|
Emmett Louis Till
Emmett Louis Till (July 25, 1941August 28, 1955) was a 14-year-old African Americans, African American boy who was abducted, tortured, and Lynching in the United States, lynched in Mississippi in 1955, after being accused of offending a white woman, Carolyn Bryant, in her family's grocery store. The brutality of his murder and the fact that his killers were acquitted drew attention to the long history of violent Anti-African racism in the United States, persecution of African Americans in the United States. Till posthumously became an icon of the civil rights movement. Till was born and raised in Chicago, Illinois. During summer vacation in August 1955, he was visiting relatives near Money, Mississippi, in the Mississippi Delta region. He spoke to 21-year-old Carolyn Bryant, the white, married proprietor of a small grocery store there. Although what happened at the store is a matter of dispute, Till was accused of flirting with, touching, or Wolf-whistling, whistling at Brya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drew, Mississippi
Drew is a city in Sunflower County, Mississippi. The population was 1,927 at the 2010 census. Drew is in the vicinity of several plantations and the Mississippi State Penitentiary, a Mississippi Department of Corrections prison for men. It is noted for several racist murders, including the lynching of Emmett Till in 1955. History When the Yellow Dog Railroad was extended through what is now Drew, the post office was moved from the Promised Land Plantation to the Drew location. The settlement and Post Office were named for Miss Drew Daniel, daughter of Andrew Jackson Daniel. A school called the Little Red Schoolhouse was built by matching funds from the Rosenwald Fund in 1928. In the 21st century it received a grant for renovation of the large school. In the 1920s, a man named Joe Pullen was lynched near Drew after killing 13 members of his lynch mob and injuring 26 of them. One historian wrote that the white residents of Drew had "traditionally been regarded as the most recalc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wolf-whistling
A wolf whistle is a distinctive two-note glissando whistled sound made to show high interest in or approval of something or someone, especially at someone viewed as physically or sexually attractive. Today, a wolf whistle directed at a person is sometimes considered a precursor to sexual harassment, or a form of sexual harassment in itself. The name comes from the Wolf character in the popular 1943 Tex Avery cartoon ''Red Hot Riding Hood'' who whistles in this way at the sexy female character Red. He whistles at her in several other subsequent cartoons. The term appears in North American newspapers as early as 1943. It appears in British newspapers from 1949 onwards. According to Adam Edwards of ''Daily Express'', the wolf whistle originates from the navy General Call made with a boatswain's pipe. The General Call is made on a ship to get the attention of all hands for an announcement. Sailors in harbour would whistle the General Call upon seeing an attractive woman to draw f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hate Crime
A hate crime (also known as a bias-motivated crime or bias crime) is a prejudice-motivated crime which occurs when a perpetrator targets a victim because of their membership (or perceived membership) of a certain social group or racial demographic. Examples of such groups can include, and are almost exclusively limited to ethnicity, disability, language, nationality, physical appearance, age, religion, gender identity, or sexual orientation. "A hate crime or bias motivated crime occurs when the perpetrator of the crime intentionally selects the victim because of their membership in a certain group."Streissguth, Tom (2003). ''Hate Crimes'' (Library in a Book), p. 3. . Non-criminal actions that are motivated by these reasons are often called "bias incidents". "Hate crime" generally refers to criminal acts which are seen to have been motivated by bias against one or more of the social groups listed above, or by bias against their derivatives. Incidents may involve physical assault, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emmett Till Antilynching Act
The Emmett Till Antilynching Act is a landmark United States federal law which makes lynching a federal hate crime. The act amends the Matthew Shepard and James Byrd Jr. Hate Crimes Prevention Act and prior hate crime laws to define lynching as any conspired bias-motivated offense which results in death or serious bodily injury. It was passed by the U.S House of Representatives on February 28, 2022, and U.S. Senate on March 7, 2022, and signed into law on March 29, 2022, by President Joe Biden. Background The bill was named after 14-year-old Emmett Till, who was lynched in Mississippi in 1955, sparking national and international outrage. A federal antilynching bill had been in discussion for over a century and had been proposed hundreds of times. Past attempts which passed at least one legislative chamber include the Dyer Anti-Lynching Bill, the Costigan-Wagner Bill and the Justice for Victims of Lynching Act. 116th Congress Representative Bobby Rush introduced a bill, , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montgomery Bus Boycott
The Montgomery bus boycott was a political and social protest campaign against the policy of racial segregation on the public transit system of Montgomery, Alabama. It was a foundational event in the civil rights movement in the United States. The campaign lasted from December 5, 1955—the Monday after Rosa Parks, an African-American woman, was arrested for her refusal to surrender her seat to a white person—to December 20, 1956, when the federal ruling ''Browder v. Gayle'' took effect, and led to a United States Supreme Court decision that declared the Alabama and Montgomery laws that segregated buses were unconstitutional. Background Before the bus boycott, Jim Crow laws mandated the racial segregation of the Montgomery Bus Line. As a result of this segregation, African Americans were not hired as drivers, were forced to ride in the back of the bus, and were frequently ordered to surrender their seats to white people even though black passengers made up 75% of the bus sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Look (American Magazine)
''Look'' was a biweekly, general-interest magazine published in Des Moines, Iowa, from 1937 to 1971, with editorial offices in New York City. It had an emphasis on photographs and photojournalism in addition to human interest and lifestyle articles. A large-sized magazine of , it was a direct competitor to market leader ''Life'', which began publication months earlier and ended in 1972, a few months after ''Look'' shut down. Origin Gardner "Mike" Cowles Jr. (1903–1985), the magazine's co-founder (with his brother John) and first editor, was executive editor of ''The Des Moines Register'' and '' The Des Moines Tribune''. When the first issue went on sale in early 1937, it sold 705,000 copies. Although planned to begin with the January 1937 issue, the actual first issue of ''Look'' to be distributed was the February 1937 issue, numbered as Volume 1, Number 2. It was published monthly for five issues (February–May 1937), then switched to biweekly starting with the May 11, 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Jeopardy Clause
The Double Jeopardy Clause of the Fifth Amendment to the United States Constitution provides: ''" r shall any person be subject for the same offence to be twice put in jeopardy of life or limb..."'' The four essential protections included are prohibitions against, for the same offense: *retrial after an acquittal; *retrial after a conviction; *retrial after certain mistrials; and *multiple punishment Jeopardy attaches in jury trial when the jury is empaneled and sworn in, in a bench trial when the court begins to hear evidence after the first witness is sworn in, or when a court accepts a defendant's plea unconditionally. Jeopardy does not attach in a retrial of a conviction that was reversed on appeal on procedural grounds (as opposed to evidentiary insufficiency grounds), in a retrial for which "manifest necessity" has been shown following a mistrial, and in the seating of another grand jury if the prior one refuses to return an indictment. "Same offense" In ''United Sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
All-white Jury
Racial discrimination in jury selection is specifically prohibited by law in many jurisdictions throughout the world. In the United States, it has been defined through a series of judicial decisions. However, juries composed solely of one racial group are legal in the United States and other countries. While the racial composition of juries is not dictated by law, racial discrimination in the selection of jurors (regardless of the jury's ultimate composition) is specifically prohibited. Depending on context, the phrases "all-white jury" or "all-black jury" can raise a host of expectationsamong them, as MIT social neuroscientist Rebecca Saxe notes, "the expectation that deliberations may be less than fair." Australia In Australia, the right to a representative jury is severely limited. Australian Aboriginals are overrepresented in the criminal justice system, but seldom appear on juries even in parts of Australia where they represent a sizable portion of the population. Courts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Racism In The United States
Racism in the United States comprises negative attitudes and views on race or ethnicity which are related to each other, are held by various people and groups in the United States, and have been reflected in discriminatory laws, practices and actions (including violence) at various times in the history of the United States against racial or ethnic groups. Throughout American history, white Americans have generally enjoyed legally or socially sanctioned privileges and rights, which have been denied to members of various ethnic or minority groups at various times. European Americans, particularly affluent white Anglo-Saxon Protestants, are said to have enjoyed advantages in matters of education, immigration, voting rights, citizenship, land acquisition, and criminal procedure. Racism against various ethnic or minority groups has existed in the United States since the early colonial era. Before 1865, most African Americans were enslaved and even afterwards, they have faced seve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
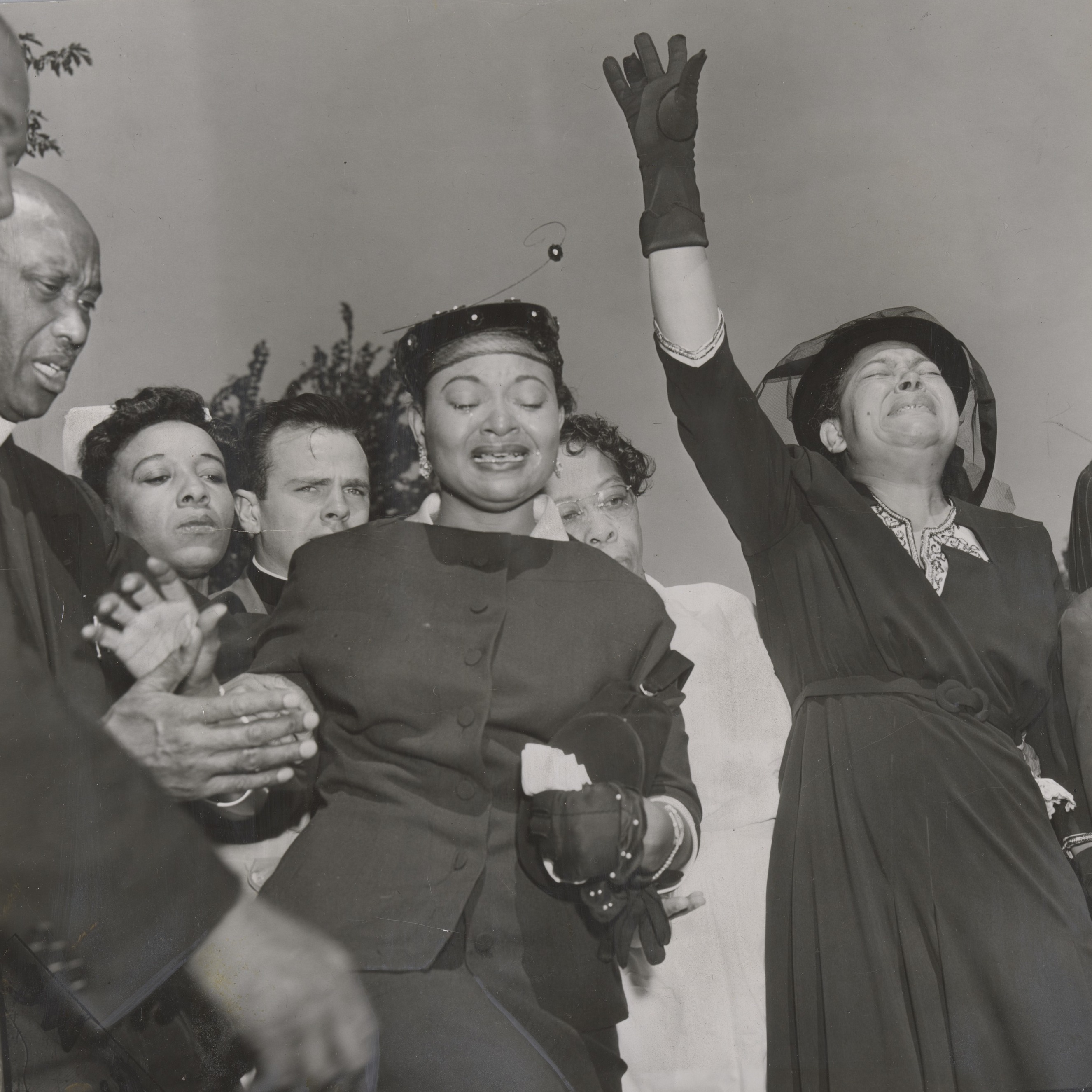
Mamie Till Bradley
Mamie Elizabeth Till-Mobley (born Mamie Elizabeth Carthan; November 23, 1921 – January 6, 2003) was an American educator and activist. She was the mother of Emmett Till, the 14-year-old boy murdered in Mississippi on August 28, 1955, after accusations that he had whistled at a white woman, a grocery store cashier named Carolyn Bryant. For Emmett's funeral, in Chicago, Mamie Till insisted that the casket containing his body be left open, because, in her words, "I wanted the world to see what they did to my baby." Born in Mississippi, she had moved, as a child, with her parents to the Chicago area during the " Great Migration". After her son's murder, she became an educator and activist in the Civil Rights Movement. Early life Born Mamie Elizabeth Carthan on November 23, 1921 in Webb, Mississippi, she was a young child when her family relocated from the Southern United States during the Great Migration, the period when hundred thousands of African-Americans moved to the Northern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roberts Temple Church Of God In Christ
Roberts Temple Church of God in Christ is a Christian house of worship located in the Bronzeville neighborhood of Chicago, Illinois. The church was the site of Emmett Till's open-casket funeral in 1955. The church was designated as a Chicago landmark in 2005 and was included on the National Trust for Historic Preservation's 2020 list of 11 Most Endangered Historic Places. The Church was designated as part of Emmett Till and Mamie Till-Mobley National Monument on July 25, 2023. Establishment Roberts Temple Church of God in Christ was founded by Elder William Roberts in 1916. Its services were held in various Chicago buildings until 1922 when its permanent building was constructed at 4021 S. State Street. The church was initially built as a one-story brick structure. A second story was added in 1927. In 1992, a tan brick exterior was added and the sanctuary was renovated. Funeral of Emmett Till In the summer of 1955, Emmett Till, a fourteen-year-old African American boy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open Casket Funeral
A funeral is a ceremony connected with the final disposition of a corpse, such as a burial or cremation, with the attendant observances. Funerary customs comprise the complex of beliefs and practices used by a culture to remember and respect the dead, from interment, to various monuments, prayers, and rituals undertaken in their honor. Customs vary between cultures and religious groups. Funerals have both normative and legal components. Common secular motivations for funerals include mourning the deceased, celebrating their life, and offering support and sympathy to the bereaved; additionally, funerals may have religious aspects that are intended to help the soul of the deceased reach the afterlife, resurrection or reincarnation. The funeral usually includes a ritual through which the corpse receives a final disposition. Depending on culture and religion, these can involve either the destruction of the body (for example, by cremation or sky burial) or its preservation (for ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


.jpg)