|
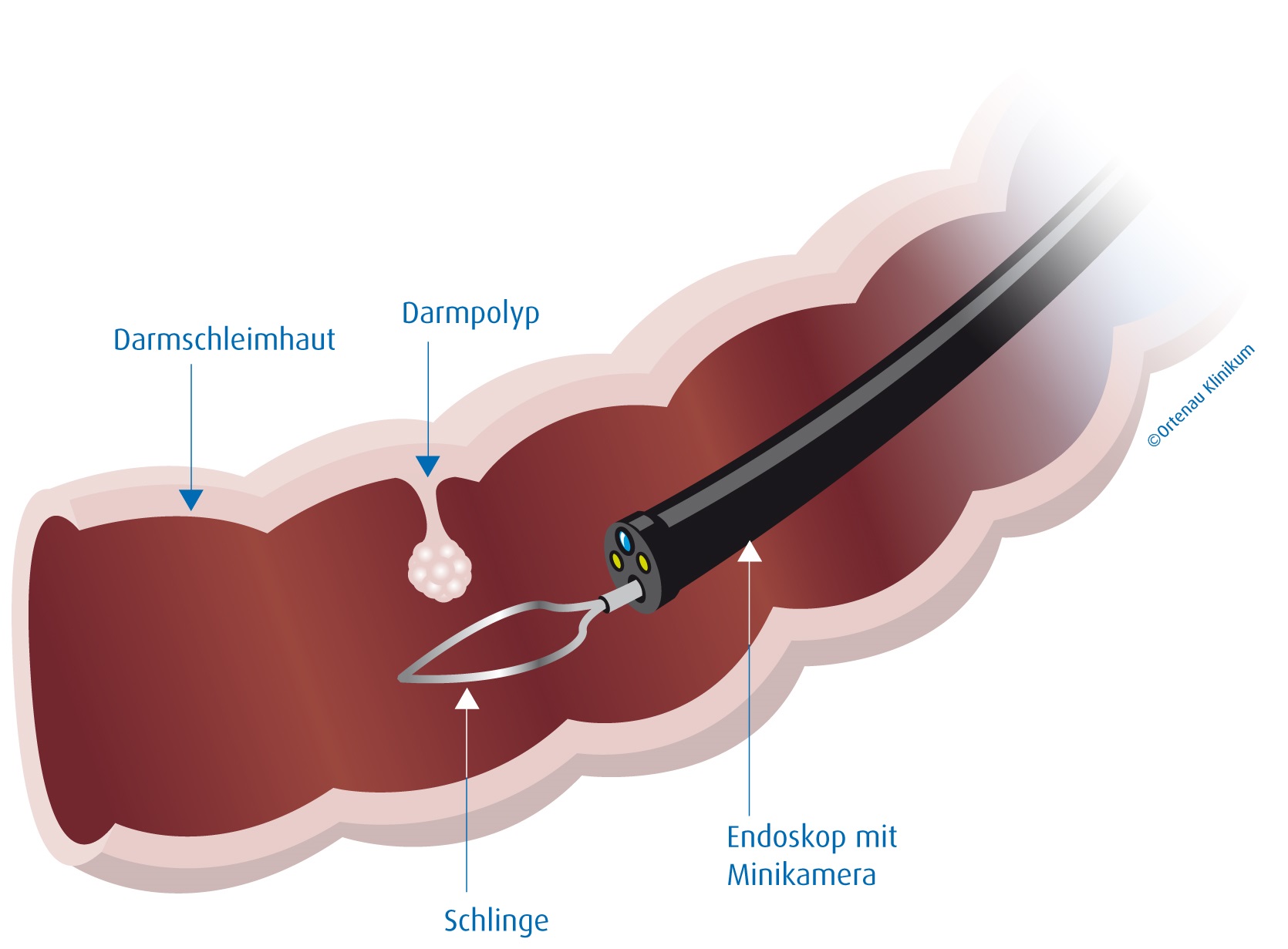
Endoscopic Mucosal Resection
Endoscopic mucosal resection is a technique used to remove cancerous or other abnormal lesions found in the digestive tract. It is one method of performing a mucosectomy. For the esophagous Endoscopic mucosal resection has been advocated for early esophageal cancers (that is, those that are superficial and confined to the mucosa only) and has been shown to be a less invasive, safe, and effective therapy for early squamous cell carcinoma. It has also been shown to be safe and effective for early adenocarcinoma arising in Barrett’s esophagus. The prognosis after treatment with this method is comparable to surgical resection. This technique can be attempted in patients who have no evidence of nodal or distant metastases, with differentiated tumors that are slightly raised and less than 2 cm in diameter, or in differentiated tumors that are ulcerated and less than 1 cm in diameter. The most commonly employed modalities of endoscopic mucosal resection include strip biopsy, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastroenterology
Gastroenterology (from the Greek gastḗr- “belly”, -énteron “intestine”, and -logía "study of") is the branch of medicine focused on the digestive system and its disorders. The digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract, sometimes referred to as the ''GI tract,'' which includes the esophagus, stomach, small intestine and large intestine as well as the accessory organs of digestion which includes the pancreas, gallbladder, and liver. The digestive system functions to move material through the GI tract via peristalsis, break down that material via digestion, absorb nutrients for use throughout the body, and remove waste from the body via defecation. Physicians who specialize in the medical specialty of gastroenterology are called gastroenterologists or sometimes ''GI doctors''. Some of the most common conditions managed by gastroenterologists include gastroesophageal reflux disease, gastrointestinal bleeding, irritable bowel syndrome, irritable bow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tumor
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists in growing abnormally, even if the original trigger is removed. This abnormal growth usually forms a mass, when it may be called a tumor. ICD-10 classifies neoplasms into four main groups: benign neoplasms, in situ neoplasms, malignant neoplasms, and neoplasms of uncertain or unknown behavior. Malignant neoplasms are also simply known as cancers and are the focus of oncology. Prior to the abnormal growth of tissue, as neoplasia, cells often undergo an abnormal pattern of growth, such as metaplasia or dysplasia. However, metaplasia or dysplasia does not always progress to neoplasia and can occur in other conditions as well. The word is from Ancient Greek 'new' and 'formation, creation'. Types A neoplasm can be benign, potenti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemostasis
In biology, hemostasis or haemostasis is a process to prevent and stop bleeding, meaning to keep blood within a damaged blood vessel (the opposite of hemostasis is hemorrhage). It is the first stage of wound healing. This involves coagulation, which changes blood from a liquid to a gel. Intact blood vessels are central to moderating blood's tendency to form clots. The endothelial cells of intact vessels prevent blood clotting with a heparin-like molecule and thrombomodulin, and prevent platelet aggregation with nitric oxide and prostacyclin. When endothelium of a blood vessel is damaged, the endothelial cells stop secretion of coagulation and aggregation inhibitors and instead secrete von Willebrand factor, which initiate the maintenance of hemostasis after injury. Hemostasis involves three major steps: * vasoconstriction * temporary blockage of a hole in a damaged blood vessel by a platelet plug * blood coagulation (formation of fibrin clots) These processes seal the injury ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postoperative Bleeding
Surgery ''cheirourgikē'' (composed of χείρ, "hand", and ἔργον, "work"), via la, chirurgiae, meaning "hand work". is a medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a person to investigate or treat a pathological condition such as a disease or injury, to help improve bodily function, appearance, or to repair unwanted ruptured areas. The act of performing surgery may be called a surgical procedure, operation, or simply "surgery". In this context, the verb "operate" means to perform surgery. The adjective surgical means pertaining to surgery; e.g. surgical instruments or surgical nurse. The person or subject on which the surgery is performed can be a person or an animal. A surgeon is a person who practices surgery and a surgeon's assistant is a person who practices surgical assistance. A surgical team is made up of the surgeon, the surgeon's assistant, an anaesthetist, a circulating nurse and a surgical technologist. Surgery usually spans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resection Margin
A resection margin or surgical margin is the margin of apparently non-tumorous tissue around a tumor that has been surgically removed, called " resected", in surgical oncology. The resection is an attempt to remove a cancer tumor so that no portion of the malignant growth extends past the edges or margin of the removed tumor and surrounding tissue. These are retained after the surgery and examined microscopically by a pathologist to see if the margin is indeed free from tumor cells. If cancerous cells are found at the edges the operation is much less likely to achieve the desired results. Residual tumour at the primary site after treatment (it does not address the surgical margin as commonly believed) is classified by the pathologist as (AJCC 8th Edition): * R0 - no cancer cells seen microscopically at the primary tumour site. * R1 - cancer cells present microscopically at the primary tumour site. * R2 - Macroscopic residual tumour at primary cancer site or regional lymph nodes. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forceps
Forceps (plural forceps or considered a plural noun without a singular, often a pair of forceps; the Latin plural ''forcipes'' is no longer recorded in most dictionaries) are a handheld, hinged instrument used for grasping and holding objects. Forceps are used when fingers are too large to grasp small objects or when many objects needed to be held at one time while the hands are used to perform a task. The term "forceps" is used almost exclusively in the fields of biology and medicine. Outside biology and medicine, people usually refer to forceps as tweezers, tongs, pliers, clips or clamps. Mechanically, forceps employ the principle of the lever to grasp and apply pressure. Depending on their function, basic surgical forceps can be categorized into the following groups: # Non-disposable forceps. They should withstand various kinds of physical and chemical effects of body fluids, secretions, cleaning agents, and sterilization methods. # Disposable forceps. They are usually made ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endoscope
An endoscope is an inspection instrument composed of image sensor, optical lens, light source and mechanical device, which is used to look deep into the body by way of openings such as the mouth or anus. A typical endoscope applies several modern technologies including optics, ergonomics, precision mechanics, electronics, and software engineering. With an endoscope, it is possible to observe lesions that cannot be detected by X-ray, making it useful in medical diagnosis. Endoscopes use tubes which are only a few millimeters thick to transfer illumination in one direction and high-resolution images in real time in the other direction, resulting in minimally invasive surgeries. It is used to examine the internal organs like the throat or esophagus. Specialized instruments are named after their target organ. Examples include the cystoscope (bladder), nephroscope (kidney), bronchoscope (bronchus), arthroscope (joints) and colonoscope (colon), and laparoscope (abdomen or pelvis). T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epinephrine
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands and by a small number of neurons in the medulla oblongata. It plays an essential role in the fight-or-flight response by increasing blood flow to muscles, heart output by acting on the SA node, pupil dilation response, and blood sugar level. It does this by binding to alpha and beta receptors. It is found in many animals, including humans, and some single-celled organisms. It has also been isolated from the plant ''Scoparia dulcis'' found in Northern Vietnam. Medical uses As a medication, it is used to treat several conditions, including allergic reaction anaphylaxis, cardiac arrest, and superficial bleeding. Inhaled adrenaline may be used to improve the symptoms of croup. It may also be used for asthma when other treatments are not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polypectomy
In medicine, a polypectomy is the removal of an abnormal growth of tissue called a polyp. Polypectomy can be performed by excision if the polyp is external (on the skin). See also * Colonic polypectomy Colonic polypectomy is the removal of colorectal polyps in order to prevent them from turning cancerous. Gastrointestinal polyps can be removed endoscopically through colonoscopy or esophagogastroduodenoscopy, or surgically if the polyp is too ... * Non-lifting sign References {{surgery-stub Surgical procedures and techniques ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a disease. The tissue is then fixed, dehydrated, embedded, sectioned, stained and mounted before it is generally examined under a microscope by a pathologist; it may also be analyzed chemically. When an entire lump or suspicious area is removed, the procedure is called an excisional biopsy. An incisional biopsy or core biopsy samples a portion of the abnormal tissue without attempting to remove the entire lesion or tumor. When a sample of tissue or fluid is removed with a needle in such a way that cells are removed without preserving the histological architecture of the tissue cells, the procedure is called a needle aspiration biopsy. Biopsies are most commonly performed for insight into possible cancerous or inflammatory conditions. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metastases
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spread from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, then, are metastases (mets). It is generally distinguished from cancer invasion, which is the direct extension and penetration by cancer cells into neighboring tissues. Cancer occurs after cells are genetically altered to proliferate rapidly and indefinitely. This uncontrolled proliferation by mitosis produces a primary heterogeneic tumour. The cells which constitute the tumor eventually undergo metaplasia, followed by dysplasia then anaplasia, resulting in a malignant phenotype. This malignancy allows for invasion into the circulation, followed by invasion to a second site for tumorigenesis. Some cancer cells known as circulating tumor cells acquire the ability to penetrate the walls of lymphatic or blood vessels, after which they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal bleeding, prolonged cough, unexplained weight loss, and a change in bowel movements. While these symptoms may indicate cancer, they can also have other causes. Over 100 types of cancers affect humans. Tobacco use is the cause of about 22% of cancer deaths. Another 10% are due to obesity, poor diet, lack of physical activity or excessive drinking of alcohol. Other factors include certain infections, exposure to ionizing radiation, and environmental pollutants. In the developing world, 15% of cancers are due to infections such as '' Helicobacter pylori'', hepatitis B, hepatitis C, human papillomavirus infection, Epstein–Barr virus and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). These factors act, at least partly, by changing the genes o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)