|
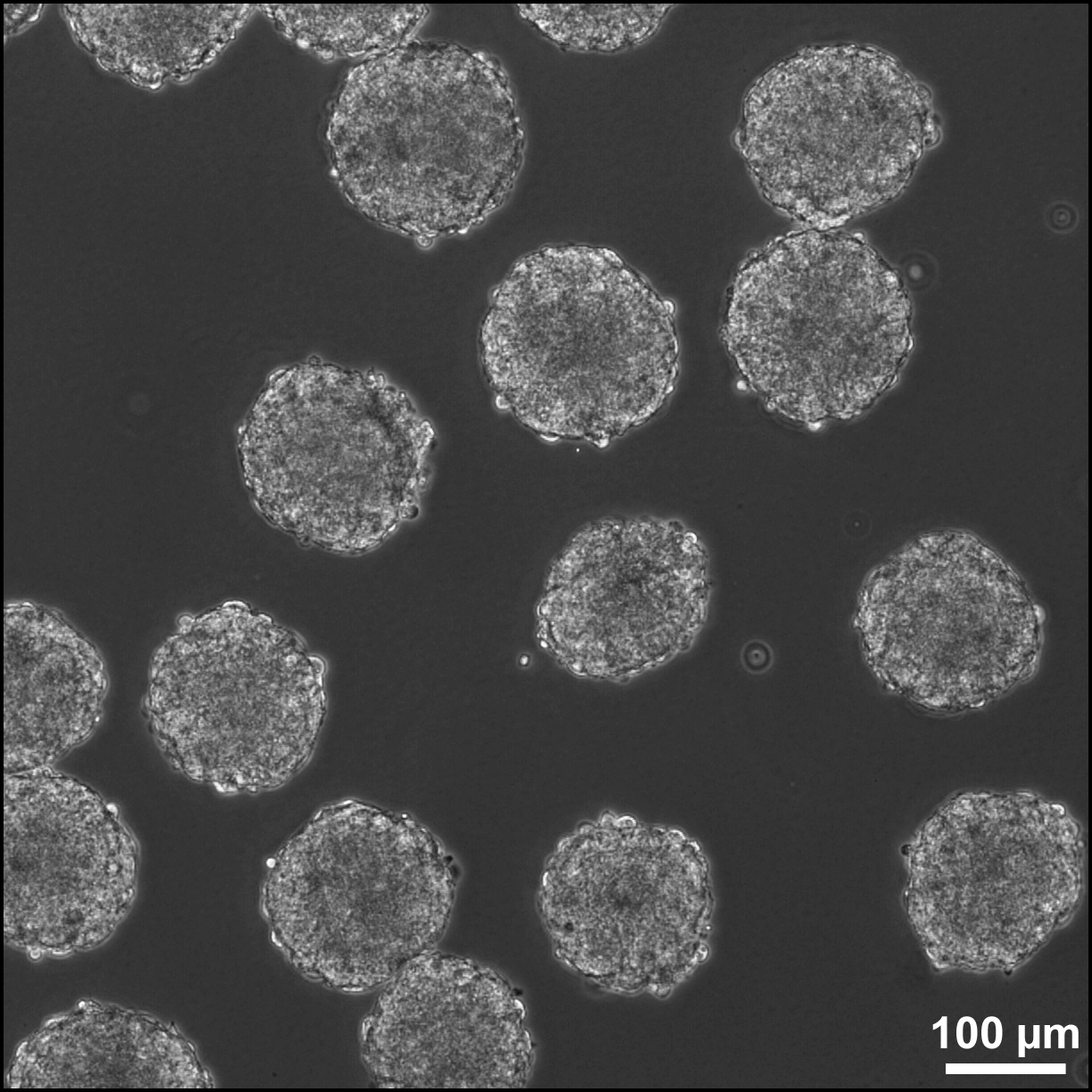
Embryoid Body
Embryoid bodies (EBs) are three-dimensional aggregates of pluripotent stem cells. EBs are differentiation of human embryonic stem cells into embryoid bodies comprising the three embryonic germ layers. Background The pluripotent cell types that comprise embryoid bodies include embryonic stem cells (ESCs) derived from the blastocyst stage of embryos from mouse (mESC), primate, and human (hESC) sources. Additionally, EBs can be formed from embryonic stem cells derived through alternative techniques, including somatic cell nuclear transfer or the reprogramming of somatic cells to yield induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS). Similar to ESCs cultured in monolayer formats, ESCs within embryoid bodies undergo differentiation and cell specification along the three germ lineages – endoderm, ectoderm, and mesoderm – which comprise all somatic cell types. In contrast to monolayer cultures, however, the spheroid structures that are formed when ESCs aggregate enables the non ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MESC EBs
The acronym MESC stands for ''Material and Equipment Standards and Code''. It is a tool of the materials department Department may refer to: * Departmentalization, division of a larger organization into parts with specific responsibility Government and military *Department (administrative division), a geographical and administrative division within a country, ... for standardisation and handling of materials used in business. It was created in 1932 for internal use by Shell, but later on licensed to every company who wished to pay for it. The system is a catalogue of specifications in the English language, to allow buyers to purchase standardised materials all over the world. When MESC was initially introduced, materials were allocated a unique 7-digit number. This was increased to ten digits in 1946.McDonald, KMaterials Management Programme in Shell accessed 26 December 2016 The system has a numerical "coding schedule" of 10 digits to code the materials. It consists of g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agar
Agar ( or ), or agar-agar, is a jelly-like substance consisting of polysaccharides obtained from the cell walls of some species of red algae, primarily from ogonori ('' Gracilaria'') and "tengusa" ('' Gelidiaceae''). As found in nature, agar is a mixture of two components, the linear polysaccharide agarose and a heterogeneous mixture of smaller molecules called agaropectin. It forms the supporting structure in the cell walls of certain species of algae and is released on boiling. These algae are known as agarophytes, belonging to the Rhodophyta (red algae) phylum. The processing of food-grade agar removes the agaropectin, and the commercial product is essentially pure agarose. Agar has been used as an ingredient in desserts throughout Asia and also as a solid substrate to contain culture media for microbiological work. Agar can be used as a laxative; an appetite suppressant; a vegan substitute for gelatin; a thickener for soups; in fruit preserves, ice cream, and ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurite
A neurite or neuronal process refers to any projection from the cell body of a neuron. This projection can be either an axon or a dendrite. The term is frequently used when speaking of immature or developing neurons, especially of cells in culture, because it can be difficult to tell axons from dendrites before differentiation is complete. Neurite development The development of a neurite requires a complex interplay of both extracellular and intracellular signals. At every given point along a developing neurite, there are receptors detecting both positive and negative growth cues from every direction in the surrounding space. The developing neurite sums together all of these growth signals in order to determine which direction the neurite will ultimately grow towards. While not all of the growth signals are known, several have been identified and characterized. Among the known extracellular growth signals are netrin, a midline chemoattractant, and semaphorin, ephrin and col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endoderm
Endoderm is the innermost of the three primary germ layers in the very early embryo. The other two layers are the ectoderm (outside layer) and mesoderm (middle layer). Cells migrating inward along the archenteron form the inner layer of the gastrula, which develops into the endoderm. The endoderm consists at first of flattened cells, which subsequently become columnar. It forms the epithelial lining of multiple systems. In plant biology, endoderm corresponds to the innermost part of the cortex (bark) in young shoots and young roots often consisting of a single cell layer. As the plant becomes older, more endoderm will lignify. Production The following chart shows the tissues produced by the endoderm. The embryonic endoderm develops into the interior linings of two tubes in the body, the digestive and respiratory tube. Liver and pancreas cells are believed to derive from a common precursor. In humans, the endoderm can differentiate into distinguishable organs afte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesoderm
The mesoderm is the middle layer of the three germ layers that develops during gastrulation in the very early development of the embryo of most animals. The outer layer is the ectoderm, and the inner layer is the endoderm.Langman's Medical Embryology, 11th edition. 2010. The mesoderm forms mesenchyme, mesothelium, non-epithelial blood cells and coelomocytes. Mesothelium lines coeloms. Mesoderm forms the muscles in a process known as myogenesis, septa (cross-wise partitions) and mesenteries (length-wise partitions); and forms part of the gonads (the rest being the gametes). Myogenesis is specifically a function of mesenchyme. The mesoderm differentiates from the rest of the embryo through intercellular signaling, after which the mesoderm is polarized by an organizing center. The position of the organizing center is in turn determined by the regions in which beta-catenin is protected from degradation by GSK-3. Beta-catenin acts as a co-factor that alters the activity of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fetal Bovine Serum
Fetal bovine serum (FBS) is derived from the blood drawn from a bovine fetus via a closed system of collection at the slaughterhouse. Fetal bovine serum is the most widely used serum-supplement for the in vitro cell culture of eukaryotic cells. This is due to it having a very low level of antibodies and containing more growth factors, allowing for versatility in many different cell culture applications. The globular protein, bovine serum albumin (BSA), is a major component of fetal bovine serum. The rich variety of proteins in fetal bovine serum maintains cultured cells in a medium in which they can survive, grow, and divide. Because it is a biological product, FBS is not a fully defined media component, and as such varies in composition between batches. As a result of this and in an attempt to minimize the possibility of transfer of adventitious agents, serum-free and chemically defined media (CDM) have been developed. The effectiveness of serum-free media is limited, however a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neural Crest
Neural crest cells are a temporary group of cells unique to vertebrates that arise from the embryonic ectoderm germ layer, and in turn give rise to a diverse cell lineage—including melanocytes, craniofacial cartilage and bone, smooth muscle, peripheral and enteric neurons and glia. After gastrulation, neural crest cells are specified at the border of the neural plate and the non-neural ectoderm. During neurulation, the borders of the neural plate, also known as the neural folds, converge at the dorsal midline to form the neural tube. Subsequently, neural crest cells from the roof plate of the neural tube undergo an epithelial to mesenchymal transition, delaminating from the neuroepithelium and migrating through the periphery where they differentiate into varied cell types. The emergence of neural crest was important in vertebrate evolution because many of its structural derivatives are defining features of the vertebrate clade. Underlying the development of neura ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basement Membrane
The basement membrane is a thin, pliable sheet-like type of extracellular matrix that provides cell and tissue support and acts as a platform for complex signalling. The basement membrane sits between epithelial tissues including mesothelium and endothelium, and the underlying connective tissue. Structure As seen with the electron microscope, the basement membrane is composed of two layers, the basal lamina and the reticular lamina. The underlying connective tissue attaches to the basal lamina with collagen VII anchoring fibrils and fibrillin microfibrils. The basal lamina layer can further be subdivided into two layers based on their visual appearance in electron microscopy. The lighter-colored layer closer to the epithelium is called the lamina lucida, while the denser-colored layer closer to the connective tissue is called the lamina densa. The electron-dense lamina densa layer is about 30–70 nanometers thick and consists of an underlying network of reticular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
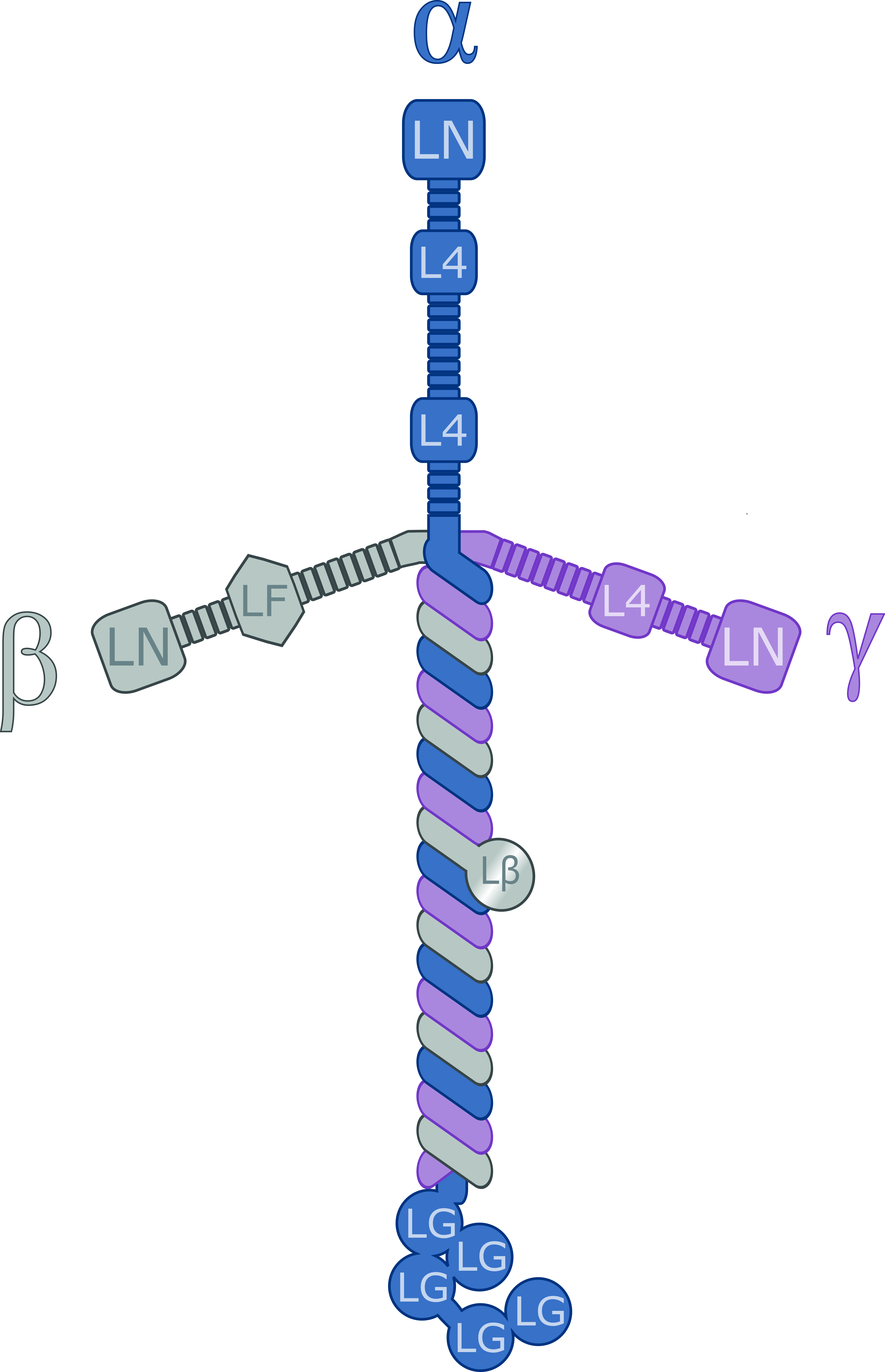
Laminin
Laminins are a family of glycoproteins of the extracellular matrix of all animals. They are major components of the basal lamina (one of the layers of the basement membrane), the protein network foundation for most cells and organs. The laminins are an important and biologically active part of the basal lamina, influencing cell differentiation, migration, and adhesion. Laminins are heterotrimeric proteins with a high molecular mass (~400 to ~900 kDa). They contain three different chains (α, β and γ) encoded by five, four, and three paralogous genes in humans, respectively. The laminin molecules are named according to their chain composition. Thus, laminin-511 contains α5, β1, and γ1 chains. Fourteen other chain combinations have been identified ''in vivo''. The trimeric proteins intersect to form a cross-like structure that can bind to other cell membrane and extracellular matrix molecules. The three shorter arms are particularly good at binding to other laminin molecule ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collagen Type IV
Collagen IV (ColIV or Col4) is a type of collagen found primarily in the basal lamina. The collagen IV C4 domain at the C-terminus is not removed in post-translational processing, and the fibers link head-to-head, rather than in parallel. Also, collagen IV lacks the regular glycine in every third residue necessary for the tight, collagen helix. This makes the overall arrangement more sloppy with kinks. These two features cause the collagen to form in a sheet, the form of the basal lamina. Collagen IV is the more common usage, as opposed to the older terminology of "type-IV collagen". Collagen IV exists in all metazoan phyla, to whom they served as an evolutionary stepping stone to multicellularity. There are six human genes associated with it: * COL4A1, COL4A2, COL4A3, COL4A4, COL4A5, COL4A6 Clinical significance The alpha-3 subunit (COL4A3) of collagen IV is thought to be the antigen implicated in Goodpasture syndrome, wherein the immune system attacks the basement membranes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extracellular Matrix
In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM), also called intercellular matrix, is a three-dimensional network consisting of extracellular macromolecules and minerals, such as collagen, enzymes, glycoproteins and hydroxyapatite that provide structural and biochemical support to surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM. The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest. Each type of conn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)