|
Eleutheroside A
Daucosterol (eleutheroside A) is a natural phytosterol-like compound. It is the glucoside of β-sitosterol β-sitosterol (beta-sitosterol) is one of several phytosterols (plant sterols) with chemical structures similar to that of cholesterol. It is a white, waxy powder with a characteristic odor, and is one of the components of the food additive E499. .... References {{steroid-stub Sterols Glucosides Saponins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eleutheroside
Eleutherosides are a diverse group of chemical compounds that were isolated from roots of the herb ''Eleutherococcus senticosus'' which is commercially offered mostly as extracts. Eleutheroside A is a saponin and sterol glycoside while other eleutherosides, such as eleutheroside B (syringin), are phenyl propanoid glycosides. They serve as marker compounds for the Thin layer chromatography identification of ''Eleutherococcus senticosus'' herbal preparations and dietary supplements. Eleutheroside E is an optical isomer of acanthoside D, which is one of the glycosides isolated from the cluster-flowering acanthopanax and represents the di-β-D-glucoside of (−)-syringaresinol Syringaresinol is a lignan found in ''Castela emoryi'', in ''Prunus mume''. This compound inhibits ''Helicobacter pylori'' motility ''in vitro ''In vitro'' (meaning in glass, or ''in the glass'') studies are performed with microorganisms, c ....Identity of eleutheroside E with acanthoside D. Yu. S. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytosterol
Phytosterols are phytosteroids, similar to cholesterol, that serve as structural components of biological membranes of plants. They encompass plant sterols and stanols. More than 250 sterols and related compounds have been identified. Free phytosterols extracted from oils are insoluble in water, relatively insoluble in oil, and soluble in alcohols. Phytosterol-enriched foods and dietary supplements have been marketed for decades. Despite well-documented LDL cholesterol-lowering effects from long-term consumption of phytosterols, there is insufficient evidence for an effect on cardiovascular diseases, fasting blood sugar, glycated hemoglobin, or overall mortality rate. Structure They have a fused polycyclic structure and vary in carbon side chains and / or presence or absence of a double bond (saturation). They are divided into 4,4-dimethyl phytosterols, 4-monomethyl phytosterols, and 4-desmethyl phytosterols based on the location of methyl groups at the carbon-4 position. St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucoside
A glucoside is a glycoside that is derived from glucose. Glucosides are common in plants, but rare in animals. Glucose is produced when a glucoside is hydrolysed by purely chemical means, or decomposed by fermentation or enzymes. The name was originally given to plant products of this nature, in which the other part of the molecule was, in the greater number of cases, an aromatic aldehydic or phenolic compound (exceptions are Jinigrin and Jalapin or Scammonin). It has now been extended to include synthetic ethers, such as those obtained by acting on alcoholic glucose solutions with hydrochloric acid, and also the polysaccharoses, e.g. cane sugar, which appear to be ethers also. Although glucose is the most common sugar present in glucosides, many are known which yield rhamnose or iso-dulcite; these may be termed pentosides. Much attention has been given to the non-sugar parts (aglyca) of the molecules; the constitutions of many have been determined, and the compounds synthesi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
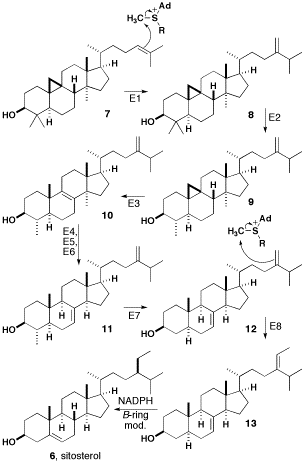
β-sitosterol
β-sitosterol (beta-sitosterol) is one of several phytosterols (plant sterols) with chemical structures similar to that of cholesterol. It is a white, waxy powder with a characteristic odor, and is one of the components of the food additive E499. Phytosterols are hydrophobic and soluble in alcohols. Natural occurrences and food β-sitosterol is widely distributed in the plant kingdom. It is found in vegetable oil, nuts, avocados, and derived prepared foods such as salad dressings. Human research β-sitosterol is being studied for its potential to reduce benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and blood cholesterol levels. Genetic disorder While plant sterols are usually beneficial, there is a rare autosomal recessive genetic disorder phytosterolemia which causes over-absorption of phytosterols. Precursor of anabolic steroid boldenone Being a steroid, β-sitosterol is a precursor of anabolic steroid boldenone. Boldenone undecylenate is commonly used in veterinary medicine to induce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sterols
Sterol is an organic compound with formula , whose molecule is derived from that of gonane by replacement of a hydrogen atom in position 3 by a hydroxyl group. It is therefore an alcohol of gonane. More generally, any compounds that contain the gonane structure, additional functional groups, and/or modified ring systems derived from gonane are called steroids. Therefore, sterols are a subgroup of the steroids. They occur naturally in most eukaryotes, including plants, animals, and fungi, and can also be produced by some bacteria (however likely with different functions). The most familiar type of animal sterol is cholesterol, which is vital to cell membrane structure, and functions as a precursor to fat-soluble vitamins and steroid hormones. While technically alcohols, sterols are classified by biochemists as lipids (fats in the broader sense of the term). Types Sterols of plants are called ''phytosterols'' and sterols of animals are called ''zoosterols''. The most important ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucosides
A glucoside is a glycoside that is derived from glucose. Glucosides are common in plants, but rare in animals. Glucose is produced when a glucoside is hydrolysed by purely chemical means, or decomposed by fermentation or enzymes. The name was originally given to plant products of this nature, in which the other part of the molecule was, in the greater number of cases, an aromatic aldehydic or phenolic compound (exceptions are Jinigrin and Jalapin or Scammonin). It has now been extended to include synthetic ethers, such as those obtained by acting on alcoholic glucose solutions with hydrochloric acid, and also the polysaccharoses, e.g. cane sugar, which appear to be ethers also. Although glucose is the most common sugar present in glucosides, many are known which yield rhamnose or iso-dulcite; these may be termed pentosides. Much attention has been given to the non-sugar parts (aglyca) of the molecules; the constitutions of many have been determined, and the compounds synthes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |