|
Elne Station
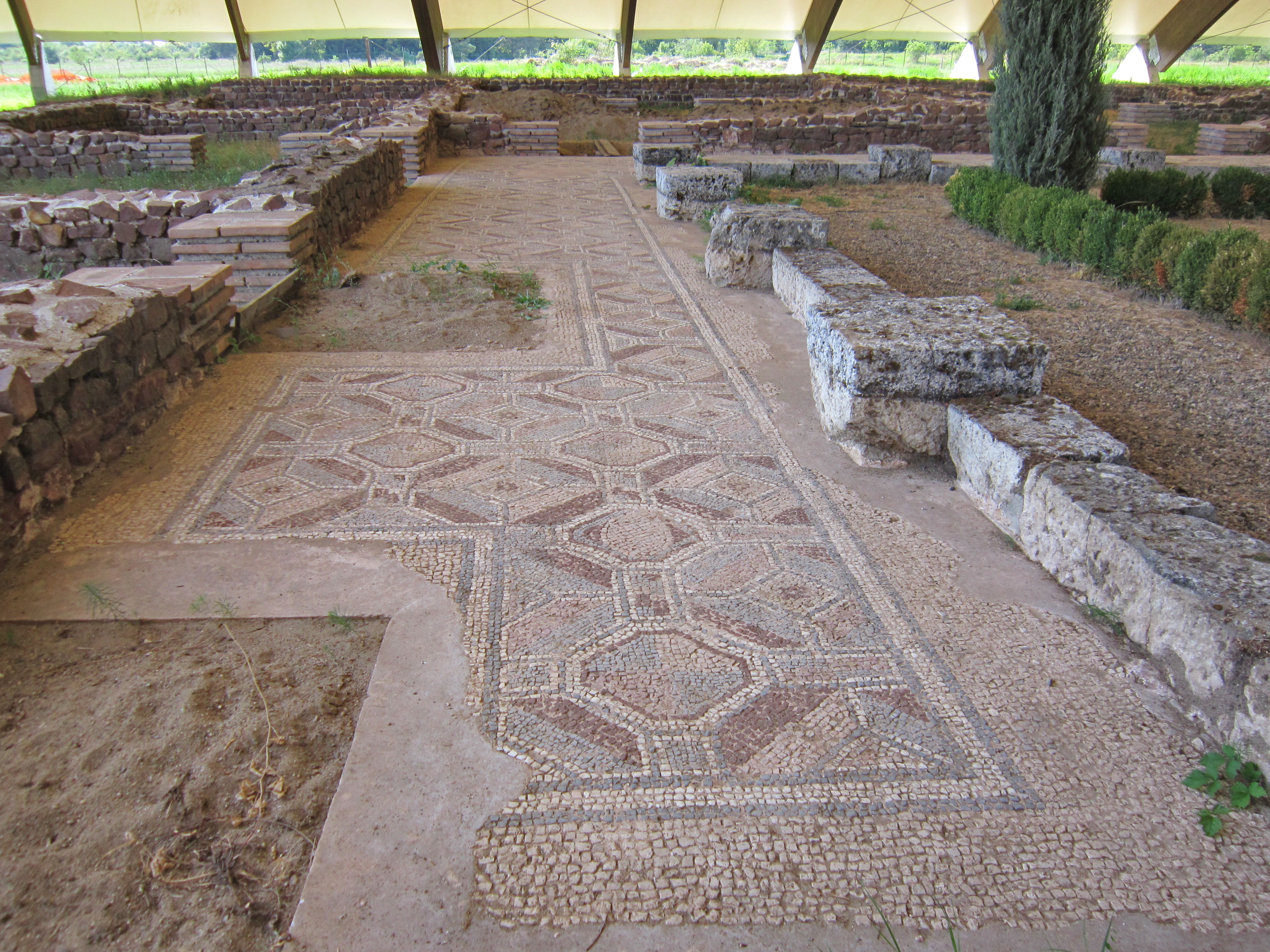
Elne (; ca, Elna ) is a commune in the Pyrénées-Orientales department in southern France. It lies in the former province of Roussillon, of which it was the first capital, being later replaced by Perpignan. Its inhabitants are still called ''Illibériens'' in reference to the city's Iberian name, Illiberis, one that it shared with the Illiberis that became Granada, Spain. Geography Elne is located in the canton of La Plaine d'Illibéris and in the arrondissement of Perpignan. It is situated from the Mediterranean near the Tech River, in Pyrénées-Orientales, from Perpignan and from Argelès. History Elne, from the heights of its fortified site, dominates the narrow plain of Roussillon between the Pyrenees and the Mediterranean. Numerous archeological researches have shown that the surrounding countryside has been occupied since Neolithic times. Elne was an Iberian '' oppidum'' or fortified town. Elne is the oldest town in Roussillon and since it is situated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communes Of France
The () is a level of administrative division in the French Republic. French are analogous to civil townships and incorporated municipalities in the United States and Canada, ' in Germany, ' in Italy, or ' in Spain. The United Kingdom's equivalent are civil parishes, although some areas, particularly urban areas, are unparished. are based on historical geographic communities or villages and are vested with significant powers to manage the populations and land of the geographic area covered. The are the fourth-level administrative divisions of France. vary widely in size and area, from large sprawling cities with millions of inhabitants like Paris, to small hamlets with only a handful of inhabitants. typically are based on pre-existing villages and facilitate local governance. All have names, but not all named geographic areas or groups of people residing together are ( or ), the difference residing in the lack of administrative powers. Except for the municipal arrondi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oppidum
An ''oppidum'' (plural ''oppida'') is a large fortified Iron Age settlement or town. ''Oppida'' are primarily associated with the Celtic late La Tène culture, emerging during the 2nd and 1st centuries BC, spread across Europe, stretching from Britain and Iberia in the west to the edge of the Hungarian plain in the east. These settlements continued to be used until the Romans conquered Southern and Western Europe. Many subsequently became Roman-era towns and cities, whilst others were abandoned. In regions north of the rivers Danube and Rhine, such as most of Germania, where the populations remained independent from Rome, ''oppida'' continued to be used into the 1st century AD. Definition is a Latin word meaning 'defended (fortified) administrative centre or town', originally used in reference to non-Roman towns as well as provincial towns under Roman control. The word is derived from the earlier Latin , 'enclosed space', possibly from the Proto-Indo-European , 'occupi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrenees
The Pyrenees (; es, Pirineos ; french: Pyrénées ; ca, Pirineu ; eu, Pirinioak ; oc, Pirenèus ; an, Pirineus) is a mountain range straddling the border of France and Spain. It extends nearly from its union with the Cantabrian Mountains to Cap de Creus on the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean coast. It reaches a maximum altitude of at the peak of Aneto. For the most part, the main crest forms a divide between Spain and France, with the microstate of Andorra sandwiched in between. Historically, the Crown of Aragon and the Kingdom of Navarre extended on both sides of the mountain range. Etymology In Greek mythology, Pyrene (mythology), Pyrene is a princess who eponym, gave her name to the Pyrenees. The Greek historiography, Greek historian Herodotus says Pyrene is the name of a town in Celts, Celtic Europe. According to Silius Italicus, she was the virgin daughter of Bebryx, a king in Narbonensis, Mediterranean Gaul by whom the hero Hercules was given hospitality during his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peace And Truce Of God
The Peace and Truce of God ( lat, Pax et treuga Dei) was a movement in the Middle Ages led by the Catholic Church and one of the most influential mass peace movements in history. The goal of both the ''Pax Dei'' and the ''Treuga Dei'' was to limit the violence of feuding endemic to the western half of the former Carolingian Empire – following its collapse in the middle of the 9th century – using the threat of spiritual sanctions. The eastern half of the former Carolingian Empire did not experience the same collapse of central authority, and neither did England. The Peace of God was first proclaimed in 989, at the Council of Charroux. It sought to protect ecclesiastical property, agricultural resources and unarmed clerics. The Truce of God, first proclaimed in 1027 at the Council of Toulouges, attempted to limit the days of the week and times of year that the nobility engaged in violence. The movement survived in some form until the thirteenth century. Other strategies to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toulouges
Toulouges (; ca, Toluges, ) is a commune in the Pyrénées-Orientales department in southern France. Geography Toulouges is located between Thuir and Perpignan, in the canton of Perpignan-6 and in the arrondissement of Perpignan. The town covers an area of , with 669 inhabitants per km2. Toulouges borders the following municipalities: Perpignan, Canohès, Thuir, El Soler, and Baho. History Toulouges probably grew upon a Roman villa. It was first mentioned in 904 at the same time mentioning the church called Tulogias. Other names that are presumably Toulouges are Tologis (in a 937 document), Tulujes (1027), Tuluges (1030), Toluges (1119). Toulouges hosted an ecumenical council known as the Council of Elge-Toulouges in 1027. It aimed to promote peace among the feudal lords of France by declaring the Truce of God, attempting to limit the days of the week and times of year that the nobility could engage in violence. During the 14th and 15th centuries Toulouges grew rapidly. A w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Council Of Toledo
From the 5th century to the 7th century AD, about thirty synods, variously counted, were held at Toledo (''Concilia toletana'') in what would come to be part of Spain. The earliest, directed against Priscillianism, assembled in 400. The "third" synod of 589 marked the epoch-making conversion of King Reccared from Arianism to orthodox Chalcedonian Christianity. The " fourth", in 633, probably under the presidency of the noted Isidore of Seville, regulated many matters of discipline and decreed uniformity of liturgy throughout the kingdom. The British Celts of Galicia accepted the Latin rite and stringent measures were adopted against baptized Jews who had gone back to their former faith. The "twelfth" council in 681 assured to the archbishop of Toledo the primacy of Hispania (present Iberian Peninsula). As nearly one hundred early canons of Toledo found a place in the ''Decretum Gratiani'', they exerted an important influence on the development of ecclesiastical law. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Of Biclarum
John of Biclaro, Biclar, or Biclarum (''c.'' 540 – after 621), also ''Iohannes Biclarensis'', was a Visigoth chronicler. He was born in Lusitania, in the city of ''Scallabis'' (modern Santarém in Portugal). He was also bishop of Girona. Early life He was educated at Constantinople, where he devoted between 7-17 years to the study of Latin and Greek. Career Imprisonment When he returned to his homeland, he was imprisoned for several years in Barcelona. Isidore of Seville ascribes this to his refusal to join the Arian Church of the Visigothic realm in Hispania. Modern historians note that other contemporary Iberian sources, including John's own ''Chronicle'' do not attest a Visigothic campaign of persecution of Catholics until the revolt of Hermenegild divided Visigothic loyalties. The Visigothic persecutions of dissenters and Jews may be a more recent Catholic myth. Indeed, John wrote that, in 578, "Leovigild had peace to reside with his own people." A more likely re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Septimania
Septimania (french: Septimanie ; oc, Septimània ) is a historical region in modern-day Southern France. It referred to the western part of the Roman province of Gallia Narbonensis that passed to the control of the Visigoths in 462, when Septimania was ceded to their king, Theodoric II. The region was also variously known as Gallia, Arbuna or Narbonensis. The territory of Septimania roughly corresponds with the modern French former administrative region of Languedoc-Roussillon that merged into the new administrative region of Occitania (administrative region), Occitanie. Septimania was conquered by the Muslims in the 8th century, when it was known as Arbuna and was made part of Al-Andalus. It passed briefly to the Emirate of Córdoba, which had been expanding from the south during the eighth century, before its subsequent conquest by the Franks, who by the end of the ninth century termed it Gothia or the Gothic March (''Marca Gothica''). Septimania became a March (territorial ent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constans
Flavius Julius Constans ( 323 – 350), sometimes called Constans I, was Roman emperor from 337 to 350. He held the imperial rank of ''caesar'' from 333, and was the youngest son of Constantine the Great. After his father's death, he was made ''augustus'' alongside his brothers in September 337. Constans was given the administration of the praetorian prefectures of Italy, Illyricum, and Africa. He defeated the Sarmatians in a campaign shortly afterwards. Quarrels over the sharing of power led to a civil war with his eldest brother and co-emperor Constantine II, who invaded Italy in 340 and was killed in battle with Constans's forces near Aquileia. Constans gained from him the praetorian prefecture of Gaul. Thereafter there were tensions with his remaining brother and co-''augustus'' Constantius II (), including over the exiled bishop Athanasius of Alexandria. In the following years he campaigned against the Franks, and in 343 he visited Roman Britain, the last legitimate emp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantine I (emperor)
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to convert to Christianity. Born in Naissus, Dacia Mediterranea (now Niš, Serbia), he was the son of Flavius Constantius, a Roman army officer of Illyrian origin who had been one of the four rulers of the Tetrarchy. His mother, Helena, was a Greek Christian of low birth. Later canonized as a saint, she is traditionally attributed with the conversion of her son. Constantine served with distinction under the Roman emperors Diocletian and Galerius. He began his career by campaigning in the eastern provinces (against the Persians) before being recalled in the west (in AD 305) to fight alongside his father in Britain. After his father's death in 306, Constantine became emperor. He was acclaimed by his army at Eboracum (York, England), and eventually emerged victorious in the civil wars against emperors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helena (empress)
Flavia Julia Helena ''Augusta'' (also known as Saint Helena and Helena of Constantinople, ; grc-gre, Ἑλένη, ''Helénē''; AD 246/248– c. 330) was an '' Augusta'' and Empress of the Roman Empire and mother of Emperor Constantine the Great. She was born in the lower classes''Anonymus Valesianus'1.2 "Origo Constantini Imperatoris". traditionally in the Greek city of Drepanon, Bithynia, in Asia Minor, which was renamed Helenopolis in her honor, though several locations have been proposed for her birthplace and origin. Helena ranks as an important figure in the history of Christianity. In her final years, she made a religious tour of Syria Palaestina and Jerusalem, during which ancient tradition claims that she discovered the True Cross. The Eastern Orthodox Church, Catholic Church, Oriental Orthodox Churches, and Anglican Communion revere her as a saint, and the Lutheran Church commemorates her. Early life Sources agree that Helena was a Greek, probably from Asia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliny The Younger
Gaius Plinius Caecilius Secundus, born Gaius Caecilius or Gaius Caecilius Cilo (61 – c. 113), better known as Pliny the Younger (), was a lawyer, author, and magistrate of Ancient Rome. Pliny's uncle, Pliny the Elder, helped raise and educate him. Pliny the Younger wrote hundreds of letters, of which 247 survive, and which are of great historical value. Some are addressed to reigning emperors or to notables such as the historian Tacitus. Pliny served as an imperial magistrate under Trajan (reigned 98–117), and his letters to Trajan provide one of the few surviving records of the relationship between the imperial office and provincial governors. Pliny rose through a series of civil and military offices, the ''cursus honorum''. He was a friend of the historian Tacitus and might have employed the biographer Suetonius on his staff. Pliny also came into contact with other well-known men of the period, including the philosophers Artemidorus and Euphrates the Stoic, during his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |