|
Emden–Chandrasekhar Equation
In astrophysics, the Emden–Chandrasekhar equation is a dimensionless form of the Poisson equation for the density distribution of a spherically symmetric isothermal gas sphere subjected to its own gravitational force, named after Robert Emden and Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar. The equation was first introduced by Robert Emden in 1907. The equation reads :\frac \frac\left(\xi^2 \frac\right)= e^ where \xi is the dimensionless radius and \psi is the related to the density of the gas sphere as \rho=\rho_c e^, where \rho_c is the density of the gas at the centre. The equation has no known explicit solution. If a polytropic fluid is used instead of an isothermal fluid, one obtains the Lane–Emden equation. The isothermal assumption is usually modeled to describe the core of a star. The equation is solved with the initial conditions, :\psi =0, \quad \frac =0 \quad \text \quad \xi=0. The equation appears in other branches of physics as well, for example the same equation appears in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chandrasekhar Equation
Chandrasekhar, Chandrashekhar or Chandra Shekhar is an Indian name and may refer to a number of individuals. The name comes from the name of an incarnation of the Hindu god Shiva. In this form he married the goddess Parvati. Etymologically, the name comes from the Sanskrit words "चन्द्र (''candra'')", meaning "moon", and "शेखर (''śekhara'')", meaning "crest" or "crown", which is an epithet of the Shiva. Notable people with this name In politics and activism: * Chandra Shekhar Azad (1906–1931), known as Azad ("The Free"), Indian revolutionary who organised the Hindustan Socialist Republican Army (HSRA) * K. M. Chandrasekhar (born 1948), Indian Cabinet Secretary * Sripati Chandrasekhar (1918–2001), an Indian demographer and politician * Chandra Shekhar Dubey (born 1946), member of the 14th Lok Sabha of India * Chandrashekhar Prasad (died 1997), assassinated Indian student activist * Kalvakuntla Chandrashekar Rao (born 1954), known as K.C.R., Indian politic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boltzmann Constant
The Boltzmann constant ( or ) is the proportionality factor that relates the average relative kinetic energy of particles in a gas with the thermodynamic temperature of the gas. It occurs in the definitions of the kelvin and the gas constant, and in Planck's law of black-body radiation and Boltzmann's entropy formula, and is used in calculating thermal noise in resistors. The Boltzmann constant has dimensions of energy divided by temperature, the same as entropy. It is named after the Austrian scientist Ludwig Boltzmann. As part of the 2019 redefinition of SI base units, the Boltzmann constant is one of the seven " defining constants" that have been given exact definitions. They are used in various combinations to define the seven SI base units. The Boltzmann constant is defined to be exactly . Roles of the Boltzmann constant Macroscopically, the ideal gas law states that, for an ideal gas, the product of pressure and volume is proportional to the product of amount of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluid Dynamics
In physics and engineering, fluid dynamics is a subdiscipline of fluid mechanics that describes the flow of fluids— liquids and gases. It has several subdisciplines, including ''aerodynamics'' (the study of air and other gases in motion) and hydrodynamics (the study of liquids in motion). Fluid dynamics has a wide range of applications, including calculating forces and moments on aircraft, determining the mass flow rate of petroleum through pipelines, predicting weather patterns, understanding nebulae in interstellar space and modelling fission weapon detonation. Fluid dynamics offers a systematic structure—which underlies these practical disciplines—that embraces empirical and semi-empirical laws derived from flow measurement and used to solve practical problems. The solution to a fluid dynamics problem typically involves the calculation of various properties of the fluid, such as flow velocity, pressure, density, and temperature, as functions of space and time. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equations Of Physics
In mathematics, an equation is a formula that expresses the equality of two expressions, by connecting them with the equals sign . The word ''equation'' and its cognates in other languages may have subtly different meanings; for example, in French an ''équation'' is defined as containing one or more variables, while in English, any well-formed formula consisting of two expressions related with an equals sign is an equation. ''Solving'' an equation containing variables consists of determining which values of the variables make the equality true. The variables for which the equation has to be solved are also called unknowns, and the values of the unknowns that satisfy the equality are called solutions of the equation. There are two kinds of equations: identities and conditional equations. An identity is true for all values of the variables. A conditional equation is only true for particular values of the variables. An equation is written as two expressions, connected by an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chandrasekhar's White Dwarf Equation
In astrophysics, Chandrasekhar's white dwarf equation is an initial value ordinary differential equation introduced by the Indian American astrophysicist Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar, in his study of the gravitational potential of completely degenerate white dwarf stars. The equation reads as :\frac 1 \frac d \left(\eta^2 \frac\right) + (\varphi^2 - C)^ = 0 with initial conditions :\varphi(0)=1, \quad \varphi'(0)=0 where \varphi measures the density of white dwarf, \eta is the non-dimensional radial distance from the center and C is a constant which is related to the density of the white dwarf at the center. The boundary \eta=\eta_\infty of the equation is defined by the condition :\varphi(\eta_\infty) = \sqrt. such that the range of \varphi becomes \sqrt\leq\varphi\leq 1. This condition is equivalent to saying that the density vanishes at \eta=\eta_\infty. Derivation From the quantum statistics of a completely degenerate electron gas (all the lowest quantum states are occup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Arthur Milne
Edward Arthur Milne FRS (; 14 February 1896 – 21 September 1950) was a British astrophysicist and mathematician. Biography Milne was born in Hull, Yorkshire, England. He attended Hymers College and from there he won an open scholarship in mathematics and natural science to study at Trinity College, Cambridge in 1914, gaining the largest number of marks which had ever been awarded in the examination. In 1916 he joined a group of mathematicians led by A. V. Hill for the Ministry of munitions working on the ballistics of anti-aircraft gunnery, they became known as ′Hill's Brigands′. Later Milne became an expert on sound localisation. In 1917 he became a lieutenant in the Royal Navy Volunteer Reserve. He was a fellow of Trinity College, Cambridge, 1919–1925, being assistant director of the solar physics observatory, 1920–1924, mathematical lecturer at Trinity, 1924–1925, and university lecturer in astrophysics, 1922–1925. He was Beyer professor of applied mat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Singular Solution
A singular solution ''ys''(''x'') of an ordinary differential equation is a solution that is singular or one for which the initial value problem (also called the Cauchy problem by some authors) fails to have a unique solution at some point on the solution. The set on which a solution is singular may be as small as a single point or as large as the full real line. Solutions which are singular in the sense that the initial value problem fails to have a unique solution need not be singular functions. In some cases, the term ''singular solution'' is used to mean a solution at which there is a failure of uniqueness to the initial value problem at every point on the curve. A singular solution in this stronger sense is often given as tangent to every solution from a family of solutions. By ''tangent'' we mean that there is a point ''x'' where ''ys''(''x'') = ''yc''(''x'') and ''y's''(''x'') = ''y'c''(''x'') where ''yc'' is a solution in a family of solutions parameterized by ''c''. This m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chandra2
Chandra ( sa, चन्द्र, Candra, shining' or 'moon), also known as Soma ( sa, सोम), is the Hindu god of the Moon, and is associated with the night, plants and vegetation. He is one of the Navagraha (nine planets of Hinduism) and Dikpala (guardians of the directions). Etymology and other names The word "Chandra" literally means "bright, shining or glittering" and is used for the "Moon" in Sanskrit and other Indian languages.''Graha Sutras'' by Ernst Wilhelm, published by Kala Occult Publishers p. 51 It is also the name of various other figures in Hindu mythology, including an asura and a Suryavanshi king. It is also a common Indian name and surname. Both male and female name variations exists in many South Asian languages that originate from Sanskrit. Some of the synonyms of Chandra include ''Soma'' (distill), ''Indu'' (bright drop), ''Atrisuta'' (son of Atri), ''Shashin'' or ''Shachin'' (marked by hare), ''Taradhipa'' (lord of stars) and ''Nishakara'' (the ni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravitational Constant
The gravitational constant (also known as the universal gravitational constant, the Newtonian constant of gravitation, or the Cavendish gravitational constant), denoted by the capital letter , is an empirical physical constant involved in the calculation of gravitational effects in Sir Isaac Newton's law of universal gravitation and in Albert Einstein's theory of general relativity. In Newton's law, it is the proportionality constant connecting the gravitational force between two bodies with the product of their masses and the inverse square of their distance. In the Einstein field equations, it quantifies the relation between the geometry of spacetime and the energy–momentum tensor (also referred to as the stress–energy tensor). The measured value of the constant is known with some certainty to four significant digits. In SI units, its value is approximately The modern notation of Newton's law involving was introduced in the 1890s by C. V. Boys. The first impl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stefan–Boltzmann Constant
The Stefan–Boltzmann constant (also Stefan's constant), a physical constant denoted by the Greek letter ''σ'' (sigma), is the constant of proportionality in the Stefan–Boltzmann law: "the total intensity radiated over all wavelengths increases as the temperature increases", of a black body which is proportional to the fourth power of the thermodynamic temperature. The theory of thermal radiation lays down the theory of quantum mechanics, by using physics to relate to molecular, atomic and sub-atomic levels. Slovenian physicist Josef Stefan formulated the constant in 1879; it was formally derived in 1884 by his former student and collaborator, the Austrian physicist Ludwig Boltzmann. The equation can also be derived from Planck's law, by integrating over all wavelengths at a given temperature, which will represent a small flat black body box. "The amount of thermal radiation emitted increases quickly and the principal frequency of the radiation becomes higher with increasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Weight
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and biochemistry, the distinction from ions is dropped and ''molecule'' is often used when referring to polyatomic ions. A molecule may be homonuclear, that is, it consists of atoms of one chemical element, e.g. two atoms in the oxygen molecule (O2); or it may be heteronuclear, a chemical compound composed of more than one element, e.g. water (two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom; H2O). In the kinetic theory of gases, the term ''molecule'' is often used for any gaseous particle regardless of its composition. This relaxes the requirement that a molecule contains two or more atoms, since the noble gases are individual atoms. Atoms and complexes connected by non-covalent interactions, such as hydrogen bonds or ionic bonds, are typically not consi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
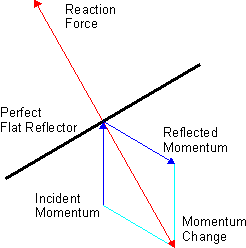
Radiation Pressure
Radiation pressure is the mechanical pressure exerted upon any surface due to the exchange of momentum between the object and the electromagnetic field. This includes the momentum of light or electromagnetic radiation of any wavelength that is absorbed, reflected, or otherwise emitted (e.g. black-body radiation) by matter on any scale (from macroscopic objects to dust particles to gas molecules). The associated force is called the radiation pressure force, or sometimes just the force of light. The forces generated by radiation pressure are generally too small to be noticed under everyday circumstances; however, they are important in some physical processes and technologies. This particularly includes objects in outer space, where it is usually the main force acting on objects besides gravity, and where the net effect of a tiny force may have a large cumulative effect over long periods of time. For example, had the effects of the Sun's radiation pressure on the spacecraft of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |