|
Energy Diplomacy
Energy diplomacy is a form of diplomacy, and a subfield of international relations. It is closely related to its principal, foreign policy, and to overall national security, specifically energy security. Energy diplomacy began in the first half of the twentieth century and emerged as a term during the second oil crisis as a means of describing OPEC's actions. It has since mainly focused on the securitization of energy supplies, primarily fossil fuels, but also nuclear energy and increasingly sustainable energy, on a country or bloc basis. Background Energy diplomacy emerged as a term during the second oil crisis as a means of describing OPEC's actions and of characterizing the quest for the United States to secure energy independence and the Cold War relationship between Russia and satellite states regarding oil and gas exports. Since the oil crises, energy diplomacy has mainly focused on the securitization of energy supplies on a country or bloc basis and on the foreign policy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diplomacy
Diplomacy comprises spoken or written communication by representatives of states (such as leaders and diplomats) intended to influence events in the international system.Ronald Peter Barston, ''Modern diplomacy'', Pearson Education, 2006, p. 1 Diplomacy is the main instrument of foreign policy which represents the broader goals and strategies that guide a state's interactions with the rest of the world. International treaties, agreements, alliances, and other manifestations of international relations are usually the result of diplomatic negotiations and processes. Diplomats may also help to shape a state by advising government officials. Modern diplomatic methods, practices, and principles originated largely from 17th-century European custom. Beginning in the early 20th century, diplomacy became professionalized; the 1961 Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations, ratified by most of the world's sovereign states, provides a framework for diplomatic procedures, methods, and co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
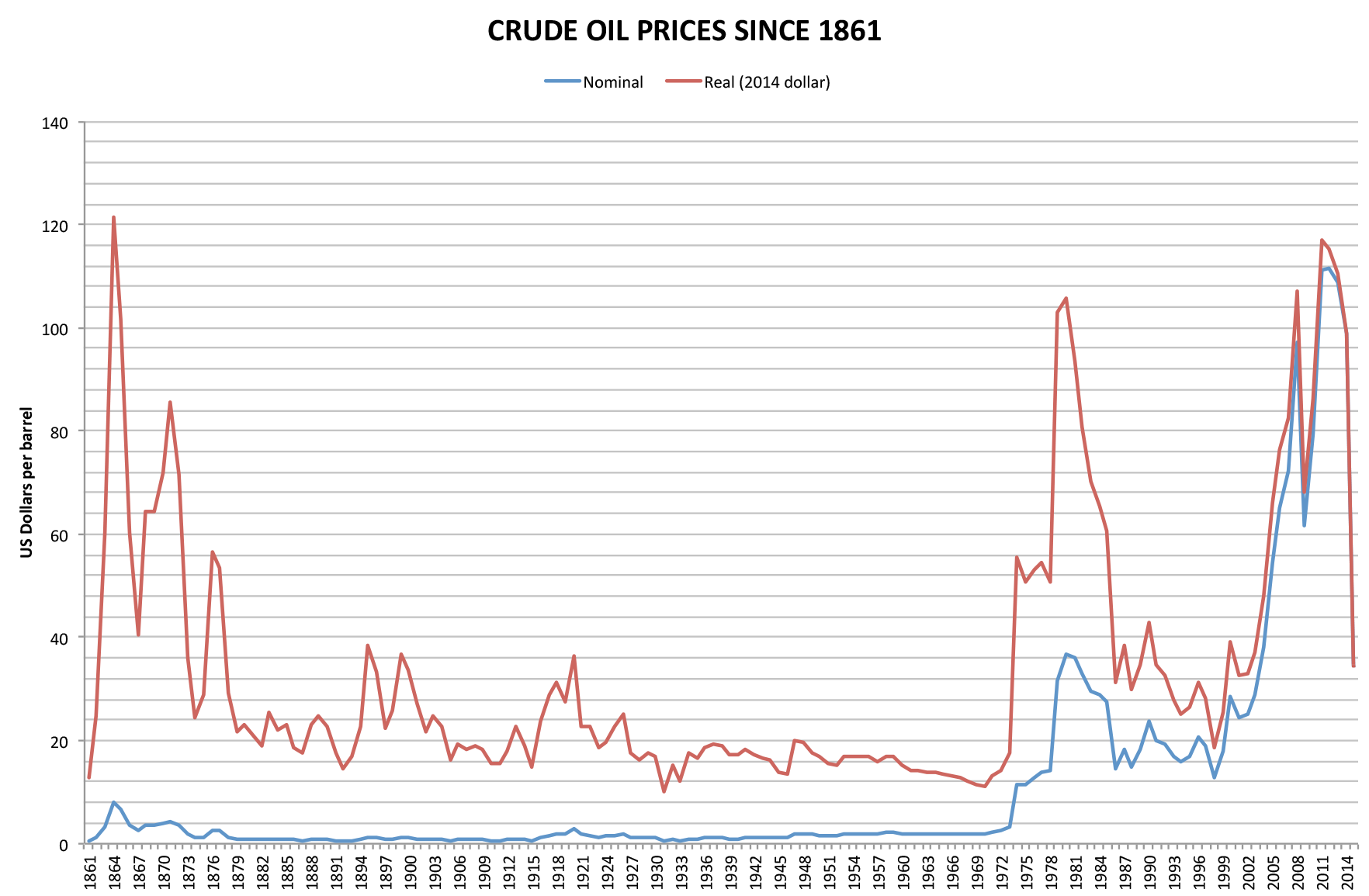
1973 Oil Crisis
The 1973 oil crisis or first oil crisis began in October 1973 when the members of the Organization of Arab Petroleum Exporting Countries (OAPEC), led by Saudi Arabia, proclaimed an oil embargo. The embargo was targeted at nations that had supported Israel during the Yom Kippur War. The initial nations targeted were Canada, Japan, the Netherlands, the United Kingdom and the United States, though the embargo also later extended to Portugal, Rhodesia and South Africa. By the end of the embargo in March 1974, the price of oil had risen nearly 300%, from US to nearly globally; US prices were significantly higher. The embargo caused an oil crisis, or "shock", with many short- and long-term effects on global politics and the global economy. It was later called the "first oil shock", followed by the 1979 oil crisis, termed the "second oil shock". Background Arab-Israeli conflict Ever since the recreation of the State of Israel in 1948 there has been Arab–Israeli conflict in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advocacy
Advocacy is an Action (philosophy), activity by an individual or advocacy group, group that aims to influence decision making, decisions within political, economic, and social institutions. Advocacy includes activities and publications to influence public policy, laws and budgets by using facts, their relationships, the media, and messaging to educate government officials and the public. Advocacy can include many activities that a person or organization undertakes, including media campaigns, public speaking, commissioning and publishing research. Lobbying (often by lobby groups) is a form of advocacy where a direct approach is made to legislators on a specific issue or specific piece of legislation. Research has started to address how advocacy groups in the United States and Canada are using social media to facilitate civic engagement and collective action. Forms There are several forms of advocacy, each representing a different approach in a way to initiate changes in the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lobbying
In politics, lobbying, persuasion or interest representation is the act of lawfully attempting to influence the actions, policies, or decisions of government officials, most often legislators or members of regulatory agency, regulatory agencies. Lobbying, which usually involves direct, face-to-face contact, is done by many types of people, associations and organized groups, including individuals in the private sector, corporations, fellow legislators or government officials, or advocacy groups (interest groups). Lobbyists may be among a legislator's Electoral district, constituencies, meaning a Voting, voter or Voting bloc, bloc of voters within their electoral district; they may engage in lobbying as a business. Professional lobbyists are people whose business is trying to influence legislation, regulation, or other government decisions, actions, or policies on behalf of a group or individual who hires them. Individuals and nonprofit organizations can also lobby as an act of vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negotiation
Negotiation is a dialogue between two or more people or parties to reach the desired outcome regarding one or more issues of conflict. It is an interaction between entities who aspire to agree on matters of mutual interest. The agreement can be beneficial for all or some of the parties involved. The negotiators should establish their own needs and wants while also seeking to understand the wants and needs of others involved to increase their chances of closing deals, avoiding conflicts, forming relationships with other parties, or maximizing mutual gains. The goal of negotiation is to resolve points of difference, gain an advantage for an individual or collective, or craft outcomes to satisfy various interests. Distributive negotiations, or compromises, are conducted by putting forward a position and making concessions to achieve an agreement. The degree to which the negotiating parties trust each other to implement the negotiated solution is a major factor in determining ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diplomacy
Diplomacy comprises spoken or written communication by representatives of states (such as leaders and diplomats) intended to influence events in the international system.Ronald Peter Barston, ''Modern diplomacy'', Pearson Education, 2006, p. 1 Diplomacy is the main instrument of foreign policy which represents the broader goals and strategies that guide a state's interactions with the rest of the world. International treaties, agreements, alliances, and other manifestations of international relations are usually the result of diplomatic negotiations and processes. Diplomats may also help to shape a state by advising government officials. Modern diplomatic methods, practices, and principles originated largely from 17th-century European custom. Beginning in the early 20th century, diplomacy became professionalized; the 1961 Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations, ratified by most of the world's sovereign states, provides a framework for diplomatic procedures, methods, and co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Market
Energy markets are national and international regulated markets that deal specifically with the trade and supply of energy. Energy market may refer to an electricity market, but can also refer to other sources of energy. Typically energy development is the result of a government creating an energy policy that encourages the development of an energy industry in a competitive manner. Until the 1970s when energy markets underwent dramatic changes, they were characterised by monopoly-based organisational structures. Most of the world's petroleum reserves were controlled by the Seven Sisters. Circumstances changed considerably in 1973 as the influence of OPEC grew and the repercussions of the 1973 oil crisis affected global energy markets. Liberalization and regulation Energy markets have been liberalized in some countries; they are regulated by national and international authorities (including liberalized markets) to protect consumer rights and avoid oligopolies. Regulators i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Energy Resources
World energy resources are the estimated maximum capacity for energy production given all available resources on Earth. They can be divided by type into fossil fuel, nuclear fuel and renewable resources. Fossil fuel Remaining reserves of fossil fuel are estimated as: These are the proven energy reserves; real reserves may be four or more times larger. These numbers are very uncertain. Estimating the remaining fossil fuels on the planet depends on a detailed understanding of Earth's crust. With modern drilling technology, we can drill wells in up to 3 km of water to verify the exact composition of the geology; but half of the ocean is deeper than 3 km, leaving about a third of the planet beyond the reach of detailed analysis. There is uncertainty in the total amount of reserves, but also in how much of these can be recovered gainfully, for technological, economic and political reasons, such as the accessibility of fossil deposits, the levels of sulfur and other p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Energy Agency
The International Energy Agency (IEA) is a Paris-based autonomous intergovernmental organisation, established in 1974, that provides policy recommendations, analysis and data on the entire global energy sector, with a recent focus on curbing carbon emissions and reaching global climate targets, including the Paris Agreement. The 31 member countries and 11 association countries of the IEA represent 75% of global energy demand. The IEA was set up under the framework of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) in the aftermath of the 1973 oil crisis to respond to physical disruptions in global oil supplies, provide data and statistics about the global oil market and energy sector, promote energy savings and conservation, and establish international technical collaboration on innovation and research. Since its founding, the IEA has also coordinated use of the oil reserves that its members are required to hold. In subsequent decades, the IEA's role expanded t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2009 Russia–Ukraine Gas Dispute
In 2009, Russian natural gas company Gazprom refused to conclude a supply contract unless Ukrainian gas company Naftogaz paid its accumulating debts for previous gas supplies. The dispute began in the closing weeks of 2008 with a series of failed negotiations, and on January 1, 2009 Russia cut off gas supplies to Ukraine. On January 7 the dispute turned to crisis when all Russian gas flows through Ukraine were halted for 13 days, completely cutting off supplies to Southeastern Europe, most of which depends on Russian gas, and partially to other European countries.The Russo-Ukrainian gas dispute of January 2009: a comprehensive assessment |
2000s Energy Crisis
From the mid-1980s to September 2003, the inflation-adjusted price of a barrel of crude oil on NYMEX was generally under US$25/barrel in 2008 dollars. During 2003, the price rose above $30, reached $60 by 11 August 2005, and peaked at $147.30 in July 2008. Commentators attributed these price increases to many factors, including Middle East tension, soaring demand from China, the falling value of the U.S. dollar, reports showing a decline in petroleum reserves, worries over peak oil, and financial speculation. For a time, geopolitical events and natural disasters had strong short-term effects on oil prices, such as North Korean missile tests, the 2006 conflict between Israel and Lebanon, worries over Iranian nuclear plans in 2006, Hurricane Katrina, and various other factors. By 2008, such pressures appeared to have an insignificant impact on oil prices given the onset of the global recession. The recession caused demand for energy to shrink in late 2008, with oil prices c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2003 Invasion Of Iraq
The 2003 invasion of Iraq was a United States-led invasion of the Republic of Iraq and the first stage of the Iraq War. The invasion phase began on 19 March 2003 (air) and 20 March 2003 (ground) and lasted just over one month, including 26 days of major combat operations, in which a combined force of troops from the United States, the United Kingdom, Australia, and Poland invaded Iraq. Twenty-two days after the first day of the invasion, the capital city of Baghdad was captured by Coalition forces on 9 April 2003 after the six-day-long Battle of Baghdad. This early stage of the war formally ended on 1 May 2003 when U.S. President George W. Bush declared the "end of major combat operations" in his Mission Accomplished speech, after which the Coalition Provisional Authority (CPA) was established as the first of several successive transitional governments leading up to the first Iraqi parliamentary election in January 2005. U.S. military forces later remained in Iraq unt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |