|
Embedment
Embedment is a phenomenon in mechanical engineering in which the surfaces between mechanical members of a loaded joint embed. It can lead to failure by fatigue as described below, and is of particular concern when considering the design of critical fastener joints. Mechanism The mechanism behind embedment is different from creep. When the loading of the joint varies (e.g. due to vibration or thermal expansion) the protruding points of the imperfect surfaces will see local stress concentrations and yield until the stress concentration is relieved. Over time, surfaces can flatten an appreciable amount in the order of thousandths of an inch. Consequences In critical fastener joints, embedment can mean loss of preload. Flattening of a surface allows the strain of a screw to relax, which in turn correlates with a loss in tension and thus preload. In bolted joints with particularly short grip lengths, the loss of preload due to embedment can be especially significant, causing com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatigue (material)
In materials science, fatigue is the initiation and propagation of cracks in a material due to cyclic loading. Once a fatigue crack has initiated, it grows a small amount with each loading cycle, typically producing striations on some parts of the fracture surface. The crack will continue to grow until it reaches a critical size, which occurs when the stress intensity factor of the crack exceeds the fracture toughness of the material, producing rapid propagation and typically complete fracture of the structure. Fatigue has traditionally been associated with the failure of metal components which led to the term metal fatigue. In the nineteenth century, the sudden failing of metal railway axles was thought to be caused by the metal ''crystallising'' because of the brittle appearance of the fracture surface, but this has since been disproved. Most materials, such as composites, plastics and ceramics, seem to experience some sort of fatigue-related failure. To aid in predicting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanical Engineering
Mechanical engineering is the study of physical machines that may involve force and movement. It is an engineering branch that combines engineering physics and mathematics principles with materials science, to design, analyze, manufacture, and maintain mechanical systems. It is one of the oldest and broadest of the engineering branches. Mechanical engineering requires an understanding of core areas including mechanics, dynamics, thermodynamics, materials science, structural analysis, and electricity. In addition to these core principles, mechanical engineers use tools such as computer-aided design (CAD), computer-aided manufacturing (CAM), and product lifecycle management to design and analyze manufacturing plants, industrial equipment and machinery, heating and cooling systems, transport systems, aircraft, watercraft, robotics, medical devices, weapons, and others. Mechanical engineering emerged as a field during the Industrial Revolution in Europe in the 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
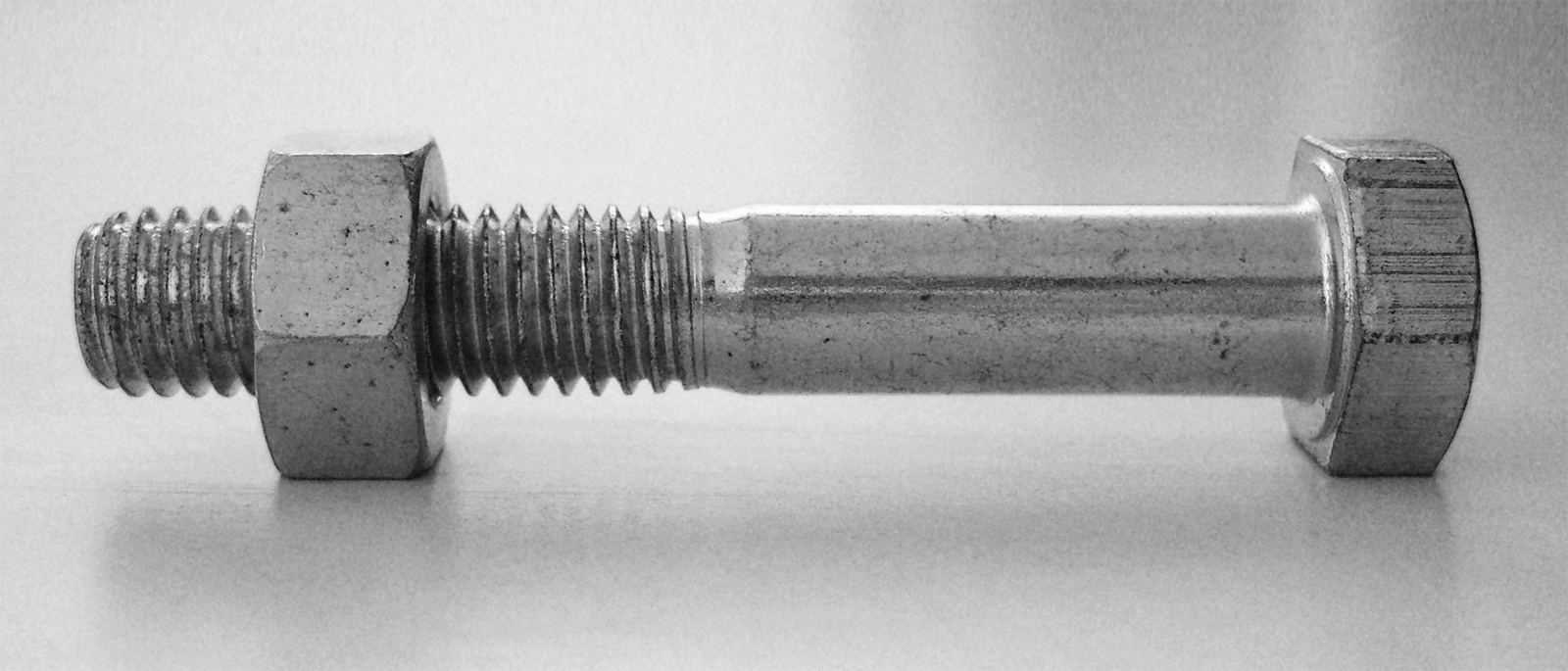
Bolted Joint
A bolted joint is one of the most common elements in construction and machine design. It consists of a male threaded fastener (e. g., a bolt) that captures and joins other parts, secured with a matching female screw thread. There are two main types of bolted joint designs: tension joints and shear joints. Joint types In a tension joint, the bolt and clamped components of the joint are designed to transfer an applied tension load through the joint by way of the clamped components by the design of a proper balance of joint and bolt stiffness. The joint should be designed such that the clamp load is never overcome by the external tension forces acting to separate the joint. If the external tension forces overcome the clamp load (bolt preload) the clamped joint components will separate, allowing relative motion of the components. The second type of bolted joint transfers the applied load in shear of the bolt shank and relies on the shear strength of the bolt. Tension loads on such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Creep (deformation)
In materials science, creep (sometimes called cold flow) is the tendency of a solid material to move slowly or deform permanently under the influence of persistent mechanical stresses. It can occur as a result of long-term exposure to high levels of stress that are still below the yield strength of the material. Creep is more severe in materials that are subjected to heat for long periods and generally increases as they near their melting point. The rate of deformation is a function of the material's properties, exposure time, exposure temperature and the applied structural load. Depending on the magnitude of the applied stress and its duration, the deformation may become so large that a component can no longer perform its function – for example creep of a turbine blade could cause the blade to contact the casing, resulting in the failure of the blade. Creep is usually of concern to engineers and metallurgists when evaluating components that operate under high stresses or hig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vibration
Vibration is a mechanical phenomenon whereby oscillations occur about an equilibrium point. The word comes from Latin ''vibrationem'' ("shaking, brandishing"). The oscillations may be periodic, such as the motion of a pendulum—or random, such as the movement of a tire on a gravel road. Vibration can be desirable: for example, the motion of a tuning fork, the reed in a woodwind instrument or harmonica, a mobile phone, or the cone of a loudspeaker. In many cases, however, vibration is undesirable, wasting energy and creating unwanted sound. For example, the vibrational motions of engines, electric motors, or any mechanical device in operation are typically unwanted. Such vibrations could be caused by imbalances in the rotating parts, uneven friction, or the meshing of gear teeth. Careful designs usually minimize unwanted vibrations. The studies of sound and vibration are closely related. Sound, or pressure waves, are generated by vibrating structures (e.g. vocal cords); ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Expansion
Thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to change its shape, area, volume, and density in response to a change in temperature, usually not including phase transitions. Temperature is a monotonic function of the average molecular kinetic energy of a substance. When a substance is heated, molecules begin to vibrate and move more, usually creating more distance between themselves. Substances which contract with increasing temperature are unusual, and only occur within limited temperature ranges (see examples below). The relative expansion (also called strain) divided by the change in temperature is called the material's coefficient of linear thermal expansion and generally varies with temperature. As energy in particles increases, they start moving faster and faster weakening the intermolecular forces between them, therefore expanding the substance. Overview Predicting expansion If an equation of state is available, it can be used to predict the values of the thermal ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preload (engineering)
Preload is an engineering term with several meanings. In the general sense, it refers to the internal application of stress to certain mechanical systems. Fastener preload ' The most common usage is to describe the load applied to a fastener as a result of its being installed, i.e., before any external loads are applied (e.g., tightening the nut on a bolt). Preload in such cases is important for several reasons. First, a tightened bolt experiences only a small fraction of any external load that will be applied later, so that a fully tightened bolt can (depending on the exact application) sustain a much greater load than a loosely tightened bolt. Second, a nut that is correctly tightened will resist becoming loose under the influence of vibration, temperature cycling, etc. Bearing preload Internal stress to a bearing through application of negative clearance is known as bearing preloading. Advantages of preloading include the following: maintain axial and radial position for a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grip Length
A bolt is a form of threaded fastener with an external male thread requiring a matching pre-formed female thread such as a nut. Bolts are very closely related to screws. Bolts vs. screws The distinction between a bolt and a screw is poorly-defined. The academic distinction, per ''Machinery's Handbook'', is in their intended design: bolts are designed to pass through an unthreaded hole in a component and be fastened with the aid of a nut, although such a fastener can be used without a nut to tighten into a threaded component such as a nut-plate or tapped housing. Screws in contrast are used in components which contain their own thread, or to cut its own internal thread into them. This definition allows ambiguity in the description of a fastener depending on the application it is actually used for, and the terms screw and bolt are widely used by different people or in different countries to apply to the same or varying fastener. Bolts are often used to make a bolted joint. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hardness
In materials science, hardness (antonym: softness) is a measure of the resistance to localized plastic deformation induced by either mechanical indentation or abrasion (mechanical), abrasion. In general, different materials differ in their hardness; for example hard metals such as titanium and beryllium are harder than soft metals such as sodium and metallic tin, or wood and common plastics. Macroscopic hardness is generally characterized by strong intermolecular bonds, but the behavior of solid materials under force is complex; therefore, hardness can be measured in different ways, such as scratch hardness, indentation hardness, and rebound hardness. Hardness is dependent on ductility, elasticity (physics), elastic stiffness, plasticity (physics), plasticity, deformation (mechanics), strain, strength of materials, strength, toughness, viscoelasticity, and viscosity. Common examples of hard matter are ceramics, concrete, certain metals, and superhard materials, which can be cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Roughness
Surface roughness, often shortened to roughness, is a component of surface finish (surface texture). It is quantified by the deviations in the direction of the normal vector of a real surface from its ideal form. If these deviations are large, the surface is rough; if they are small, the surface is smooth. In surface metrology, roughness is typically considered to be the high-frequency, short-wavelength component of a measured surface. However, in practice it is often necessary to know both the amplitude and frequency to ensure that a surface is fit for a purpose. Roughness plays an important role in determining how a real object will interact with its environment. In tribology, rough surfaces usually wear more quickly and have higher friction coefficients than smooth surfaces. Roughness is often a good predictor of the performance of a mechanical component, since irregularities on the surface may form nucleation sites for cracks or corrosion. On the other hand, roughness ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belleville Washer
A Belleville washer, also known as a coned-disc spring, conical spring washer, disc spring, Belleville spring or cupped spring washer, is a conical shell which can be loaded along its axis either statically or dynamically. A Belleville washer is a type of spring shaped like a washer. It is the frusto-conical shape that gives the washer its characteristic spring. The "Belleville" name comes from the inventor Julien Belleville who in Dunkerque, France, in 1867 patented a spring design which already contained the principle of the disc spring. The real inventor of Belleville washers is unknown. Through the years, many profiles for disc springs have been developed. Today the most used are the profiles with or without contact flats, while some other profiles, like disc springs with trapezoidal cross-section, have lost importance. Features and use In the different fields, if they are used as springs or to apply a flexible pre-load to a bolted joint or bearing, Belleville wash ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stress Relaxation
In materials science, stress relaxation is the observed decrease in stress in response to strain generated in the structure. This is primarily due to keeping the structure in a strained condition for some finite interval of time hence causing some amount of plastic strain. This should not be confused with creep, which is a constant state of stress with an increasing amount of strain. Since relaxation relieves the state of stress, it has the effect of also relieving the equipment reactions. Thus, relaxation has the same effect as cold springing, except it occurs over a longer period of time. The amount of relaxation which takes place is a function of time, temperature and stress level, thus the actual effect it has on the system is not precisely known, but can be bounded. Stress relaxation describes how polymers relieve stress under constant strain. Because they are viscoelastic, polymers behave in a nonlinear, non-Hookean fashion.Meyers and Chawla. "Mechanical Behavior of Materi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |