|
Emlen Peaks
The Emlen Peaks () is a group of scattered peaks and nunataks, long and wide. It is south of Daniels Range in the south end of the Usarp Mountains in northern Victoria Land, Antarctica. Early exploration and name Emlen Peaks was mapped by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) from surveys and United States Navy air photos in 1960–63. It was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) after John Thompson Emlen, Jr. (1908–1997), a biologist from the University of Wisconsin. As a program leader he made penguin navigational studies on the Ross Ice Shelf, the interior of Victoria Land, and elsewhere in Antarctica in 1962–63. Glacier Gressitt Glacier . A broad glacier, about 45 mi long, draining the area between Daniels Range and Emlen Peaks in the Usarp Mountains and flowing northeast to enter the Rennick Glacier just north of rthe Morozumi Range The Morozumi Range () is a mountain range in the Usarp Mountains of North Victoria Land, Antarctica. It ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nunatak
A nunatak (from Inuit ''nunataq'') is the summit or ridge of a mountain that protrudes from an ice field or glacier that otherwise covers most of the mountain or ridge. They are also called glacial islands. Examples are natural pyramidal peaks. When rounded by glacial action, smaller rock promontories may be referred to as rognons. The word is of Greenlandic origin and has been used in English since the 1870s. Description The term is typically used in areas where a permanent ice sheet is present and the nunataks protrude above the sheet.J. J. Zeeberg, ''Climate and Glacial History of the Novaya Zemlya Archipelago, Russian Arctic''. pp. 82–84 Nunataks present readily identifiable landmark reference points in glaciers or ice caps and are often named. While some nunataks are isolated, sometimes they form dense clusters, such as Queen Louise Land in Greenland. Nunataks are generally angular and jagged, which hampers the formation of glacial ice on their tops, although snow can a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daniels Range
The Daniels Range is a principal mountain range of the Usarp Mountains, about 80 km (50 mi) long and 16 km (10 mi) wide, bounded to the north by Harlin Glacier and to the south by Gressitt Glacier. The range was mapped by USGS from surveys and U.S. Navy air photos, 1960–63. Named by US-ACAN after Ambassador Paul C. Daniels (1903–86), a leading American figure in the formulation of the Antarctic Treaty in 1959. In the southern part of Daniels Range is Bounty Nunatak. Further reading * Gunter Faure, Teresa M. Mensing, The Transantarctic Mountains: Rocks, Ice, Meteorites and Water', P 110 * R. L. Oliver, P. R. James, J. B. Jago, Antarctic Earth Science', P 113 * J.W.Sheraton, R.S.Babcock, L.P.Black, D.Wyborn, C.C.Plummer, Petrogenesis of granitic rocks of the daniels range, northern victoria land, antarctica', Precambrian Research Volume 37, Issue 4, December 1987, Pages 267-286 https://doi.org/10.1016/0301-9268(87)90078-7 * R. S. Babcock C. C. Plummer J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
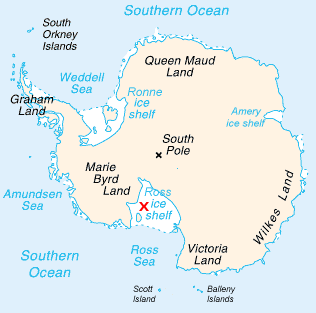
Usarp Mountains
The Usarp Mountains are a major Antarctic mountain range, lying west of the Rennick Glacier and trending north to south for about . The feature is bounded to the north by Pryor Glacier and the Wilson Hills. These mountains were discovered and first photographed from aircraft of the U.S. Navy Operation Highjump in 1946. They were first sighted and entered by the U.S. Victoria Land Traverse 1959-1960 (VLT), and the first ascent of Mount Welcome was made by John G. Weihaupt, Alfred Stuart, Claude Lorius, and Arnold Heine of that traverse team. The mountains were completely mapped by the United States Geological Survey from VLT reports, U.S. Navy air photos from 1960–63, and subsequent surveys. The name is an acronym of the United States Antarctic Research Program (USARP), and was applied by Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) in recognition of the accomplishments of that program in Antarctica. A detailed account of the Victoria Land Traverse appears in the Geologic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victoria Land
Victoria Land is a region in eastern Antarctica which fronts the western side of the Ross Sea and the Ross Ice Shelf, extending southward from about 70°30'S to 78°00'S, and westward from the Ross Sea to the edge of the Antarctic Plateau. It was discovered by Captain James Clark Ross in January 1841 and named after Queen Victoria. The rocky promontory of Minna Bluff is often regarded as the southernmost point of Victoria Land, and separates the Scott Coast to the north from the Hillary Coast of the Ross Dependency to the south. The region includes ranges of the Transantarctic Mountains and the McMurdo Dry Valleys (the highest point being Mount Abbott in the Northern Foothills), and the flatlands known as the Labyrinth. The Mount Melbourne is an active volcano in Victoria Land. Early explorers of Victoria Land include James Clark Ross and Douglas Mawson. In 1979, scientists discovered a group of 309 meteorites in Antarctica, some of which were found near the Allan Hills in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and the natural hazards that threaten it. The organization's work spans the disciplines of biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The USGS is a fact-finding research organization with no regulatory responsibility. The agency was founded on March 3, 1879. The USGS is a bureau of the United States Department of the Interior; it is that department's sole scientific agency. The USGS employs approximately 8,670 people and is headquartered in Reston, Virginia. The USGS also has major offices near Lakewood, Colorado, at the Denver Federal Center, and Menlo Park, California. The current motto of the USGS, in use since August 1997, is "science for a changing world". The agency's previous slogan, adopted on the occasion of its hundredt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage of its active battle fleet alone exceeding the next 13 navies combined, including 11 allies or partner nations of the United States as of 2015. It has the highest combined battle fleet tonnage (4,635,628 tonnes as of 2019) and the world's largest aircraft carrier fleet, with eleven in service, two new carriers under construction, and five other carriers planned. With 336,978 personnel on active duty and 101,583 in the Ready Reserve, the United States Navy is the third largest of the United States military service branches in terms of personnel. It has 290 deployable combat vessels and more than 2,623 operational aircraft . The United States Navy traces its origins to the Continental Navy, which was established during the American Revo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advisory Committee On Antarctic Names
The Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (ACAN or US-ACAN) is an advisory committee of the United States Board on Geographic Names responsible for recommending commemorative names for features in Antarctica. History The committee was established in 1943 as the Special Committee on Antarctic Names (SCAN). It became the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names in 1947. Fred G. Alberts was Secretary of the Committee from 1949 to 1980. By 1959, a structured nomenclature was reached, allowing for further exploration, structured mapping of the region and a unique naming system. A 1990 ACAN gazeeter of Antarctica listed 16,000 names. Description The United States does not recognise territorial boundaries within Antarctica, so ACAN assigns names to features anywhere within the continent, in consultation with other national nomenclature bodies where appropriate, as defined by the Antarctic Treaty System. The research and staff support for the ACAN is provided by the United States Geologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Wisconsin
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United States, the designation is reserved for colleges that have a graduate school. The word ''university'' is derived from the Latin ''universitas magistrorum et scholarium'', which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". The first universities were created in Europe by Catholic Church monks. The University of Bologna (''Università di Bologna''), founded in 1088, is the first university in the sense of: *Being a high degree-awarding institute. *Having independence from the ecclesiastic schools, although conducted by both clergy and non-clergy. *Using the word ''universitas'' (which was coined at its foundation). *Issuing secular and non-secular degrees: grammar, rhetoric, logic, theology, canon law, notarial law.Hunt Janin: "The university ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penguin
Penguins (order (biology), order List of Sphenisciformes by population, Sphenisciformes , family (biology), family Spheniscidae ) are a group of Water bird, aquatic flightless birds. They live almost exclusively in the Southern Hemisphere: only one species, the Galápagos penguin, is found north of the Equator. Highly adapted for life in the water, penguins have Countershading, countershaded dark and white plumage and flippers for swimming. Most penguins feed on krill, fish, squid and other forms of sea life which they catch with their bills and swallow it whole while swimming. A penguin has a spiny tongue and powerful jaws to grip slippery prey. They spend roughly half of their lives on land and the other half in the sea. The largest living species is the emperor penguin (''Aptenodytes forsteri''): on average, adults are about tall and weigh . The smallest penguin species is the Little penguin, little blue penguin (''Eudyptula minor''), also known as the fairy penguin, whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ross Ice Shelf
The Ross Ice Shelf is the largest ice shelf of Antarctica (, an area of roughly and about across: about the size of France). It is several hundred metres thick. The nearly vertical ice front to the open sea is more than long, and between high above the water surface. Ninety percent of the floating ice, however, is below the water surface. Most of Ross Ice Shelf is in the Ross Dependency claimed by New Zealand. It floats in, and covers, a large southern portion of the Ross Sea and the entire Roosevelt Island located in the east of the Ross Sea. The ice shelf is named after Sir James Clark Ross, who discovered it on 28 January 1841. It was originally called "The Barrier", with various adjectives including "Great Ice Barrier", as it prevented sailing further south. Ross mapped the ice front eastward to 160° W. In 1947, the U.S. Board on Geographic Names applied the name "Ross Shelf Ice" to this feature and published it in the original U.S. Antarctic Gazetteer. In Januar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rennick Glacier
Rennick Glacier is broad glacier, nearly long, which is one of the largest in Antarctica. It rises on the polar plateau westward of Mesa Range and is wide, narrowing to near the coast. It takes its name from Rennick Bay where the glacier reaches the sea. The seaward part of the glacier was photographed by U.S. Navy (USN) Operation Highjump, 1946–47. The upper reaches of the Rennick Glacier were discovered and explored by the U.S. Victoria Land Traverse (VLT) in February 1960, and the first ascent made of Welcome Mountain by John Weihaupt, Alfred Stuart, Claude Lorius and Arnold Heine of the VLT party. On February 10, 1960, Lieutenant Commander Robert L. Dale, pilot of U.S. Navy (USN) Squadron VX-6, evacuated the VLT from 7238S, 16132E, on this glacier, and then conducted an aerial photographic reconnaissance to Rennick Bay on the coast before returning the VLT team to McMurdo Station. Features * Illusion Hills, small hills on the glacier * Litell Rocks, an area of rock outcr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morozumi Range
The Morozumi Range () is a mountain range in the Usarp Mountains of North Victoria Land, Antarctica. It extends northwest–southeast for , with its northern elevations overlooking the convergence of Gressitt Glacier and Rennick Glacier. Early exploration and name The Morozumi Range was mapped by the United States Geological Survey from surveys and United States Navy air photos in 1960–63. It was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) for Henry M. Morozumi, an aurora scientist at South Pole Station in 1960, and Station Scientific Leader at Byrd Station in 1963. Geology The Morozumi Range is in the Rennick Graben, separated by the Rennick Faults from the Wilson Group rocks of the USARP mountains. Basement rocks are low-grade metasedimentary rocks that include greywacke-shale. The northern end holds the Adamellite Massif, a pluton of Granite Harbour Intrusives. Glaciers Gressitt Glacier . A broad glacier, about 45 mi long, draining the area between Da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |