|
Electronic Filter
Electronic filters are a type of signal processing filter in the form of electrical circuits. This article covers those filters consisting of lumped electronic components, as opposed to distributed-element filters. That is, using components and interconnections that, in analysis, can be considered to exist at a single point. These components can be in discrete packages or part of an integrated circuit. Electronic filters remove unwanted frequency components from the applied signal, enhance wanted ones, or both. They can be: * passive or active *analog or digital * high-pass, low-pass, band-pass, band-stop (band-rejection; notch), or all-pass. * discrete-time (sampled) or continuous-time *linear or non-linear * infinite impulse response (IIR type) or finite impulse response (FIR type) The most common types of electronic filters are linear filters, regardless of other aspects of their design. See the article on linear filters for details on their design and anal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-linear Filter
In signal processing, a nonlinear (or non-linear) filter is a filter whose output is not a linear function of its input. That is, if the filter outputs signals ''R'' and ''S'' for two input signals ''r'' and ''s'' separately, but does not always output ''αR'' + ''βS'' when the input is a linear combination ''αr'' + ''βs''. Both continuous-domain and discrete-domain filters may be nonlinear. A simple example of the former would be an electrical device whose output voltage ''R''(''t'') at any moment is the square of the input voltage ''r''(''t''); or which is the input clipped to a fixed range 'a'',''b'' namely ''R''(''t'') = max(''a'', min(''b'', ''r''(''t''))). An important example of the latter is the running-median filter, such that every output sample ''R''''i'' is the median of the last three input samples ''r''''i'', ''r''''i''−1, ''r''''i''−2. Like linear filters, nonlinear filters may be shift invariant or not. Non-linear filters h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image Parameter Filter
A composite image filter is an electronic filter consisting of multiple image filter sections of two or more different types. The image method of filter design determines the properties of filter sections by calculating the properties they have in an infinite chain of such sections. In this, the analysis parallels transmission line theory on which it is based. Filters designed by this method are called ''image parameter filters'', or just ''image filters''. An important parameter of image filters is their image impedance, the impedance of an infinite chain of identical sections. The basic sections are arranged into a ladder network of several sections, the number of sections required is mostly determined by the amount of stopband rejection required. In its simplest form, the filter can consist entirely of identical sections. However, it is more usual to use a composite filter of two or three different types of section to improve different parameters best addressed by a part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otto Zobel
Otto Julius Zobel (October 20, 1887 – January 1970) was an electrical engineer who worked for the American Telephone & Telegraph Company (AT&T) in the early part of the 20th century. Zobel's work on filter design was revolutionary and led, in conjunction with the work of John R. Carson, to significant commercial advances for AT&T in the field of frequency-division multiplex (FDM) telephone transmissions.Bray, p. 62. Although much of Zobel's work has been superseded by more modern filter designs, it remains the basis of filter theory and his papers are still referenced today. Zobel invented the m-derived filterWhite, G"The Past" ''BT Technology Journal'', Vol 18, No 1, pp. 107–132, January 2000 . and the constant-resistance filter,Zobel, O J, ''Distortion Compensator'', , filed 26 June 1924, issued 12 Feb 1929. which remains in use. Zobel and Carson helped to establish the nature of noise in electric circuits, concluding that—contrary to mainstream belief—it is not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmission Line
In electrical engineering, a transmission line is a specialized cable or other structure designed to conduct electromagnetic waves in a contained manner. The term applies when the conductors are long enough that the wave nature of the transmission must be taken into account. This applies especially to radio-frequency engineering because the short wavelengths mean that wave phenomena arise over very short distances (this can be as short as millimetres depending on frequency). However, the theory of transmission lines was historically developed to explain phenomena on very long telegraph lines, especially submarine telegraph cables. Transmission lines are used for purposes such as connecting radio transmitters and receivers with their antennas (they are then called feed lines or feeders), distributing cable television signals, trunklines routing calls between telephone switching centres, computer network connections and high speed computer data buses. RF engineers co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Ashley Campbell
George Ashley Campbell (November 27, 1870 – November 10, 1954) was an American engineer. He was a pioneer in developing and applying quantitative mathematical methods to the problems of long-distance telegraphy and telephony. His most important contributions were to the theory and implementation of the use of loading coils and the first wave filters designed to what was to become known as the image method. Both these areas of work resulted in important economic advantages for the American Telephone and Telegraph Company (AT&T). Education Campbell was educated at the McCollom Institute in New Hampshire and then at MIT, where he graduated in 1891. He then received a master's degree from Harvard University in 1893. He was awarded a fellowship which enabled him to spend three years on graduate work; one year studying advanced mathematics under Felix Klein at Göttingen, one year studying electricity and mechanics under Ludwig Boltzmann in Vienna, and one year studying under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constant K Filter
Constant k filters, also k-type filters, are a type of electronic filter designed using the image method. They are the original and simplest filters produced by this methodology and consist of a ladder network of identical sections of passive components. Historically, they are the first filters that could approach the ideal filter frequency response to within any prescribed limit with the addition of a sufficient number of sections. However, they are rarely considered for a modern design, the principles behind them having been superseded by other methodologies which are more accurate in their prediction of filter response. History Constant k filters were invented by George Campbell. He published his work in 1922, but had clearly invented the filters some time before, as his colleague at AT&T Co, Otto Zobel, was already making improvements to the design at this time. Campbell's filters were far superior to the simpler single element circuits that had been used previously. C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transition Band
The transition band, also called the skirt, is a range of frequencies that allows a transition between a passband and a stopband of a signal processing filter. The transition band is defined by a passband and a stopband cutoff frequency or corner frequency. This is the area between where a filter "turns the corner" and where it "hits the bottom". An example of this can be taken from a low-pass filter, commonly used in audio systems to allow the bass signal to pass through to a subwoofer, and cut out all unwanted frequencies above a defined point. If the cutoff point for such a filter is defined as 200 Hz, then in a perfect system, all frequencies above 200 Hz will be stopped and all frequencies below 200 Hz will be allowed to pass through. The transition band can be implemented to allow for a smooth fall off to avoid introducing audible peaks in amplitude. If the transition band of the example 200 Hz filter is 20 Hz, then the signal should start attenuati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pole (complex Analysis)
In complex analysis (a branch of mathematics), a pole is a certain type of singularity of a complex-valued function of a complex variable. In some sense, it is the simplest type of singularity. Technically, a point is a pole of a function if it is a zero of the function and is holomorphic in some neighbourhood of (that is, complex differentiable in a neighbourhood of ). A function is meromorphic in an open set if for every point of there is a neighborhood of in which either or is holomorphic. If is meromorphic in , then a zero of is a pole of , and a pole of is a zero of . This induces a duality between ''zeros'' and ''poles'', that is fundamental for the study of meromorphic functions. For example, if a function is meromorphic on the whole complex plane plus the point at infinity, then the sum of the multiplicities of its poles equals the sum of the multiplicities of its zeros. Definitions A function of a complex variable is holomorphic in an op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inductor
An inductor, also called a coil, choke, or reactor, is a passive two-terminal electrical component that stores energy in a magnetic field when electric current flows through it. An inductor typically consists of an insulated wire wound into a coil. When the current flowing through the coil changes, the time-varying magnetic field induces an electromotive force (''emf'') (voltage) in the conductor, described by Faraday's law of induction. According to Lenz's law, the induced voltage has a polarity (direction) which opposes the change in current that created it. As a result, inductors oppose any changes in current through them. An inductor is characterized by its inductance, which is the ratio of the voltage to the rate of change of current. In the International System of Units (SI), the unit of inductance is the henry (H) named for 19th century American scientist Joseph Henry. In the measurement of magnetic circuits, it is equivalent to . Inductors have values that typical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capacitor
A capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy in an electric field by virtue of accumulating electric charges on two close surfaces insulated from each other. It is a passive electronic component with two terminals. The effect of a capacitor is known as capacitance. While some capacitance exists between any two electrical conductors in proximity in a circuit, a capacitor is a component designed to add capacitance to a circuit. The capacitor was originally known as the condenser, a term still encountered in a few compound names, such as the '' condenser microphone''. The physical form and construction of practical capacitors vary widely and many types of capacitor are in common use. Most capacitors contain at least two electrical conductors often in the form of metallic plates or surfaces separated by a dielectric medium. A conductor may be a foil, thin film, sintered bead of metal, or an electrolyte. The nonconducting dielectric acts to increase the capacitor's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
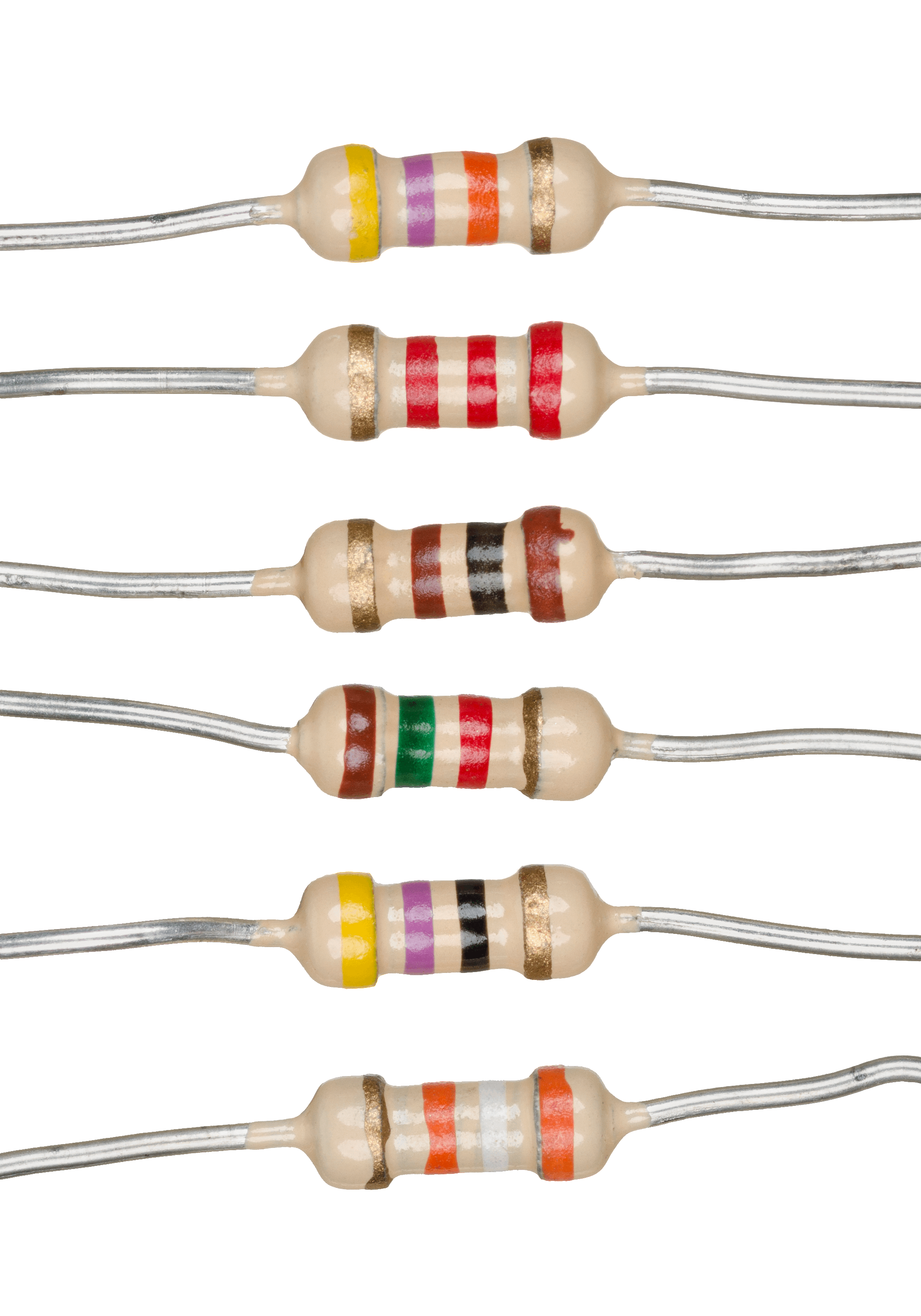
Resistors
A resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. In electronic circuits, resistors are used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, to divide voltages, bias active elements, and terminate transmission lines, among other uses. High-power resistors that can dissipate many watts of electrical power as heat may be used as part of motor controls, in power distribution systems, or as test loads for generators. Fixed resistors have resistances that only change slightly with temperature, time or operating voltage. Variable resistors can be used to adjust circuit elements (such as a volume control or a lamp dimmer), or as sensing devices for heat, light, humidity, force, or chemical activity. Resistors are common elements of electrical networks and electronic circuits and are ubiquitous in electronic equipment. Practical resistors as discrete components can be composed of various compounds and forms. Resis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)