|
Energy In The Middle East
Energy in the Middle East describes energy and electricity production, consumption and import in the Middle East. Energy policy of the Middle East will describe the politics of the Middle East related to energy more in detail. Primary energy use Energy export Energy export from the Middle East in 2010 was 12,228 TWh. The major exporters were Saudi Arabia 37.2%, Qatar 14.3% and Iran 12.9%. Oil In 2009 the largest share of oil production was in the Middle East (24 million barrels daily, or 31 per cent of global production). According to Transparency International based on BP data regionally the largest share of proved oil reserves is in the Middle East (754 billion barrels, constituting 51 per cent of global reserves including oil sands and 57 per cent excluding them). According to BP of the world oil reserves were in Saudi Arabia 18%, Iran 9%, Iraq 8%, Kuwait 7% and UAE 7%. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Energy Resources And Consumption
World energy supply and consumption is global production and preparation of fuel, generation of electricity, energy transport, and energy consumption. It is a basic part of economic activity. It includes heat, but not energy from food. This article provides a brief description of energy supply and consumption, using statistics summarized in tables, of the countries and regions that produce and consume most. Energy production is 80% fossil. Half of that is produced by China, the United States and the Arab states of the Persian Gulf. The Gulf States and Russia export most of their production, largely to the European Union and China, where not enough energy is produced to satisfy demand. Energy production is increasing 1 to 2% per year, except for solar and wind energy which averaged 20% per year in the 2010s. Produced energy, for instance crude oil, is processed to make it suitable for consumption by end users. The supply chain between production and final consumption involves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, north and Oman to the Oman–Yemen border, northeast and shares maritime borders with Eritrea, Djibouti, and Somalia. Yemen is the second-largest Arabs, Arab sovereign state in the peninsula, occupying , with a coastline stretching about . Its constitutionally stated Capital city, capital, and largest city, is Sanaa. As of 2021, Yemen has an estimated population of some 30.4 million. In ancient times, Yemen was the home of the Sabaeans, a trading state that included parts of modern-day Ethiopia and Eritrea. Later in 275 AD, the Himyarite Kingdom was influenced by Judaism. Christianity arrived in the fourth century. Islam spread quickly in the seventh century and Yemenite troops were crucial in the early Islamic conquests. Several Dynasty, dynasties ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy In Bahrain
Energy in Bahrain describes energy and electricity production, consumption and import in Bahrain. Bahrain is a net energy exporter. Primary energy use was in Bahrain in 2009 110 TWh and 139 TWh per million persons and in 2008 107 TWh and 139 TWh/million people.IEA Key energy statistics 2011 an Statistics 2010 Page: Country specific indicator numbers from page 48 Overview Oil Bahrain was the first place on the Arabian side of the where oil was discovered. The |
Energy In Yemen
Energy in Yemen describes energy and electricity production, consumption and import in Yemen. Yemen is net energy exporter. Primary energy use in Yemen was 87 TWh and 4 TWh/million people in 2008 and 88 TWh (4 TWh/M) in 2009.IEA Key energy statistics 2010 an 2011 Page: Country specific indicator numbers from page 48 Overview According to the World Bank, Yemen has the lowest level of electricity connection in the Middle East, with only 40% of the population having access to electricity. Rural areas are particularly badly affected. Industrial concerns, hospitals and hotels have their own back-up generators. To address these shortages, a 34 ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy In Egypt
This article describes the energy and electricity production, consumption and import in Egypt. Overview Electrical power Egypt is classified as having a “high power system size (24,700 MW installed generation capacity in 2010 with more than 40 grid-connected plants).” As of 2010, 100% of the Egyptian population has access to electricity. History When electricity was first introduced in Egypt in 1893, the generation and distribution of electricity was practiced exclusively by private companies. In 1962, the generation, transmission, and distribution of electricity were nationalized under three authorities (the Electricity Production Authority, the Electricity Distribution Authority, and the Electricity Projects Implementation Authority) leaving the government as the sole owner and operator of all electrical companies. These three authorities were replaced in 1965 by the public Egyptian Corporation for Electricity which remained active until 1976 when it was converted in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
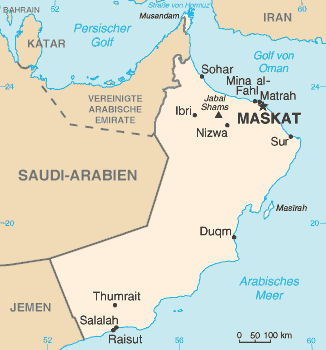
Energy In Oman
Energy use in Oman was 381 TWh in 2020, almost double the consumption in 2010. Economy Oman is a country in the Middle East. Its current GDP per capita has expanded continuously over the past 50 years. It grew 339% in the 1960s and reached a peak growth of 1,370% in 1976.. Oman both imports and exports energy. When Oman declined as an entrepot for arms and Slavery, slaves in the mid-19th century, much of its former prosperity vanished; the economy turned almost exclusively to agriculture, camel and goat herding, fishing, and traditional handicrafts. Today, petroleum (oil) exports fuel the economy. Revenues from petroleum products have enabled Oman's dramatic development and modernization over the past 300 years. Overview Oil Oil was first discovered in 1964, near Fahud in the western desert. Petroleum Development Oman (PDO) began production in August 1967. The Omani Government owns 60% of PDO, and foreign interests own 40% (Royal Dutch Shell owns 34%; the remaining 6% is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |