|
Energy Supply
Energy supply is the delivery of fuels or transformed fuels to point of consumption. It potentially encompasses the extraction, transmission, generation, distribution and storage of fuels. It is also sometimes called energy flow. This supply of energy can be disrupted by several factors, including imposition of higher energy prices due to action by OPEC or other cartel, war, political disputes, economic disputes, or physical damage to the energy infrastructure due to terrorism. The security of the energy supply is a major concern of national security and energy law. Other uses Some sources refer to "energy supply" when actually referring to the oil reserves or other potential sources of energy. New York Consolidated Laws includes a statutory code called "Energy Law".N.Y. Energy Law § 1-101, found aNew York State Legislature official web site go to "ENG", then "Article 1", finally "1–101 – Short title". Accessed January 31, 2011. Article 21 of this code is called "E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resource Extraction
Extractivism is the process of extracting natural resources from the Earth to sell on the world market. It exists in an economy that depends primarily on the extraction or removal of natural resources that are considered valuable for exportation worldwide. Some examples of resources that are obtained through extraction include gold, diamonds, lumber and oil. This economic model has become popular in many Latin American countries but is becoming increasingly prominent in other regions as well. Many factors are involved in the process of extractivism. These include but are not limited to community members, transnational corporations (TNCs) and the government. Trends have demonstrated that countries do not often extract their own resources; extraction is often led from abroad. These interactions have contributed to extractivism being rooted in the hegemonic order of global capitalism. Extractivism is controversial because it exists at the intersection where economic growth and environ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
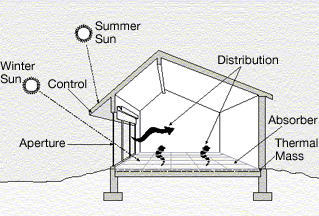
Energy Conservation
Energy conservation is the effort to reduce wasteful energy consumption by using fewer energy services. This can be done by using energy more effectively (using less energy for continuous service) or changing one's behavior to use less service (for example, by driving less). Energy conservation can be achieved through energy efficiency, which has a number of advantages, including a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions, a smaller carbon footprint, and cost, water, and energy savings. Energy conservation is an essential factor in building design and construction. It has increased in importance since the 1970s, as 40% of energy use in the U.S. is in buildings. Recently, concern over the effects of climate change and global warming has emphasized the importance of energy conservation. Energy can only be transformed from one form to another, such as when heat energy is converted into vehicle motive power or when water flow's kinetic energy is converted into electricity in hydroelectr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Energy Consumption
World energy supply and consumption is global production and preparation of fuel, generation of electricity, energy transport, and energy consumption. It is a basic part of economic activity. It includes heat, but not energy from food. This article provides a brief description of energy supply and consumption, using statistics summarized in tables, of the countries and regions that produce and consume most. Energy production is 80% fossil. Half of that is produced by China, the United States and the Arab states of the Persian Gulf. The Gulf States and Russia export most of their production, largely to the European Union and China, where not enough energy is produced to satisfy demand. Energy production is increasing 1 to 2% per year, except for solar and wind energy which averaged 20% per year in the 2010s. Produced energy, for instance crude oil, is processed to make it suitable for consumption by end users. The supply chain between production and final consumption involve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Market Transformation
Market transformation describes both a policy objective and a program strategyYork, D. A Discussion and Critique of Market Transformation' , Review 186-1. Energy Center of Wisconsin, June 1999 to promote the value and self-sustaining presence of energy-efficient technologies in the marketplace. It is a strategic process of market intervention which aims to alter market behavior by removing identified barriers and leveraging opportunities to further the internalization of cost-effective energy efficiency as a matter of standard practice. Market transformation has rapidly become the objective of many privately and publicly supported energy efficiency programs in the United States and other countries. Background First coined in a paper presented at the ACEEE Summer Study in 1992,Nadel, Thorne, Sacks, Prindle, Elliott. Market Transformation: Substantial Progress from a Decade of Work' American Council for an Energy-Efficient Economy, April 2003. the term "market transformation" is u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Energy Topics
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to energy: Energy – in physics, this is an indirectly observed quantity often understood as the ability of a physical system to do work on other physical systems. Since work is defined as a force acting through a distance (a length of space), energy is always equivalent to the ability to exert force (a pull or a push) against an object that is moving along a definite path of certain length. Forms of energy * Chemical energy – energy contained in molecules * Electrical energy – energy from electric fields *Electro-centric energy – energy sustaining the continuous motion of free electron* Gravitational energy – energy from gravitational fields * Ionization energy – energy that binds an electron to its atom or molecule * Kinetic energy – (), energy of the motion of a body * Magnetic energy – energy from magnetic fields * Mechanical energy – The sum of (usually macroscopic) kinetic a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Introduction To Entropy
In thermodynamics, entropy is a numerical quantity that shows that many physical processes can go in only one direction in time. For example, you can pour cream into coffee and mix it, but you cannot "unmix" it; you can burn a piece of wood, but you cannot "unburn" it. The word 'entropy' has entered popular usage to refer a lack of order or predictability, or of a gradual decline into disorder. A more physical interpretation of thermodynamic entropy refers to spread of energy or matter, or to extent and diversity of microscopic motion. If you reversed a movie of coffee being mixed or wood being burned, you would see things that are impossible in the real world. Another way of saying that those reverse processes are impossible is to say that mixing coffee and burning wood are "irreversible". Irreversibility is described by an important law of nature known as the second law of thermodynamics, which says that in an isolated system (a system not connected to any other system) which i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entropy (energy Dispersal)
The interpretation of entropy as a measure of energy dispersal has been exercised against the background of the traditional view, introduced by Ludwig Boltzmann, of entropy as a quantitative measure of disorder. The energy dispersal approach avoids the ambiguous term 'disorder'. An early advocate of the energy dispersal conception was Edward Armand Guggenheim in 1949, using the word 'spread'.Dugdale, J.S. (1996). ''Entropy and its Physical Meaning'', Taylor & Francis, London, , Dugdale cites only Guggenheim, on page 101.Guggenheim, E.A. (1949), Statistical basis of thermodynamics, ''Research: A Journal of Science and its Applications'', 2, Butterworths, London, pp. 450–454. In this alternative approach, entropy is a measure of energy ''dispersal'' or ''spread'' at a specific temperature. Changes in entropy can be quantitatively related to the distribution or the spreading out of the energy of a thermodynamic system, divided by its temperature. Some educators propose that the en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Quality
Energy quality is a measure of the ease with which a form of energy can be converted to useful work or to another form of energy: i.e. its content of thermodynamic free energy. A high quality form of energy has a high content of thermodynamic free energy, and therefore a high proportion of it can be converted to work; whereas with low quality forms of energy, only a small proportion can be converted to work, and the remainder is dissipated as heat. The concept of energy quality is also used in ecology, where it is used to track the flow of energy between different trophic levels in a food chain and in thermoeconomics, where it is used as a measure of economic output per unit of energy. Methods of evaluating energy quality often involve developing a ranking of energy qualities in hierarchical order. Examples: Industrialization, Biology The consideration of energy quality was a fundamental driver of industrialization from the 18th through 20th centuries. Consider for examp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Price (other)
{{Disambig ...
The following articles relate to the price of energy: *Carbon price *Energy crisis *Price of oil * Gas prices (other) *Hubbert peak theory, or peak oil *Energy economics *Electricity market *Electricity pricing *Cost of electricity by source Different methods of electricity generation can incur a variety of different costs, which can be divided into three general categories: 1) wholesale costs, or all costs paid by utilities associated with acquiring and distributing electricity to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Policy
Energy policy is the manner in which a given entity (often governmental) has decided to address issues of energy development including energy conversion, distribution and use as well as reduction of greenhouse gas emissions in order to contribute to climate change mitigation. The attributes of energy policy may include legislation, international treaties, incentives to investment, guidelines for energy conservation, taxation and other public policy techniques. Energy is a core component of modern economies. A functioning economy requires not only labor and capital but also energy, for manufacturing processes, transportation, communication, agriculture, and more. Energy planning is more detailed than energy policy. Energy policy is closely related to climate change policy because totalled worldwide the energy sector emits more greenhouse gas than other sectors. Purposes Access to energy is critical for basic social needs, such as lighting, heating, cooking, and heal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Derivative
An energy derivative is a derivative contract based on (derived from) an underlying energy asset, such as natural gas, crude oil, or electricity. Energy derivatives are exotic derivatives and include exchange-traded contracts such as futures and options, and over-the-counter (i.e., privately negotiated) derivatives such as forwards, swaps and options. Major players in the energy derivative markets include major trading houses, oil companies, utilities, and financial institutions. Energy derivatives were criticized after the 2008 financial crisis, with critics pointing out that the market artificially inflates the price of oil and other energy providers. Definition The basic building blocks for all derivative contracts are futures contracts and swaps contracts. In energy markets, these are traded on the New York Mercantile Exchange NYMEX, in Tokyo TOCOM and online through the IntercontinentalExchange. Futures contracts A futures contract is an agreement to buy or sel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
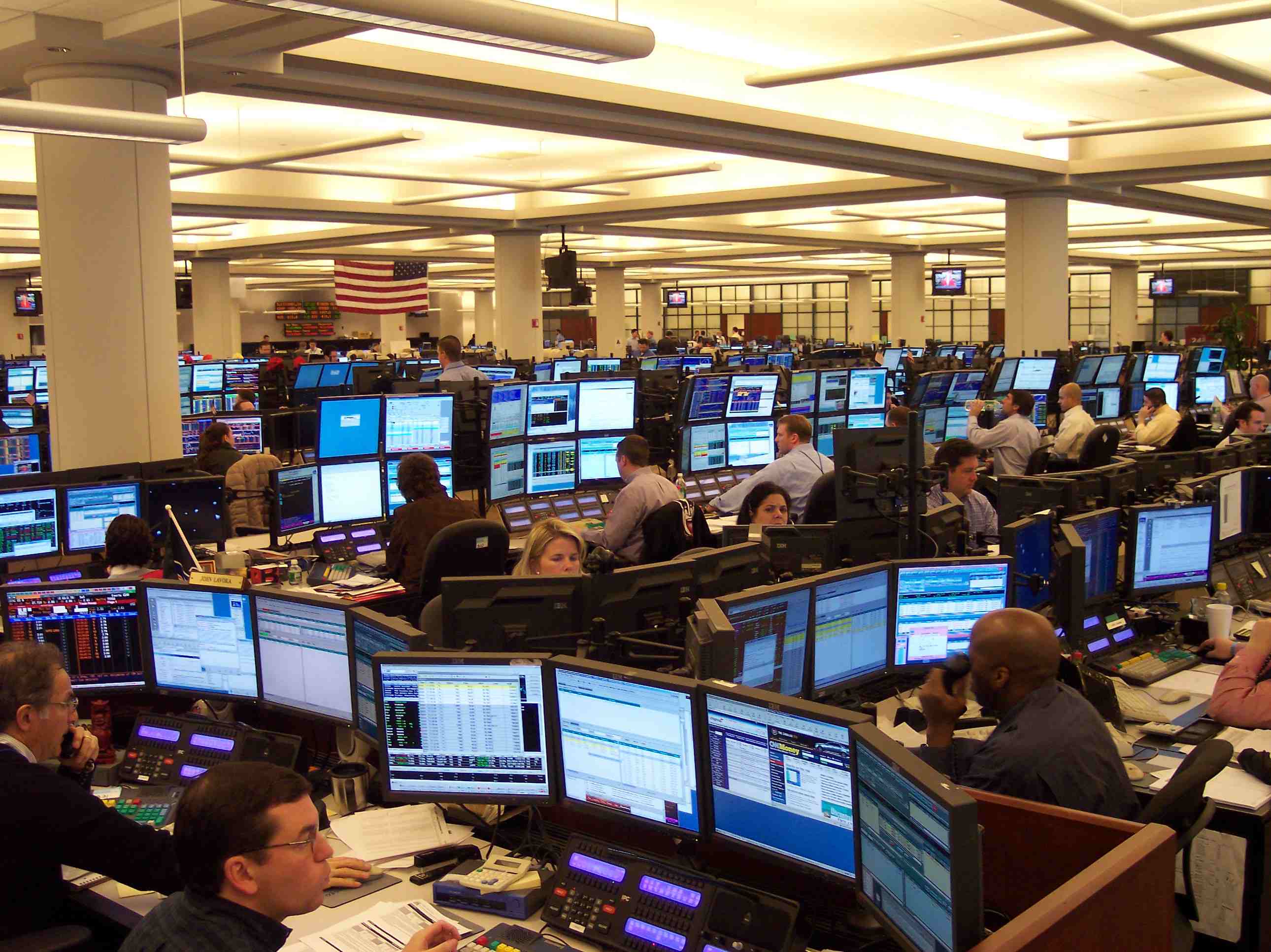
Energy Market
Energy markets are national and international regulated markets that deal specifically with the trade and supply of energy. Energy market may refer to an electricity market, but can also refer to other sources of energy. Typically energy development is the result of a government creating an energy policy that encourages the development of an energy industry in a competitive manner. Until the 1970s when energy markets underwent dramatic changes, they were characterised by monopoly-based organisational structures. Most of the world's petroleum reserves were controlled by the Seven Sisters. Circumstances changed considerably in 1973 as the influence of OPEC grew and the repercussions of the 1973 oil crisis affected global energy markets. Liberalization and regulation Energy markets have been liberalized in some countries; they are regulated by national and international authorities (including liberalized markets) to protect consumer rights and avoid oligopolies. Regulators in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |