|
Ellsworth Land
Ellsworth Land is a portion of the Antarctic continent bounded on the west by Marie Byrd Land, on the north by Bellingshausen Sea, on the northeast by the base of Antarctic Peninsula, and on the east by the western margin of the Filchner–Ronne Ice Shelf. It extends between 103°24'W and 79°45'W. The area west of 90°W is unclaimed, the area between 84°W and 90°W is claimed by Chile only, and the remainder by Chile and the United Kingdom as a part of the British Antarctic Territory. Eights Coast stretches between 103°24'W and 89°35'W, and Bryan Coast between 89°35'W and 79°45'W. It is largely a high ice plateau, but includes the Ellsworth Mountains and a number of scattered mountain groups: Hudson, Jones, Behrendt, Hauberg, Merrick, Sweeney and Scaife Mountains. This land lies near the center of the area traversed by American explorer Lincoln Ellsworth on an airplane flight during November–December 1935. It was named for him by the Advisory Committee on Antarc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
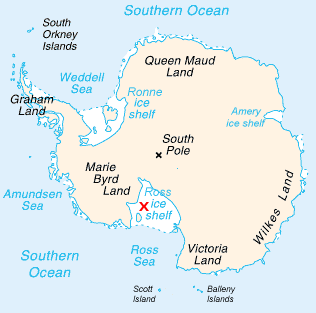
Antarctica And The Southern Ocean
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where veg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jones Mountains
The Jones Mountains are an isolated group of mountains, trending generally east–west for 43 km (27 mi), situated on the Eights Coast, Ellsworth Land, about 80 km (50 mi) south of Dustin Island in Antarctica. The charts of the USAS, 1939–41, show mountains in this approximate location and relationship to Dustin and Thurston Islands, indicating they were sighted in the flight from the ship ''Bear'', February 27, 1940. The mountains appear in distant air photos taken by US Navy Operation Highjump, December 30, 1946, and were observed from USN aircraft by Edward Thiel and J. Campbell Craddock, January 22, 1960. The naming was proposed by Thiel and Craddock after Dr. Thomas O. Jones (1908–93), American chemist; senior National Science Foundation, NSF official in charge of the U.S. Antarctic Research Program, 1958–78; Director, Division of Environmental Science, NSF, 1965–69; Deputy Assistant Director for National and International Programs, NSF, 1969–78. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ross Ice Shelf
The Ross Ice Shelf is the largest ice shelf of Antarctica (, an area of roughly and about across: about the size of France). It is several hundred metres thick. The nearly vertical ice front to the open sea is more than long, and between high above the water surface. Ninety percent of the floating ice, however, is below the water surface. Most of Ross Ice Shelf is in the Ross Dependency claimed by New Zealand. It floats in, and covers, a large southern portion of the Ross Sea and the entire Roosevelt Island located in the east of the Ross Sea. The ice shelf is named after Sir James Clark Ross, who discovered it on 28 January 1841. It was originally called "The Barrier", with various adjectives including "Great Ice Barrier", as it prevented sailing further south. Ross mapped the ice front eastward to 160° W. In 1947, the U.S. Board on Geographic Names applied the name "Ross Shelf Ice" to this feature and published it in the original U.S. Antarctic Gazetteer. In Ja ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dundee Island
Dundee Island is an ice-covered island lying east of the northeastern tip of Antarctic Peninsula and south of Joinville Island. It is named after the city of Dundee in Scotland. The Petrel Base is a scientific station in Antarctica belonging to Argentina. Its coordinates are 63 ° 28′S 56 ° 17′W and it is located on rocks at 18 meters above sea level at the foot of the Rosamaría glacier in the Petrel bay, the low point of Cape Welchness on Dundee Island in the Joinville archipelago. A 10-year plan began in 2013 to convert it into a permanent base. The base infrastructure has 3600 m² under roof, a 1200 m² logistics area and 25 beds. Account for transport: 2 Zodiac with outboard motor and 1 all-terrain truck of 1.5 ton. It is from this island that the American businessman Lincoln Ellsworth, accompanied by the pilot Herbert Hollick-Kenyon, took off on the 23 November 1935 for the first crossing of the Antarctic by plane. Nearby features The Eden Rocks, a designa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advisory Committee On Antarctic Names
The Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (ACAN or US-ACAN) is an advisory committee of the United States Board on Geographic Names responsible for recommending commemorative names for features in Antarctica. History The committee was established in 1943 as the Special Committee on Antarctic Names (SCAN). It became the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names in 1947. Fred G. Alberts was Secretary of the Committee from 1949 to 1980. By 1959, a structured nomenclature was reached, allowing for further exploration, structured mapping of the region and a unique naming system. A 1990 ACAN gazeeter of Antarctica listed 16,000 names. Description The United States does not recognise territorial boundaries within Antarctica, so ACAN assigns names to features anywhere within the continent, in consultation with other national nomenclature bodies where appropriate, as defined by the Antarctic Treaty System. The research and staff support for the ACAN is provided by the United States Geolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lincoln Ellsworth
Lincoln Ellsworth (May 12, 1880 – May 26, 1951) was a polar explorer from the United States and a major benefactor of the American Museum of Natural History. Biography Lincoln Ellsworth was born on May 12, 1880, to James Ellsworth and Eva Frances Butler in Chicago, Illinois. He also lived in Hudson, Ohio, as a child. He attended The Hill School and took two years longer than usual to graduate, before entering the Sheffield Scientific School at Yale University. His academic performance was poor, and he subsequently enrolled at Columbia University and McGill before ending his academic career. Lincoln Ellsworth's father, James, a wealthy coal man from the United States, spent US$100,000 to fund Roald Amundsen's 1925 attempt to fly from Svalbard to the North Pole. Amundsen, accompanied by Lincoln Ellsworth, pilot Hjalmar Riiser-Larsen, flight mechanic Karl Feucht and two other team members, set out in two Dornier Wal flying boats, the N24 and N25, in an attempted to reach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scaife Mountains
The Scaife Mountains () is a group of mountains rising west of Prehn Peninsula and between the Ketchum and Ueda glaciers, in Palmer Land, at the base of Antarctic Peninsula. Discovered by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition (RARE) under Finn Ronne, 1947–48, who named these mountains for Alan M. Scaife of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, a contributor to the expedition. List of mountains * Mount Brundage () is a mountain located 12 nautical miles (22 km) west-southwest of Mount Terwileger in the south part of the Scaife Mountains. Discovered by RARE who named it for Burr Brundage, United States Department of State, who assisted in making arrangements for the expedition. *Mount Macnowski () is a mountain in the northern part of the Scaife Mountains, about west-southwest of Schmitt Mesa, near the base of the Antarctic Peninsula. Discovered by RARE, and mapped by the United States Geological Survey from surveys and U.S. Navy air photos, 1961–67. The mountain was named by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sweeney Mountains
The Sweeney Mountains () is a group of mountains of moderate height and about extent, located north of the Hauberg Mountains in Palmer Land, Antarctica. Discovered by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition (RARE), 1947–48, under Finn Ronne, who named these mountains after Commander Edward C. Sweeney, a contributor to the expedition. __NOTOC__ List of mountains * Mount Edward – A prominent rock mountain located centrally along the southern margin of the range. It was discovered by RARE, who named this summit for Commander Edward C. Sweeney, USNR, a contributor to the expedition. * Hagerty Peak A peak in the southeast extremity of the range. Mapped by United States Geological Survey (USGS) from ground surveys and U.S. Navy air photos, 1961–67. Named by Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) for Cornelius J. Hagerty, photographer with the McMurdo Station McMurdo Station is a United States Antarctic research station on the south tip of Ross Island, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merrick Mountains
The Merrick Mountains () are a cluster of mountains, 13 km (8 mi) long, standing 11 km (7 mi) northeast of the Behrendt Mountains in Ellsworth Land, Antarctica. Discovered and photographed from the air by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition, 1947–1948, under Finn Ronne. Named by US-ACAN for Conrad G. Merrick, USGS topographic engineer with the Antarctic Peninsula Traverse Party, 1961–1962, who participated in the survey of these mountains. Features *Mount Becker *Mount Berger *Mount Boyer See also *Mount Wasilewski Mount Wasilewski () is a prominent isolated mountain (1,615 m) located 9 nautical miles (17 km) east-southeast of Merrick Mountains in Palmer Land. First seen and photographed from the air by Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition (RARE), 1947� ... References Mountain ranges of Ellsworth Land {{EllsworthLand-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hauberg Mountains
The Hauberg Mountains () are a group of mountains of about extent, located north of Cape Zumberge and south of the Sweeney Mountains in Palmer Land, Antarctica. Discovered by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition (RARE), 1947–48, led by Finn Ronne, and named by him for John Hauberg, of Rock Island, Illinois Rock Island is a city in and the county seat of Rock Island County, Illinois, Rock Island County, Illinois, United States. The original Rock Island, from which the city name is derived, is now called Rock Island Arsenal, Arsenal Island. The popul ..., a contributor to the expedition. References Mountain ranges of Palmer Land {{PalmerLand-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Behrendt Mountains
The Behrendt Mountains () is a group of mountains, 32 km (20 mi) long, aligned in the form of a horseshoe with the opening to the southwest, standing 11 km (7 mi) SW of Merrick Mountains at the base of the Antarctic Peninsula. Discovered and photographed from the air by the RARE, 1947–48, under Finn Ronne. Named by US-ACAN for John C. Behrendt, traverse seismologist at Ellsworth Station in 1957. Behrendt led the Antarctic Peninsula Traverse party to these mountains, summer 1961–62, and carried out investigations in Marie Byrd Land and the Pensacola Mountains in 1963-64 and 1965–66. See also * Mount Trimpi *Stanton Hills References * External links"IGY On the Ice" produced by Barbara Bogaev, ''Soundprint'', aired August 25, 2011 on Maine Public Broadcasting. Radio documentary includes interviews with Behrendt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hudson Mountains
The Hudson Mountains are a mountain range in western Ellsworth Land just east of Cranton Bay and Pine Island Bay at the eastern extremity of Amundsen Sea. They are of volcanic origin, consisting of low scattered mountains and nunataks that protrude through the West Antarctic Ice Sheet. The Hudson Mountains are bounded on the north by Cosgrove Ice Shelf and on the south by Pine Island Glacier. Geology The Hudson Mountains contain slightly eroded parasitic cones that overlie three extensively eroded Miocene stratovolcanoes: Mount Manthe, Teeters Nunatak and Mount Moses. Potential steam was reported in 1974 and an unconfirmed report of an eruption detected by satellite was made in 1985, indicating that the Hudson Mountains may be volcanically active. Volcanic activity of the Hudson Mountains has produced predominantly subaerial basaltic lava flows, although subglacial or subaqueous tuffs and lava flows have also been noted. A tephra layer deposited from a subglacial eruptio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |