|
Elephant Butte Dike
Elephant Butte Dam or Elephant Butte Dike, originally Engle Dam, is a concrete gravity dam on the Rio Grande near Truth or Consequences, New Mexico. The dam impounds Elephant Butte Reservoir, which is used mainly for agriculture but also provides for recreation, hydroelectricity, and flood and sediment control. The construction of the dam has reduced the flow of the Rio Grande to a small stream for most of the year, with water being released only during the summer irrigation season or during times of exceptionally heavy snow melt. Etymology Elephant Butte is an exposed volcanic plug in Sierra County, New Mexico. The sides of the volcano have eroded away and left only the solidified butte-shaped core. It is now an island in the lake except at low-water levels, when it is connected to land by an isthmus. The butte was said to have the shape of an elephant lying on its side, and its name has been applied to the area since before the dam's construction. The nearby city of Elephan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elephant Butte, New Mexico
Elephant Butte is a city in Sierra County, New Mexico, United States, located near Elephant Butte Reservoir and Elephant Butte Lake State Park. The population was 1,431 at the time of the 2010 census. History Elephant Butte was named from Elephant Butte, a butte nearby thought to resemble an elephant. Geography Elephant Butte is located at (33.189809, -107.222873). According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of , all land. Government As of January 2022 the current mayor of Elephant Butte is Phillip Mortensen while John Mascaro serves as city manager. Demographics At the 2010 census there were 1,431 people in 772 households, including 464 families, in the city. The population density was 477.0 people per square mile. There were 1,316 housing units at an average density of 438.7 per square mile. The racial makeup of the city was 92.2% White, 0.3% African American, 0.9% Native American, 0.5% Asian, 2.9% from other races, and 3.2% from two or mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albuquerque, New Mexico
Albuquerque ( ; ), ; kee, Arawageeki; tow, Vakêêke; zun, Alo:ke:k'ya; apj, Gołgéeki'yé. abbreviated ABQ, is the most populous city in the U.S. state of New Mexico. Its nicknames, The Duke City and Burque, both reference its founding in 1706 as ''La Villa de Alburquerque'' by Nuevo México governor Francisco Cuervo y Valdés''.'' Named in honor of the Viceroy of New Spain, the 10th Duke of Alburquerque, the city was an outpost on El Camino Real linking Mexico City to the northernmost territories of New Spain. Located in the Albuquerque Basin, the city is flanked by the Sandia Mountains to the east and the West Mesa to the west, with the Rio Grande and bosque flowing from north-to-south. According to the 2020 census, Albuquerque had 564,559 residents, making it the 32nd-most populous city in the United States and the fourth largest in the Southwest. It is the principal city of the Albuquerque metropolitan area, which had 916,528 residents as of July 2020, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Historic Civil Engineering Landmark
__NOTOC__ The following is a list of Historic Civil Engineering Landmarks as designated by the American Society of Civil Engineers since it began the program in 1964. The designation is granted to projects, structures, and sites in the United States (National Historic Civil Engineering Landmarks) and the rest of the world (International Historic Civil Engineering Landmarks). As of 2019, there are over 280 landmarks that have been approved by the ASCE Board of Direction. Sections or chapters of the American Society of Civil Engineers may also designate state or local landmarks within their areas; those landmarks are not listed here. See also *[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, the Gaza Strip of Palestine and Israel to the northeast, the Red Sea to the east, Sudan to the south, and Libya to the west. The Gulf of Aqaba in the northeast separates Egypt from Jordan and Saudi Arabia. Cairo is the capital and largest city of Egypt, while Alexandria, the second-largest city, is an important industrial and tourist hub at the Mediterranean coast. At approximately 100 million inhabitants, Egypt is the 14th-most populated country in the world. Egypt has one of the longest histories of any country, tracing its heritage along the Nile Delta back to the 6th–4th millennia BCE. Considered a cradle of civilisation, Ancient Egypt saw some of the earliest developments of writing, agriculture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aswan Low Dam
The Aswan Low Dam or Old Aswan Dam is a gravity masonry buttress dam on the Nile River in Aswan, Egypt. The dam was built at the former first cataract of the Nile, and is located about 1000 km up-river and 690 km (direct distance) south-southeast of Cairo. When initially constructed between 1899 and 1902, nothing of its scale had ever been attempted; on completion, it was the largest masonry dam in the world. The dam was designed to provide storage of annual floodwater and augment dry season flows to support greater irrigation development and population growth in the lower Nile. The dam, originally limited in height by conservation concerns, worked as designed, but provided inadequate storage capacity for planned development and was raised twice, between 1907 and 1912 and again in 1929–1933. These heightenings still did not meet irrigation demands and in 1946 it was nearly over-topped in an effort to maximize pool elevation. This led to the investigation and construct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elephant Butte Dam LCCN2008676677
Elephants are the largest existing land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant, the African forest elephant, and the Asian elephant. They are the only surviving members of the family Elephantidae and the order Proboscidea. The order was formerly much more diverse during the Pleistocene, but most species became extinct during the Late Pleistocene epoch. Distinctive features of elephants include a long proboscis called a trunk, tusks, large ear flaps, pillar-like legs, and tough but sensitive skin. The trunk is used for breathing, bringing food and water to the mouth, and grasping objects. Tusks, which are derived from the incisor teeth, serve both as weapons and as tools for moving objects and digging. The large ear flaps assist in maintaining a constant body temperature as well as in communication. African elephants have larger ears and concave backs, whereas Asian elephants have smaller ears, and convex or level backs. Elephants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mexicans
Mexicans ( es, mexicanos) are the citizens of the United Mexican States. The most spoken language by Mexicans is Spanish, but some may also speak languages from 68 different Indigenous linguistic groups and other languages brought to Mexico by recent immigration or learned by Mexican expats residing in other countries. In 2015, 21.5% of Mexico's population self-identified as being Indigenous. There are about 12 million Mexican nationals residing outside Mexico, with about 11.7 million living in the United States. The larger Mexican diaspora can also include individuals that trace ancestry to Mexico and self-identify as Mexican yet are not necessarily Mexican by citizenship, culture or language. The United States has the largest Mexican population after Mexico in the world at 37,186,361 (2019). The modern nation of Mexico achieved independence from the Spanish Empire in 1821, after a decade long war for independence starting in 1810; this began the process of forging a n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rio Grande Project
The Rio Grande Project is a United States Bureau of Reclamation irrigation, hydroelectricity, flood control, and interbasin water transfer project serving the upper Rio Grande basin in the southwestern United States. The project irrigates along the river in the states of New Mexico and Texas. Approximately 60 percent of this land is in New Mexico. Some water is also allotted to Mexico to irrigate some on the south side of the river. The project was authorized in 1905, but its final features were not implemented until the early 1950s. The project consists of two large storage dams, 6 small diversion dams, two flood-control dams, of canals and their branches and of drainage channels and pipes. A small hydroelectric plant at one of the project's dams also supplies electricity to the region. History Long before Texas was a state, the Pueblo Indians used the waters of the Rio Grande with simple irrigation systems that were noted by the Spanish in the 16th century while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Park Service
The National Park Service (NPS) is an agency of the United States federal government within the U.S. Department of the Interior that manages all national parks, most national monuments, and other natural, historical, and recreational properties with various title designations. The U.S. Congress created the agency on August 25, 1916, through the National Park Service Organic Act. It is headquartered in Washington, D.C., within the main headquarters of the Department of the Interior. The NPS employs approximately 20,000 people in 423 individual units covering over 85 million acres in all 50 states, the District of Columbia, and US territories. As of 2019, they had more than 279,000 volunteers. The agency is charged with a dual role of preserving the ecological and historical integrity of the places entrusted to its management while also making them available and accessible for public use and enjoyment. History Yellowstone National Park was created as the first nationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convention Providing For The Equitable Distribution Of Waters Of The Rio Grande For Irrigation Purposes
The International Boundary and Water Commission ( es, links=no, Comisión Internacional de Límites y Aguas) is an international body created by the United States and Mexico in 1889 to apply the rules for determining the location of their international boundary when meandering rivers transferred tracts of land from one bank to the other, as established under the Convention of November 12, 1884. The organization was created as the International Boundary Commission by the Convention of 1889 between the United States and Mexico. It was given its present name under the 1944 "Treaty relating to the Utilization of Waters of the Colorado and Tijuana Rivers and of the Rio Grande". Under these agreements, the IBWC has a U.S. section and a Mexican section, headquartered in the adjoining cities of El Paso, Texas, and Ciudad Juárez, Chihuahua. The U.S. section is administered by the Department of State, and the Mexican part by the Secretariat of Foreign Relations. Administration So ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesilla Valley
The Mesilla Valley is a geographic feature of Southern New Mexico and far West Texas. It was formed by repeated heavy spring floods of the Rio Grande. Background The fertile Mesilla Valley extends from Radium Springs, New Mexico, to the west side of El Paso, Texas. The valley is characterized by its few remaining bosques, as well as its native cottonwood trees, and increasingly, by invasive tamarisk, which was introduced in the late 19th century, and is known locally as ''salt cedar''. Due to the fertile nature of the valley, agriculture is a very important activity in this area. Stahmann Farms owns the world's largest pecan orchard, located south of the city of Las Cruces, New Mexico. Alfalfa, cotton, chile, onions and corn are other important cash crops grown in the Mesilla Valley. The Mesilla Valley is also known for its wine-producing capabilities, which originated with the Spanish exploration into New Mexico. It was part of Mexico until Gadsden Purchase The Gadsden P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
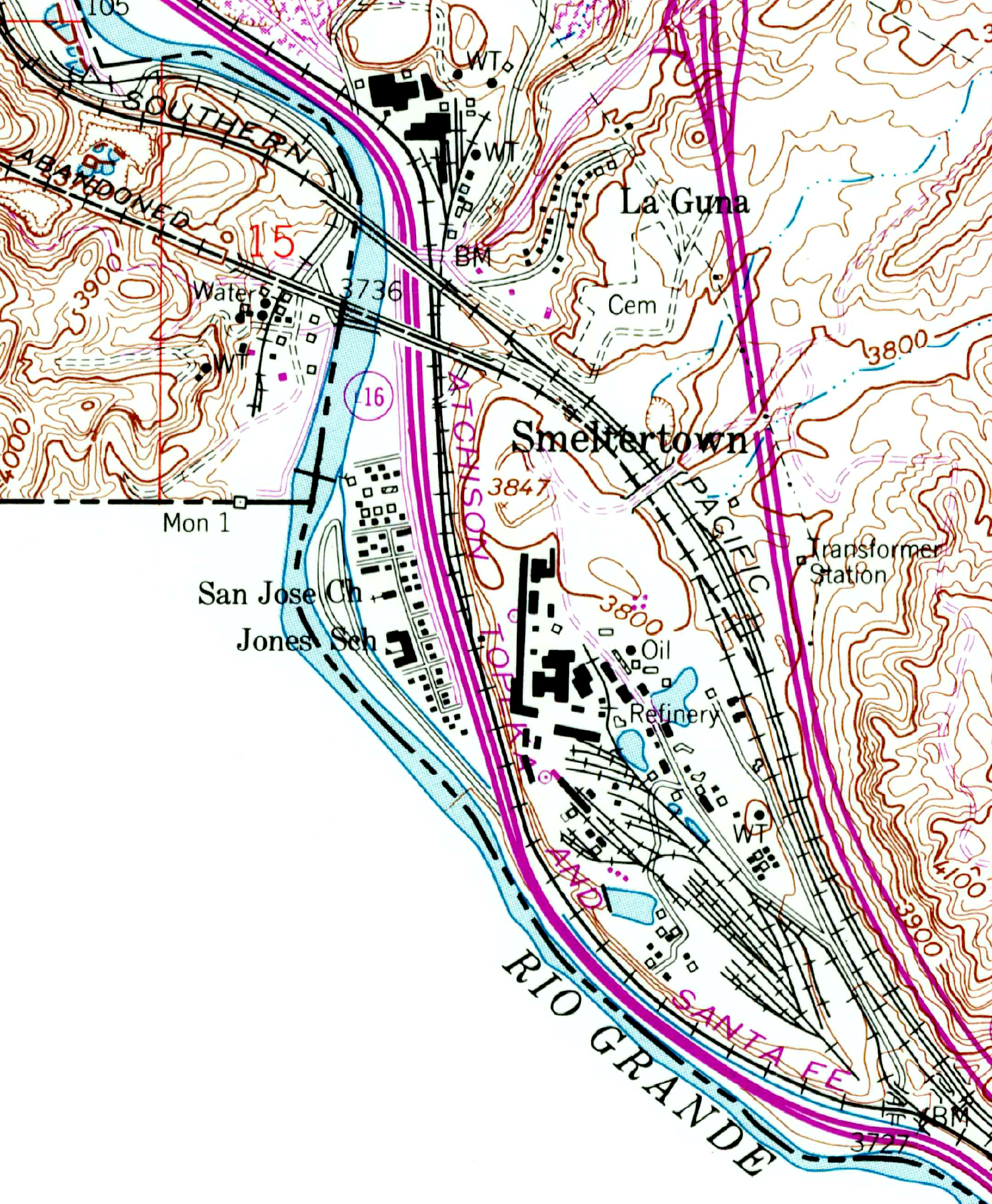
Smeltertown
Smeltertown was a residential community in El Paso County, Texas, housing the workers of the ASARCO smelter and their families, between El Paso and the Texas borders with Mexico and New Mexico. With only one small neighborhood, now known as the La Calavera Historical Neighborhood, remaining since the Smelter's closure, Smeltertown is sometimes referred to as a ghost town. The Smeltertown community was served by the San Jose church, and by the Jones School of the El Paso Independent School District. File:American Dam and Canal at Smeltertown El Paso Texas.jpg, Abandoned baja part of Smeltertown is left of center here, with the American Dam Headquarters (white building) in it, near the American Dam on the Rio Grande, in this aerial view from over downtown El Paso. La Calavera is at upper right. File:La Calavera Historic Neighborhood.jpg, Looking down into La Calavera Historic Neighborhood from beside Executive Center Blvd. File:Smeltertown cemetery adapted from NARA 545363.jp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)

_colourised.png)