|
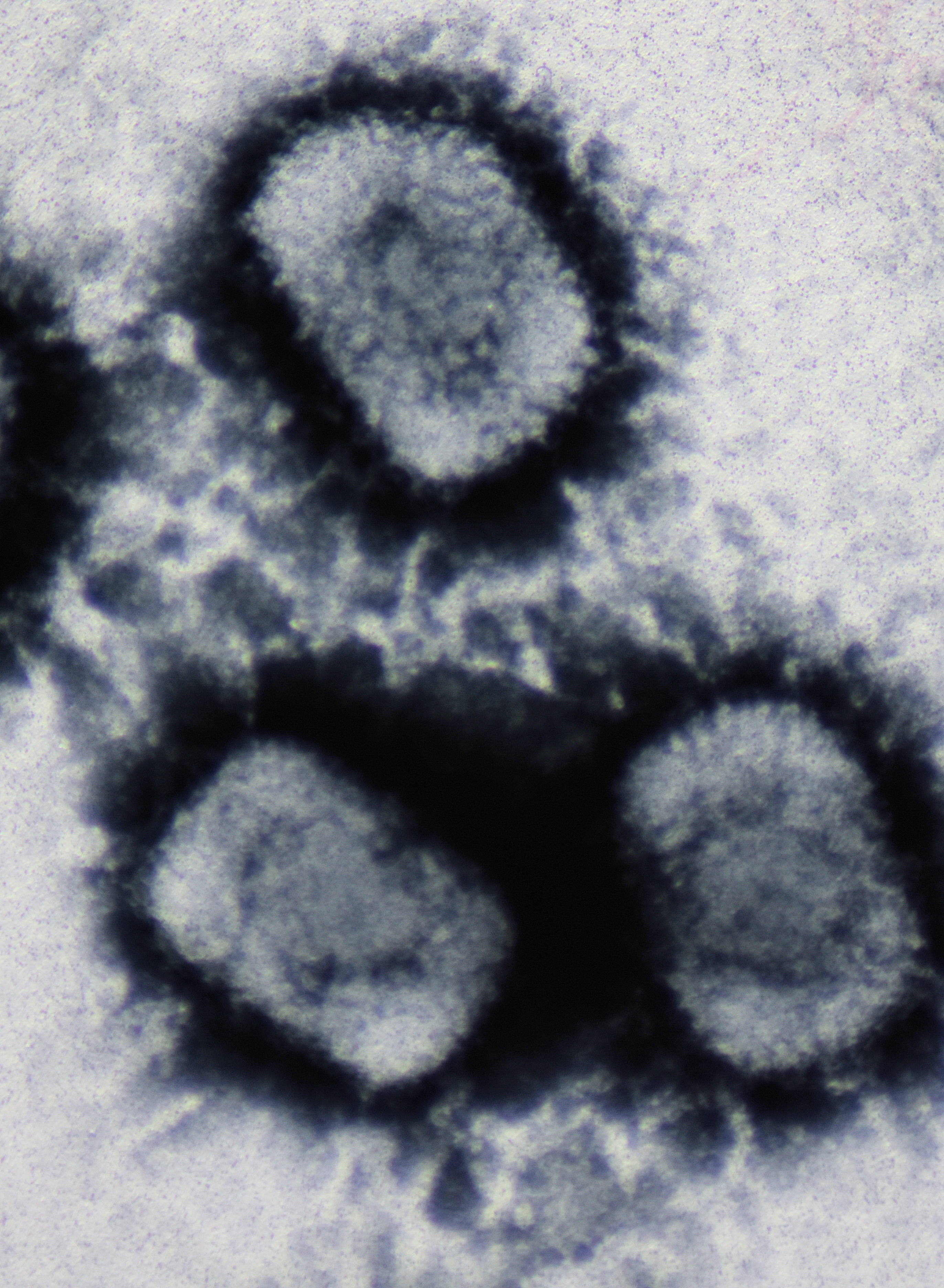
Emiliania Huxleyi Virus 86
''Coccolithovirus'' is a genus of giant double-stranded DNA virus, in the family ''Phycodnaviridae''. Algae, specifically ''Emiliania huxleyi'', a species of coccolithophore, serve as natural hosts. There is only one described species in this genus: ''Emiliania huxleyi virus 86''. Structure Coccolithoviruses are enveloped, icosahedral and have a diameter ranging from 100–220 nm. Their genomes are linear, between 410–415kb in length and predict to encode for approximately 472 proteins. Life cycle Coccolithoviruses are part of the family of ''Phycodnaviridae'', one of the five families that belong to a large and phylogenetically diverse group of viruses known as nucleocytoplasmic large dsDNA viruses ( NCLDVs). These viruses either replicate exclusively in the cytoplasm of the host cell or start their life cycle in the host nucleus but complete it in the cytoplasm. In the case of EhV-86 the infection strategy is not fully understood but Mackinder et al. (2009) have prop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Virus
A DNA virus is a virus that has a genome made of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) that is replicated by a DNA polymerase. They can be divided between those that have two strands of DNA in their genome, called double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) viruses, and those that have one strand of DNA in their genome, called single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) viruses. dsDNA viruses primarily belong to two realms: ''Duplodnaviria'' and ''Varidnaviria'', and ssDNA viruses are almost exclusively assigned to the realm ''Monodnaviria'', which also includes some dsDNA viruses. Additionally, many DNA viruses are unassigned to higher taxa. Reverse transcribing viruses, which have a DNA genome that is replicated through an RNA intermediate by a reverse transcriptase, are classified into the kingdom '' Pararnavirae'' in the realm '' Riboviria''. DNA viruses are ubiquitous worldwide, especially in marine environments where they form an important part of marine ecosystems, and infect both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zooplankton
Zooplankton are the animal component of the planktonic community ("zoo" comes from the Greek word for ''animal''). Plankton are aquatic organisms that are unable to swim effectively against currents, and consequently drift or are carried along by currents in the ocean, or by currents in seas, lakes or rivers. Zooplankton can be contrasted with phytoplankton, which are the plant component of the plankton community ("phyto" comes from the Greek word for ''plant''). Zooplankton are heterotrophic (other-feeding), whereas phytoplankton are autotrophic (self-feeding). This means zooplankton cannot manufacture their own food but must eat other plants or animals instead — in particular they eat phytoplankton. Zooplankton are generally larger than phytoplankton, most are microscopic, but some (such as jellyfish) are macroscopic and can be seen with the naked eye. Many protozoans (single-celled protists that prey on other microscopic life) are zooplankton, including zooflagellates, fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycoplasma Genitalium
''Mycoplasma genitalium'' (''MG'', commonly known as Mgen) is a sexually transmitted, small and pathogenic bacterium that lives on the mucous epithelial cells of the urinary and genital tracts in humans. Medical reports published in 2007 and 2015 state that Mgen is becoming increasingly common. Resistance to multiple antibiotics is becoming prevalent, including to azithromycin, which until recently was the most reliable treatment. The bacteria was first isolated from the urogenital tract of humans in 1981, and was eventually identified as a new species of ''Mycoplasma'' in 1983. It can cause negative health effects in men and women. It also increases the risk factor for HIV spread with higher occurrences in those previously treated with the azithromycin antibiotics. Specifically, it causes urethritis in both men and women, and also cervicitis and pelvic inflammation in women. It presents clinically similar symptoms to that of ''Chlamydia trachomatis'' infection and has shown hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mimivirus
''Mimivirus'' is a genus of giant viruses, in the family ''Mimiviridae''. Amoeba serve as their natural hosts. This genus contains a single identified species named ''Acanthamoeba polyphaga mimivirus'' (APMV). It also refers to a group of phylogenetically related large viruses. In colloquial speech, APMV is more commonly referred to as just "mimivirus". Mimivirus, short for "mimicking microbe", is so called to reflect its large size and apparent Gram-staining properties. Mimivirus has a large and complex genome compared with most other viruses. Until 2013, when a larger virus ''Pandoravirus'' was described, it had the largest capsid diameter of all known viruses. History APMV was discovered accidentally in 1992 within the amoeba '' Acanthamoeba polyphaga'', after which it is named, during research into legionellosis by researchers from Marseille and Leeds. The virus was observed in a Gram stain and mistakenly thought to be a Gram-positive bacterium. As a consequence it was nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceramide
Ceramides are a family of waxy lipid molecules. A ceramide is composed of N-acetylsphingosine and a fatty acid. Ceramides are found in high concentrations within the cell membrane of eukaryotic cells, since they are component lipids that make up sphingomyelin, one of the major lipids in the lipid bilayer. Contrary to previous assumptions that ceramides and other sphingolipids found in cell membrane were purely supporting structural elements, ceramide can participate in a variety of cellular signaling: examples include regulating differentiation, proliferation, and programmed cell death (PCD) of cells. The word ''ceramide'' comes from the Latin ''cera'' (wax) and ''amide''. Ceramide is a component of vernix caseosa, the waxy or cheese-like white substance found coating the skin of newborn human infants. Pathways for ceramide synthesis There are three major pathways of ceramide generation. First, the sphingomyelinase pathway uses an enzyme to break down sphingomyelin in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanger Institute
The Wellcome Sanger Institute, previously known as The Sanger Centre and Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute, is a non-profit organisation, non-profit British genomics and genetics research institute, primarily funded by the Wellcome Trust. It is located on the Wellcome Genome Campus by the village of Hinxton, outside Cambridge. It shares this location with the European Bioinformatics Institute. It was established in 1992 and named after double Nobel Laureate Frederick Sanger. It was conceived as a large scale DNA sequencing centre to participate in the Human Genome Project, and went on to make the largest single contribution to the gold standard sequence of the human genome. From its inception the institute established and has maintained a policy of data sharing, and does much of its research in collaboration. Since 2000, the institute expanded its mission to understand "the role of genetics in health and disease". The institute now employs around 900 people and engages in five mai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plymouth Marine Laboratory
Plymouth Marine Laboratory (abbreviated as PML) in the city of Plymouth, England, is a marine research organization and registered charity. It is a partner of the UK Research & Innovation's Natural Environment Research Council (NERC). PML's chair is Janice Timberlake, its chief executive is Prof. Icarus Allen and its patron is the film-maker James Cameron. Research and capability Research activity at PML broadly investigates global-scale issues of climate change and sustainability. PML's core capabilities are centred around biogeochemistry and systems science, ecosystem health and human health, and sustainable development and biodiversity. It has particular capacity around Earth observation, ecosystem modelling, microbial ecology, Blue biotechnology, socioeconomics and policy advice. Specific research activities include the monitoring of ocean acidity and its effects on corals and shellfish, and this information is reported to the UK government. As part of its resea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of East Anglia
The University of East Anglia (UEA) is a public research university in Norwich, England. Established in 1963 on a campus west of the city centre, the university has four faculties and 26 schools of study. The annual income of the institution for 2020–21 was £292.1 million, of which £35.2 million was from research grants and contracts, with an expenditure of £290.4 million, and had an undergraduate offer rate of 85.1% in 2021. UEA alumni and faculty include three Nobel laureates, a discoverer of Hepatitis C and of the Hepatitis D genome, a lead developer of the Oxford–AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine, one President of the Royal Society, and at least 48 Fellows of the Royal Society. Alumni also include heads of state, government and intergovernmental organisations, as well as three Booker Prize winning authors. History 1960s People in Norwich began to talk about the possibility of setting up a university in the nineteenth century, and attempts to establish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Biological Association
The Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom (MBA) is a learned society with a scientific laboratory that undertakes research in marine biology. The organisation was founded in 1884 and has been based in Plymouth since the Citadel Hill Laboratory was opened on 30 June 1888. The MBA is also home to the National Marine Biological Library, whose collections cover the marine biological sciences, and curates the Historical Collections. Throughout its history, the MBA has had a royal patron. In 2013, the MBA was granted a royal charter in recognition of the MBA's scientific preeminence in its field. Origins and foundation In 1866 the Royal Commission on the Sea Fisheries, which included among its officers Professor Thomas Henry Huxley, had reported that fears of over-exploitation of the sea fisheries were unfounded. They recommended removing existing laws regulating fishing grounds and closed seasons. However, the increase in the size and number of fishing vessels was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open Reading Frame
In molecular biology, open reading frames (ORFs) are defined as spans of DNA sequence between the start and stop codons. Usually, this is considered within a studied region of a prokaryotic DNA sequence, where only one of the six possible reading frames will be "open" (the "reading", however, refers to the RNA produced by transcription of the DNA and its subsequent interaction with the ribosome in translation). Such an ORF may contain a start codon (usually AUG in terms of RNA) and by definition cannot extend beyond a stop codon (usually UAA, UAG or UGA in RNA). That start codon (not necessarily the first) indicates where translation may start. The transcription termination site is located after the ORF, beyond the translation stop codon. If transcription were to cease before the stop codon, an incomplete protein would be made during translation. In eukaryotic genes with multiple exons, introns are removed and exons are then joined together after transcription to yield the final ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horizontal Gene Transfer
Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) or lateral gene transfer (LGT) is the movement of genetic material between Unicellular organism, unicellular and/or multicellular organisms other than by the ("vertical") transmission of DNA from parent to offspring (reproduction). HGT is an important factor in the evolution of many organisms. HGT is influencing scientific understanding of higher order evolution while more significantly shifting perspectives on bacterial evolution. Horizontal gene transfer is the primary mechanism for the spread of antibiotic resistance in bacteria, and plays an important role in the evolution of bacteria that can degrade novel compounds such as human-created Bactericide, pesticides and in the evolution, maintenance, and transmission of virulence. It often involves Temperateness (virology), temperate bacteriophages and plasmids. Genes responsible for antibiotic resistance in one species of bacteria can be transferred to another species of bacteria through various m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_now_the_Marine_Scientific_study_centre_-_geograph.org.uk_-_889854.jpg)
