|
Endolith
An endolith or endolithic is an organism ( archaeon, bacterium, fungus, lichen, algae, sponge, or amoeba) that is able to acquire the necessary resources for growth in the inner part of a rock, mineral, coral, animal shells, or in the pores between mineral grains of a rock. Many are extremophiles, living in places long considered inhospitable to life. The distribution, biomass, and diversity of endolith microorganisms are determined by the physical and chemical properties of the rock substrate, including the mineral composition, permeability, the presence of organic compounds, the structure and distribution of pores, water retention capacity, and the pH. Normally, the endoliths colonize the areas within lithic substrates to withstand intense solar radiation, temperature fluctuations, wind, and desiccation. They are of particular interest to astrobiologists, who theorize that endolithic environments on Mars and other planets constitute potential refugia for extraterrestrial mic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptoendolith
An endolith or endolithic is an organism (Archaea, archaeon, bacterium, fungus, lichen, algae, sponge, or amoeboid, amoeba) that is able to acquire the necessary resources for growth in the inner part of a Rock (geology), rock, mineral, coral, Exoskeleton, animal shells, or in the Porosity, pores between mineral grains of a rock. Many are extremophiles, living in places long considered inhospitable to life. The distribution, biomass, and diversity of endolith microorganisms are determined by the physical and chemical properties of the rock substrate, including the mineral composition, permeability, the presence of organic compounds, the structure and distribution of pores, water retention capacity, and the pH. Normally, the endoliths colonize the areas within lithic substrates to withstand intense solar radiation, temperature fluctuations, wind, and desiccation. They are of particular interest to astrobiology, astrobiologists, who theorize that endolithic environments on Mars an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
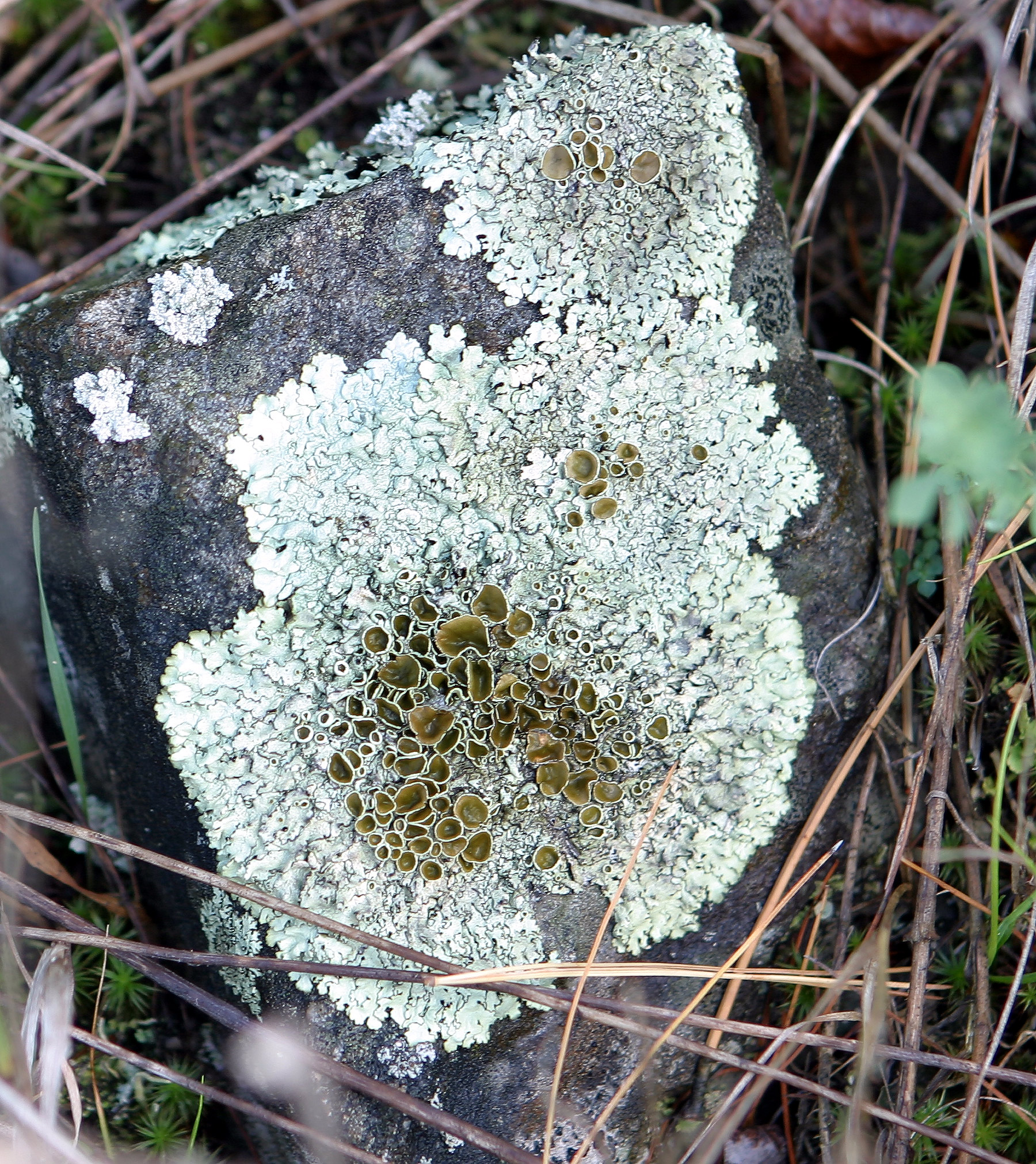
Lichen
A lichen ( , ) is a hybrid colony (biology), colony of algae or cyanobacteria living symbiotically among hypha, filaments of multiple fungus species, along with yeasts and bacteria embedded in the cortex or "skin", in a mutualism (biology), mutualistic relationship.Introduction to Lichens – An Alliance between Kingdoms . University of California Museum of Paleontology. . Lichens are the lifeform that first brought the term symbiosis (as ''Symbiotismus'') into biological context. Lichens have since been recognized as important actors in nutrient cycling and producers which many higher trophic feeders feed on, such as reindeer, gastropods, nematodes, mites, and springtails. Lichens have properties different from those of their component organisms. They come in man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean (also known as the Antarctic Ocean), it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual Climate of Antarctica#Precipitation, precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the Lowest temperature recorded on Earth, lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacterium
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit the air, soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria play a vital role in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients and the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in mutualistic, commensal and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dry Valleys
The McMurdo Dry Valleys are a row of largely snow-free valleys in Antarctica, located within Victoria Land west of McMurdo Sound. The Dry Valleys experience extremely low humidity and surrounding mountains prevent the flow of ice from nearby glaciers. The rocks there are granites and gneisses, and glacial tills dot this bedrock landscape, with loose gravel covering the ground. It is one of the driest places on Earth, though there are several anecdotal accounts of rainfall within the Dry Valleys. The region is one of the world's most extreme deserts, and includes many features including Lake Vida, a saline lake, and the Onyx River, a meltwater stream and Antarctica's longest river. Although no living organisms have been found in the permafrost here, endolithic photosynthetic bacteria have been found living in the relatively moist interior of rocks, and anaerobic bacteria, with a metabolism based on iron and sulfur, live under the Taylor Glacier. The valleys are located wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extremophile
An extremophile () is an organism that is able to live (or in some cases thrive) in extreme environments, i.e., environments with conditions approaching or stretching the limits of what known life can adapt to, such as extreme temperature, pressure, radiation, salinity, or pH level. Since the definition of an extreme environment is relative to an arbitrarily defined standard, often an anthropocentric one, these organisms can be considered Dominance (ecology), ecologically dominant in the evolutionary history of the planet. Dating back to more than 40 million years ago, extremophiles have continued to thrive in the most extreme conditions, making them one of the most abundant lifeforms. The study of extremophiles has expanded human knowledge of the limits of life, and informs speculation about extraterrestrial life. Extremophiles are also of interest because of their potential for bioremediation of environments made hazardous to humans due to pollution or contamination. Character ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strain 121
Strain 121 (''Geogemma barossii'') is a single- celled microbe of the domain Archaea. First discovered within a hydrothermal vent in the Northeast Pacific Ocean near the Endeavor segment of the Juan de Fuca Ridge, Strain 121 is a hyperthermophile capable of reproducing at , hence its name. Strain 121 is biostatic at , so while the archaeon is unable to reproduce until it has been transferred to a cooler medium, it remains viable at temperatures up to . Strain 121 possess a coccoid shape with lophotrichous flagellation, reaching approximately 1.0 μm in diameter. Strain 121 metabolizes by reducing iron oxide (Fe(III)), a molecule that is abundant within the sediment in hydrothermal vents. The maximum growth temperature of strain 121 is 8 °C higher than the previous record holder, '' Pyrolobus fumarii'' (Tmax = 113 °C). At the time of its discovery, Strain 121 was the only known form of life that could tolerate such high temperatures, but in 2008 ''Methan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subsoil
Subsoil is the layer of soil under the topsoil on the surface of the ground. Like topsoil, it is composed of a variable mixture of small particles such as sand, silt and clay, but with a much lower percentage of organic matter and humus. The subsoil is labeled the soil horizon, B Horizon in most soil mapping systems. Because it has less organic matter than topsoil, subsoil soil color, soil colour is mainly derived from iron oxides. Iron oxides and clay minerals form due to soil formation, weathering. Rainfall moves these weathering products downward as solutes and colloids by rainfall. The subsoil is the depth where these weathering products accumulate. The accumulation of clay minerals, iron, aluminum, and organic compounds is called illuviation. Whereas the topsoil tends to be the depth of greatest physical, chemical, and biological activity, the subsoil is the depth of most deposition. Due to physical, chemical, and biological activity, the subsoil generally has a soil struct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discover (magazine)
''Discover'' is an American general audience science magazine launched in October 1980 by Time Inc. It is currently owned by LabX Media Group. History Founding ''Discover'' was created primarily through the efforts of ''Time'' magazine editor Leon Jaroff. He noticed that magazine sales jumped every time the cover featured a science topic. Jaroff interpreted this as a considerable public interest in science, and in 1971, he began agitating for the creation of a science-oriented magazine. This was difficult, as a former colleague noted, because "Selling science to people who graduated to be managers was very difficult".Hevesi, Dennis"Leon Jaroff, Editor at Time and Discover Magazines, Dies at 85" ''The New York Times'', 21 October 2012 Jaroff's persistence finally paid off, and ''Discover'' magazine published its first edition in 1980. ''Discover'' was originally launched into a burgeoning market for science magazines aimed at educated non-professionals, intended to be eas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperthermophile
A hyperthermophile is an organism that thrives in extremely hot environments—from 60 °C (140 °F) upward. An optimal temperature for the existence of hyperthermophiles is often above 80 °C (176 °F). Hyperthermophiles are often within the domain Archaea, although some bacteria are also able to tolerate extreme temperatures. Some of these bacteria are able to live at temperatures greater than 100 °C, deep in the ocean where high pressures increase the boiling point of water. Many hyperthermophiles are also able to withstand other environmental extremes, such as high acidity or high radiation levels. Hyperthermophiles are a subset of extremophiles. Their existence may support the possibility of extraterrestrial life, showing that life can thrive in environmental extremes. History Hyperthermophiles isolated from hot springs in Yellowstone National Park were first reported by Thomas D. Brock in 1965. Since then, more than 70 species have been established. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypolith
In Arctic and Antarctic ecology, a hypolith is a community of photosynthetic organisms, and extremophiles, that live underneath rocks in climatically extreme deserts such as Cornwallis Island and Devon Island in the Canadian high Arctic. The community itself is the hypolithon. Hypolithons are protected by their rock from harsh ultraviolet irradiation and wind scouring. The rocks can also trap moisture and are generally translucent allowing light to penetrate while omitting incident ultra-violet light. Writing in ''Nature'', ecologist Charles S. Cockell of the British Antarctic Survey and Dale Stokes (Scripps Institution of Oceanography) describe how hypoliths reported to date (until 2004) had been found under quartz, which is one of the most common translucent minerals. However, Cockell reported that on Cornwallis Island and Devon Island, 94-95% of a random sample of 850 opaque dolomitic rocks were colonized by hypoliths, and found that the communities were dominated by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
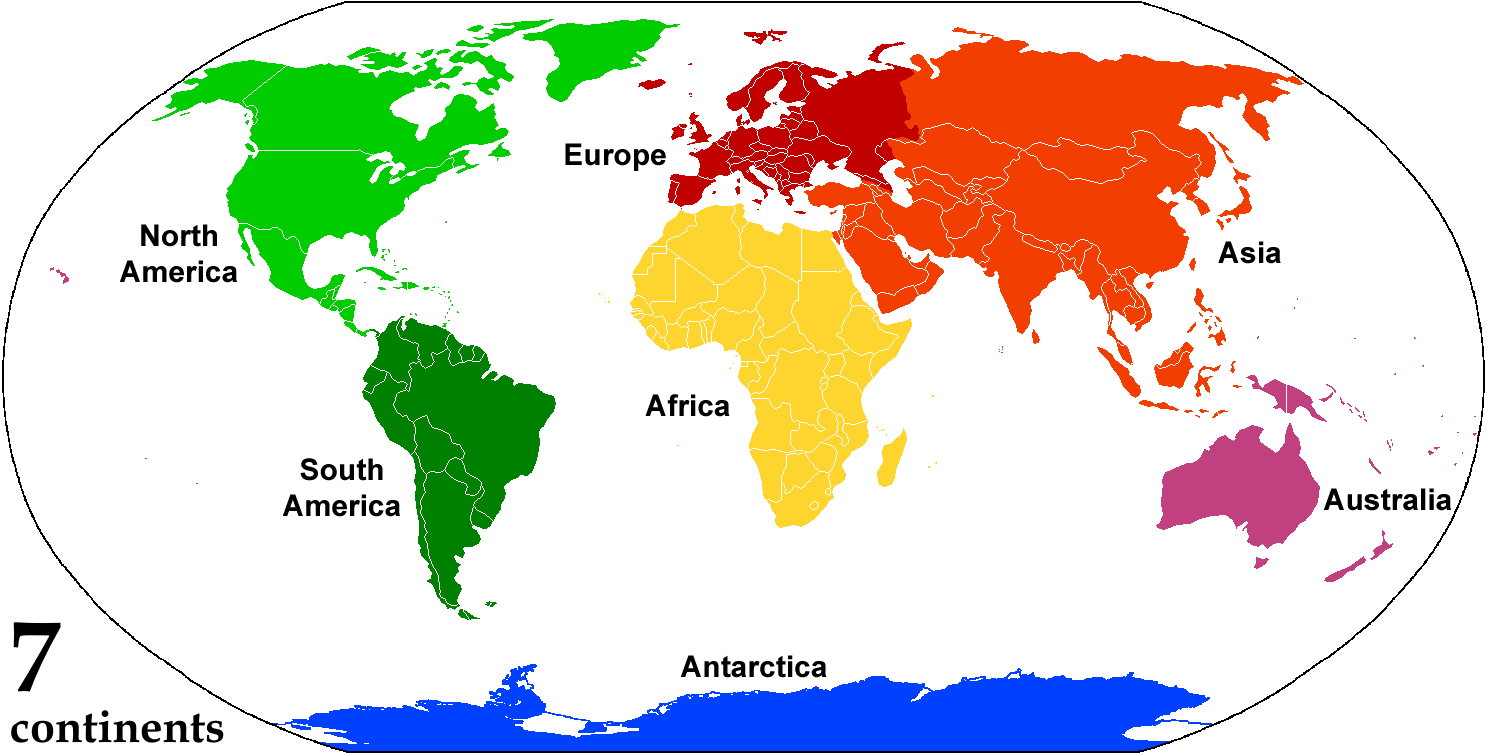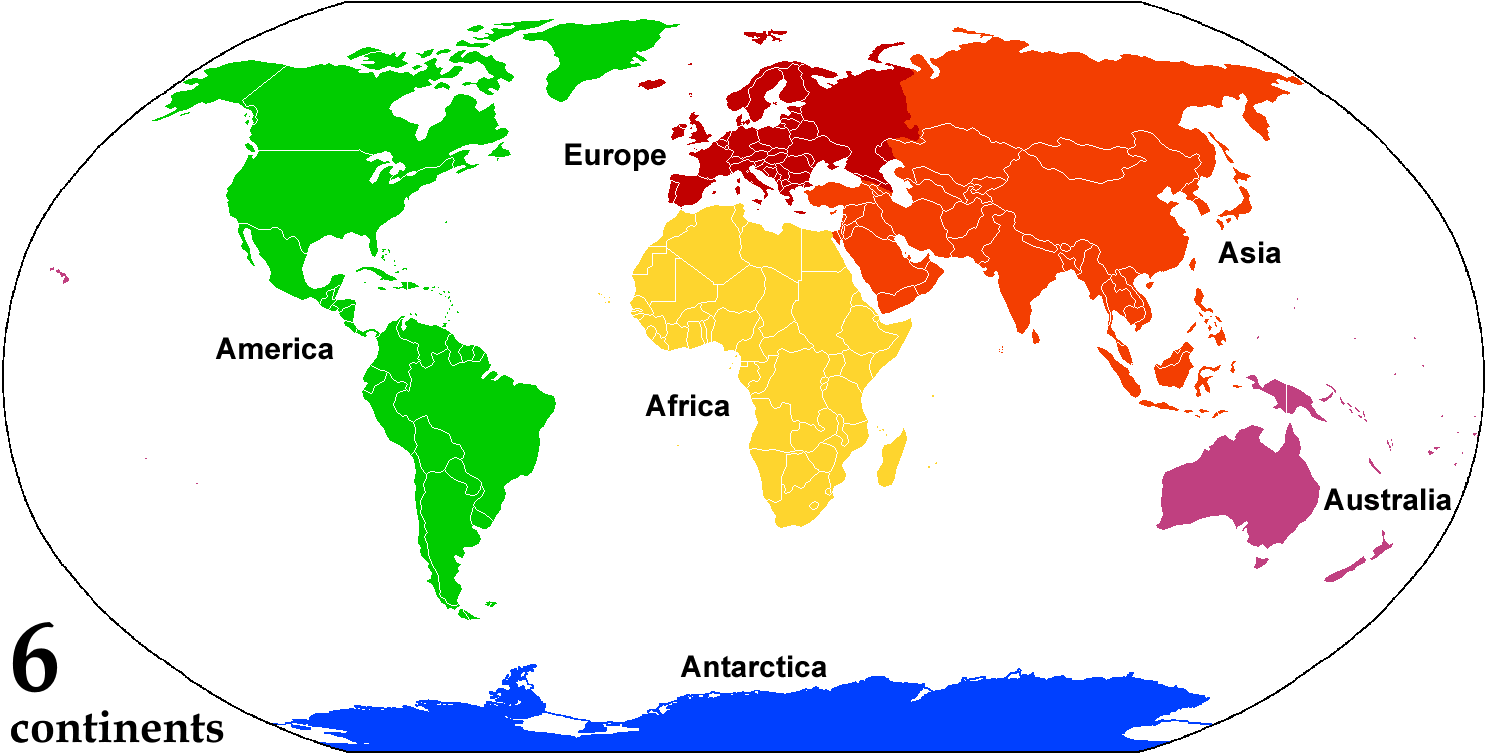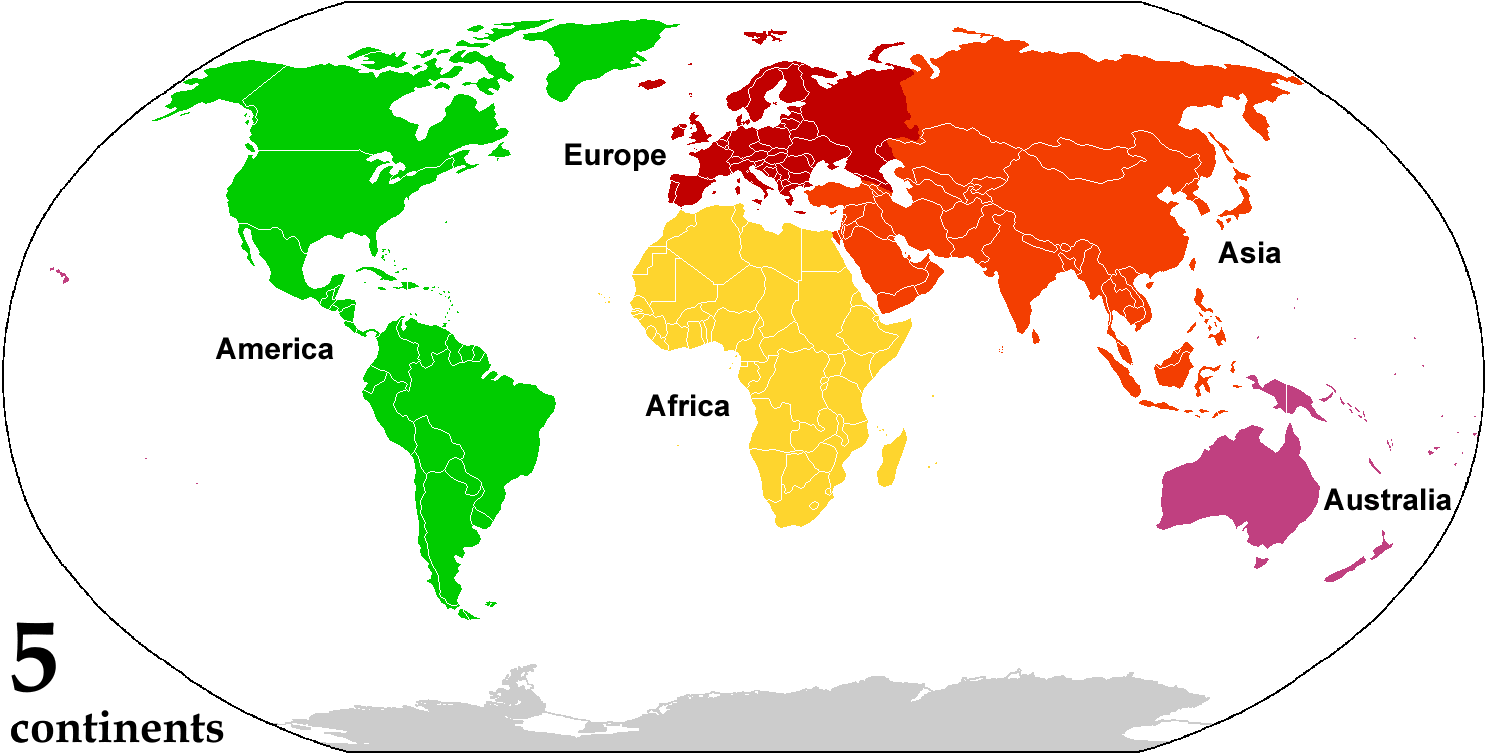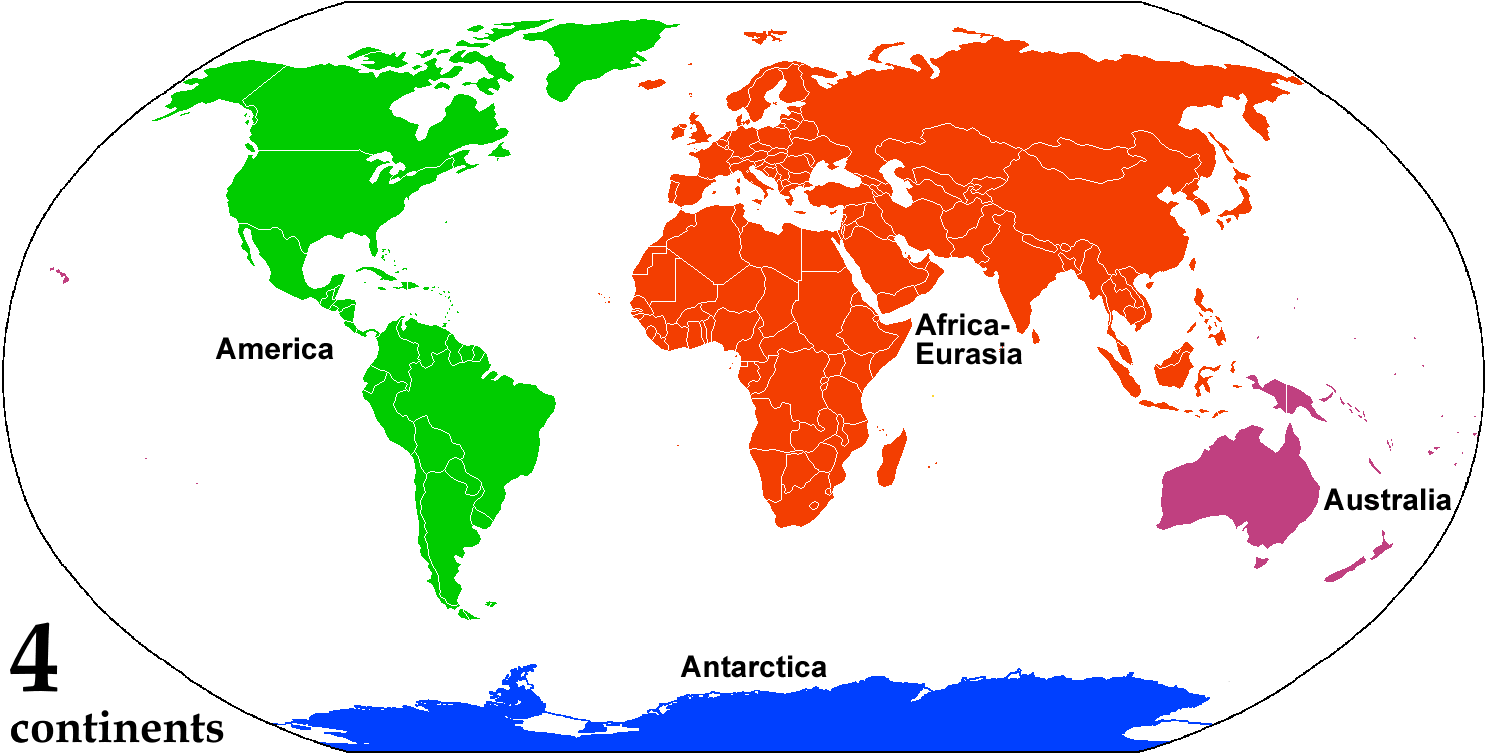
Continent
A continent is any of several large geographical regions. Continents are generally identified by convention (norm), convention rather than any strict criteria. A continent could be a single large landmass, a part of a very large landmass, as in the case of Asia or Europe within Eurasia, or a landmass and nearby islands within its continental shelf. Due to these varying definitions, the number of continents varies; up to seven or as few as four geographical regions are commonly regarded as continents. Most English-speaking world, English-speaking countries recognize seven regions as continents. In order from largest to smallest in area, these seven regions are Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe, and Australia (continent), Australia (sometimes called Oceania or Australasia). Different variations with fewer continents merge some of these regions; examples of this are merging Asia and Europe into Eurasia, "Most people recognize seven continents—Asia, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |