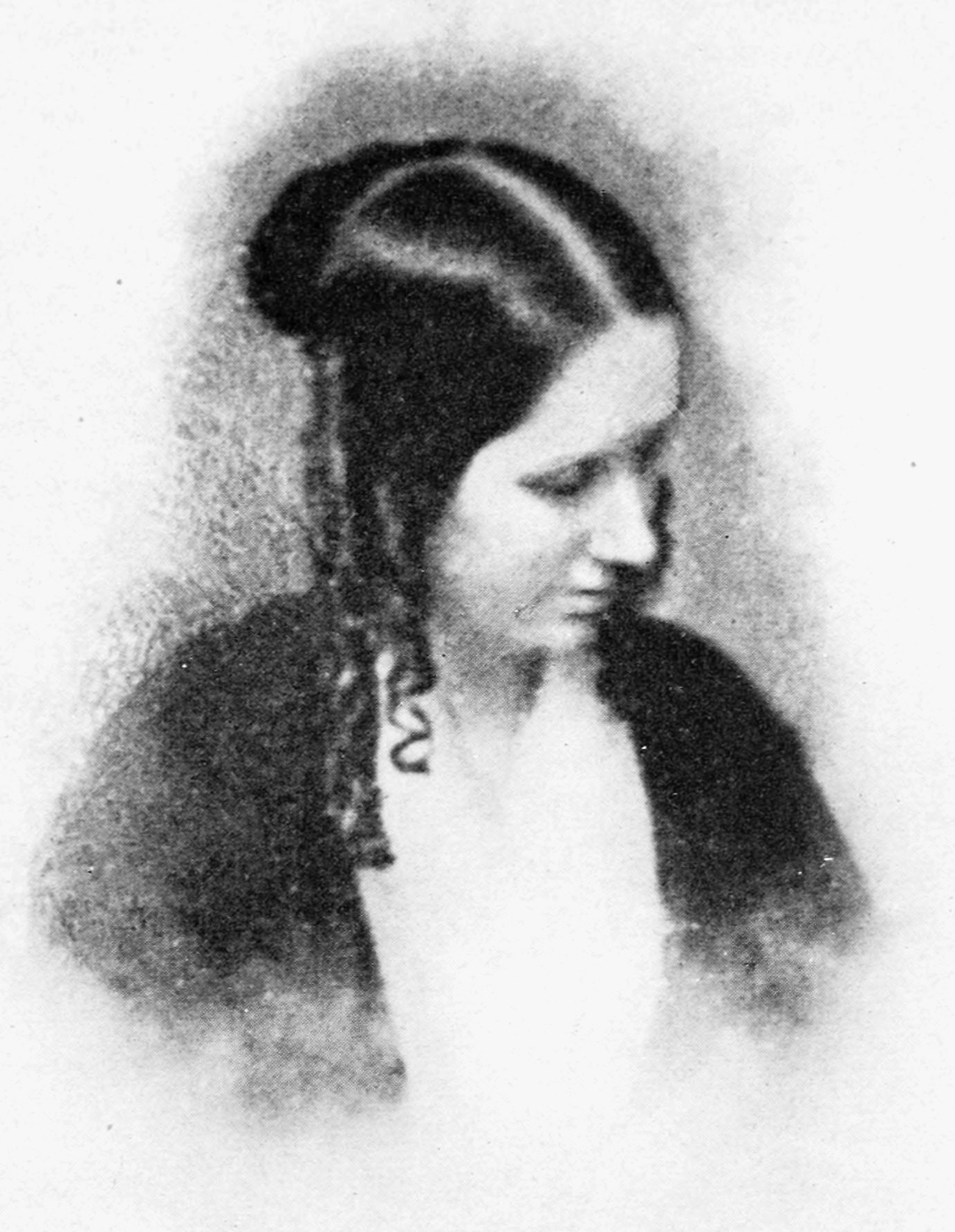|
Elizabeth Cabot Agassiz
Elizabeth Cabot Cary Agassiz (pseudonym, Actaea; December 5, 1822 – June 27, 1907) was an American educator, naturalist, writer, and the co-founder and first president of Radcliffe College. A researcher of natural history, she was an author and illustrator of natural history texts as well as a co-author of natural history texts with her husband, Louis Agassiz, and her stepson Alexander Agassiz. Agassiz accompanied her husband on his journey to Brazil in 1865-6 and on the Hassler expedition in 1871-2; of the second, she wrote an account for the '' Atlantic Monthly''. She published ''A First Lesson in Natural History'' (Boston, 1859) and edited ''Geological Sketches'' (1866). Early life and education Elizabeth Cabot Cary was born on December 5, 1822 into a Boston Brahmin family of New England ancestry. She was born at the house of her grandfather, Thomas Handasyd Perkins, on Pearl Street in Boston, Massachusetts. Her parents were Mary Ann Cushing Perkins Cary and Thomas Gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radcliffe College
Radcliffe College was a women's liberal arts college in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and functioned as the female coordinate institution for the all-male Harvard College. Considered founded in 1879, it was one of the Seven Sisters colleges and held the popular reputation of having a particularly intellectual, literary, and independent-minded female student body. Radcliffe conferred Radcliffe College diplomas on undergraduates and graduate students for approximately the first 70 years of its history. Beginning in 1963, it awarded joint Harvard-Radcliffe diplomas to undergraduates. In 1977 Radcliffe signed a formal "non-merger merger" agreement with Harvard and completed full integration with Harvard in 1999. Today, within Harvard University, Radcliffe's former administrative campus (Radcliffe Yard) is home to the Radcliffe Institute for Advanced Study. Former Radcliffe housing at the Radcliffe Quadrangle (Pforzheimer House, Cabot House, and Currier House) has been incorporated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hassler Expedition
The United States Coast Survey Schooner ''Hassler'' was the first iron-hulled steamship used in the service of the U.S. Coast Survey. Ship history Plans for a new ship to chart the waters of U.S. Pacific Coast were drawn up in early 1870 by Carlile Patterson, the Hydrographic Inspector of the U.S. Coast Survey. Patterson called for an iron-hulled ship of about 325 tons, with a draft of no more than and a top speed of . He required that the ship used no more than 2½ tons of coal per day, and could hold two months provisions for a crew of 37. The resulting ship was built in 1871 at the River Iron Works in Camden, New Jersey, under the supervision of John H. Dialogue. She was a three-masted schooner, equipped with a steeple compound engine, and cost $62,000 to build. In 1871-72 the ship sailed on the ''Hassler'' Expedition, under Commander Philip Carrigan Johnson, brother of the artist Eastman Johnson. This was the first important scientific expedition sent by the governme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Emanuel Agassiz
Alexander Emmanuel Rodolphe Agassiz (December 17, 1835March 27, 1910), son of Louis Agassiz and stepson of Elizabeth Cabot Agassiz, was an American scientist and engineer. Biography Agassiz was born in Neuchâtel, Switzerland and immigrated to the United States with his parents, Louis and Cecile (Braun) Agassiz, in 1846. He graduated from Harvard University in 1855, subsequently studying engineering and chemistry, and taking the degree of Bachelor of Science at the Lawrence Scientific School of the same institution in 1857; in 1859 became an assistant in the United States Coast Survey. Thenceforward he became a specialist in marine ichthyology. Agassiz was elected a Fellow of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences in 1862. Up until the summer of 1866, Agassiz worked as assistant curator in the museum of natural history that his father founded at Harvard. E. J. Hulbert, a friend of Agassiz's brother-in-law, Quincy Adams Shaw, had discovered a rich copper lode known as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perkins Institution For The Blind
Perkins School for the Blind, in Watertown, Massachusetts, was founded in 1829 and is the oldest school for the blind in the United States. It has also been known as the Perkins Institution for the Blind. Perkins manufactures its own Perkins Brailler, which is used to print embossed, tactile books for the blind; and the Perkins SMART Brailler, a braille teaching tool, at the Perkins Solutions division housed within the Watertown campus's former Howe Press. History Founded in 1829, Perkins was the first school for the blind established in the United States. The school was originally named the New England Asylum for the Blind and was incorporated on March 2, 1829. The name was eventually changed to Perkins School For the Blind. John Dix Fisher first considered the idea of a school for blind children based upon his visits to Paris at the National Institute for the Blind and was inspired to create such a school in Boston, but it was founded by Samuel Gridley Howe, who had also stu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harvard Annex
Radcliffe College was a women's liberal arts college in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and functioned as the female coordinate institution for the all-male Harvard College. Considered founded in 1879, it was one of the Seven Sisters colleges and held the popular reputation of having a particularly intellectual, literary, and independent-minded female student body. Radcliffe conferred Radcliffe College diplomas on undergraduates and graduate students for approximately the first 70 years of its history. Beginning in 1963, it awarded joint Harvard-Radcliffe diplomas to undergraduates. In 1977 Radcliffe signed a formal "non-merger merger" agreement with Harvard and completed full integration with Harvard in 1999. Today, within Harvard University, Radcliffe's former administrative campus (Radcliffe Yard) is home to the Radcliffe Institute for Advanced Study. Former Radcliffe housing at the Radcliffe Quadrangle (Pforzheimer House, Cabot House, and Currier House) has been incorporated i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maria Mitchell
Maria Mitchell ( /məˈraɪə/; August 1, 1818 – June 28, 1889) was an American astronomer, librarian, naturalist, and educator. In 1847, she discovered a comet named 1847 VI (modern designation C/1847 T1) that was later known as " Miss Mitchell's Comet" in her honor. She won a gold medal prize for her discovery, which was presented to her by King Christian VIII of Denmark in 1848. Mitchell was the first internationally known woman to work as both a professional astronomer and a professor of astronomy after accepting a position at Vassar College in 1865. She was also the first woman elected Fellow of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences and the American Association for the Advancement of Science. Early years (1818–1846) Maria Mitchell was born on August 1, 1818, on the island of Nantucket, Massachusetts, to Lydia Coleman Mitchell, a library worker, and William Mitchell, a schoolteacher and amateur astronomer. The third of ten children, Mitchell and her siblings w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mary Fairfax Somerville
Mary Somerville (; , formerly Greig; 26 December 1780 – 29 November 1872) was a Scottish scientist, writer, and polymath. She studied mathematics and astronomy, and in 1835 she and Caroline Herschel were elected as the first female Honorary Members of the Royal Astronomical Society. When John Stuart Mill organized a massive petition to Parliament to give women the right to vote, he made sure that the first signature on the petition would be Somerville's. In 1834 she became the first person to be described in print as a 'scientist'. When she died in 1872, ''The Morning Post'' declared in her obituary that "Whatever difficulty we might experience in the middle of the nineteenth century in choosing a king of science, there could be no question whatever as to the queen of science". Somerville College, a college of the University of Oxford, is named after her, reflecting the virtues of liberalism and academic success which the college wished to embody. She is featured on the fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Philosophical Society
The American Philosophical Society (APS), founded in 1743 in Philadelphia, is a scholarly organization that promotes knowledge in the sciences and humanities through research, professional meetings, publications, library resources, and community outreach. Considered the first learned society in the United States, it has about 1,000 elected members, and by April 2020 had had only 5,710 members since its creation. Through research grants, published journals, the American Philosophical Society Museum, an extensive library, and regular meetings, the society supports a variety of disciplines in the humanities and the sciences. Philosophical Hall, now a museum, is just east of Independence Hall in Independence National Historical Park; it was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1965. History The Philosophical Society, as it was originally called, was founded in 1743 by Benjamin Franklin, James Alexander (lawyer), James Alexander, Francis Hopkinson, John Bartram, Philip Syn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hassler
Hassler (also Haßler, Häßler, Hässler, Hasler, ...) is a toponymic surname derived from a number of places called Hasel or Hassel in German-speaking parts of Europe. Notable people with this name include: Musicians *A musical dynasty in Nuremberg **Isaak Hassler (c.1530 – 1591), organist and father of three brothers: ***Kasper Hassler (1562–1618), minor composer and publisher ***Hans Leo Hassler (1564–1612), an important German composer and organist ***Jakob Hassler (1569–1622), composer most noted for his keyboard works *Johann Wilhelm Hässler (1747–1822), German organist and composer Athletes *Nicole Hassler (1941–1996), French figure skater *Des Hasler (b. 1961), Australian rugby league footballer and coach *Thomas Häßler (b. 1966), former German football player and 1990 World Cup winner * Dominic Hassler (b. 1981), Austrian football player Other professions *Johann Hasler (b. 1548, died after 1602), Swiss theologian and physician *Ferdinand Rudolph Hass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meteorologist
A meteorologist is a scientist who studies and works in the field of meteorology aiming to understand or predict Earth's atmospheric phenomena including the weather. Those who study meteorological phenomena are meteorologists in research, while those using mathematical models and knowledge to prepare daily weather forecasts are called ''weather forecasters'' or ''operational meteorologists''. Meteorologists work in government agencies, private consulting and research services, industrial enterprises, utilities, radio and television stations, and in education. They are not to be confused with weather presenters, who present the weather forecast in the media and range in training from journalists having just minimal training in meteorology to full fledged meteorologists. Description Meteorologists study the Earth's atmosphere and its interactions with the Earth's surface, the oceans and the biosphere. Their knowledge of applied mathematics and physics allows them to understand the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geologist
A geologist is a scientist who studies the solid, liquid, and gaseous matter that constitutes Earth and other terrestrial planets, as well as the processes that shape them. Geologists usually study geology, earth science, or geophysics, although backgrounds in physics, chemistry, biology, and other sciences are also useful. Field research (field work) is an important component of geology, although many subdisciplines incorporate laboratory and digitalized work. Geologists can be classified in a larger group of scientists, called geoscientists. Geologists work in the energy and mining sectors searching for natural resources such as petroleum, natural gas, precious and base metals. They are also in the forefront of preventing and mitigating damage from natural hazards and disasters such as earthquakes, volcanoes, tsunamis and landslides. Their studies are used to warn the general public of the occurrence of these events. Geologists are also important contributors to climate ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arnold Guyot
Arnold Henry Guyot ( ) (September 28, 1807February 8, 1884) was a Swiss-American geologist and geographer. Early life Guyot was born on September 28, 1807, at Boudevilliers, near Neuchâtel, Switzerland. He was educated at Chaux-de-Fonds, then at the college of Neuchâtel. In 1825, he went to Germany and resided in Karlsruhe where he met Louis Agassiz, the beginning of a lifelong friendship. From Karlsruhe he moved to Stuttgart, where he studied at the gymnasium. He returned to Neuchâtel in 1827. He determined to enter the ministry and started at the University of Berlin to attend lectures. While pursuing his studies, he also attended lectures on philosophy and natural science. His leisure time was spent in collecting shells and plants, and he received an entrée to the Berlin Botanical Garden from Humboldt. In 1835, he received the degree of PhD from Berlin. Scientific career In 1838, at Agassiz's suggestion, he visited the Swiss glaciers and communicated the results of his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |