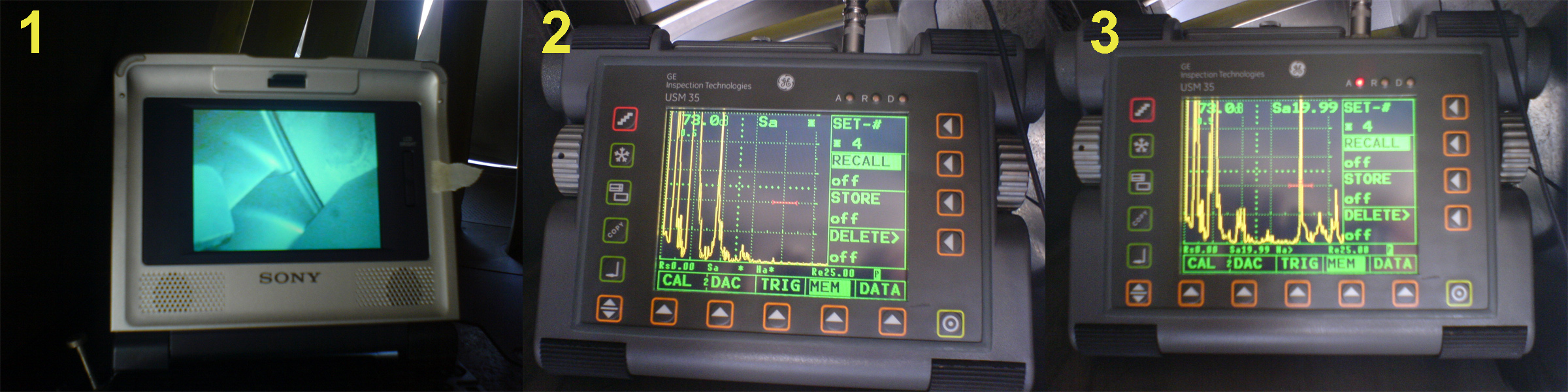
Nondestructive Testing
Nondestructive testing (NDT) is any of a wide group of analysis techniques used in science and technology industry to evaluate the properties of a material, component or system without causing damage. The terms nondestructive examination (NDE), nondestructive inspection (NDI), and nondestructive evaluation (NDE) are also commonly used to describe this technology. Because NDT does not permanently alter the article being inspected, it is a highly valuable technique that can save both money and time in product evaluation, troubleshooting, and research. The six most frequently used NDT methods are eddy-current, magnetic-particle, liquid penetrant, radiographic, ultrasonic, and visual testing. NDT is commonly used in forensic engineering, mechanical engineering, petroleum engineering, electrical engineering, civil engineering, systems engineering, aeronautical engineering, medicine, and art. Innovations in the field of nondestructive testing have had a profound impact on medical im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultrasonic Testing
Ultrasonic testing (UT) is a family of non-destructive testing techniques based on the propagation of ultrasonic waves in the object or material tested. In most common UT applications, very short ultrasonic pulse-waves with center frequencies ranging from 0.1-15 MHz, and occasionally up to 50 MHz, are transmitted into materials to detect internal flaws or to characterize materials. A common example is ultrasonic thickness measurement, which tests the thickness of the test object, for example, to monitor pipework corrosion. Ultrasonic testing is often performed on steel and other metals and alloys, though it can also be used on concrete, wood and composites, albeit with less resolution. It is used in many industries including steel and aluminium construction, metallurgy, manufacturing, aerospace, automotive and other transportation sectors. History The first efforts to use ultrasonic testing to detect flaws in solid material occurred in the 1930s.''Nondestructive F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |