|
Electromagnetic Articulography
Electromagnetic articulography (EMA) is a method of measuring the position of parts of the mouth. EMA uses sensor coils placed on the tongue and other parts of the mouth to measure their position and movement over time during speech and swallowing. Induction coils around the head produce an electromagnetic field that creates, or induces, a current in the sensors in the mouth. Because the current induced is inversely proportional to the cube of the distance, a computer is able to analyse the current produced and determine the sensor coil's location in space. EMA is used in linguistics and speech pathology to study articulation and in medicine to study oropharyngeal dysphagia. Other methods have been used to study articulation and ingestion with tradeoffs in the kind and amount of data available. Palatography allows the study of articulations that make contact with the palate such as some lingual consonants, but unlike EMA, palatographs cannot provide data on sounds which do no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trumpet Triple Tonguing Visualisation
The trumpet is a brass instrument commonly used in classical and jazz ensembles. The trumpet group ranges from the piccolo trumpet—with the highest register in the brass family—to the bass trumpet, pitched one octave below the standard B or C trumpet. Trumpet-like instruments have historically been used as signaling devices in battle or hunting, with examples dating back to at least 1500 BC. They began to be used as musical instruments only in the late 14th or early 15th century. Trumpets are used in art music styles, for instance in orchestras, concert bands, and jazz ensembles, as well as in popular music. They are played by blowing air through nearly-closed lips (called the player's embouchure), producing a "buzzing" sound that starts a standing wave vibration in the air column inside the instrument. Since the late 15th century, trumpets have primarily been constructed of brass tubing, usually bent twice into a rounded rectangular shape. There are many distinct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Wisconsin
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United States, the designation is reserved for colleges that have a graduate school. The word ''university'' is derived from the Latin ''universitas magistrorum et scholarium'', which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". The first universities were created in Europe by Catholic Church monks. The University of Bologna (''Università di Bologna''), founded in 1088, is the first university in the sense of: *Being a high degree-awarding institute. *Having independence from the ecclesiastic schools, although conducted by both clergy and non-clergy. *Using the word ''universitas'' (which was coined at its foundation). *Issuing secular and non-secular degrees: grammar, rhetoric, logic, theology, canon law, notarial law.Hunt Janin: "The university ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz ( to ) and energies in the range 145 eV to 124 keV. X-ray wavelengths are shorter than those of UV rays and typically longer than those of gamma rays. In many languages, X-radiation is referred to as Röntgen radiation, after the German scientist Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, who discovered it on November 8, 1895. He named it ''X-radiation'' to signify an unknown type of radiation.Novelline, Robert (1997). ''Squire's Fundamentals of Radiology''. Harvard University Press. 5th edition. . Spellings of ''X-ray(s)'' in English include the variants ''x-ray(s)'', ''xray(s)'', and ''X ray(s)''. The most familiar use of X-rays is checking for fractures (broken bones), but X-rays are also used in other ways. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulmonary Aspiration
Pulmonary aspiration is the entry of material such as pharyngeal secretions, food or drink, or stomach contents from the oropharynx or gastrointestinal tract, into the larynx (voice box) and lower respiratory tract, the portions of the respiratory system from the trachea (windpipe) to the lungs. A person may inhale the material, or it may be delivered into the tracheobronchial tree during positive pressure ventilation. When pulmonary aspiration occurs during eating and drinking, the aspirated material is often colloquially referred to as "going down the wrong pipe". Consequences of pulmonary aspiration range from no injury at all, to chemical pneumonitis or pneumonia, to death within minutes from asphyxiation. These consequences depend on the volume, chemical composition, particle size, and presence of infectious agents in the aspirated material, and on the underlying health status of the person. In healthy people, aspiration of small quantities of material is common and rarel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oropharyngeal Dysphagia
Oropharyngeal dysphagia arises from abnormalities of muscles, nerves or structures of the oral cavity, pharynx, and upper esophageal sphincter. Signs and symptoms Some signs and symptoms of swallowing difficulties include difficulty controlling food in the mouth, inability to control food or saliva in the mouth, difficulty initiating a swallow, coughing, choking, frequent pneumonia, unexplained weight loss, gurgly or wet voice after swallowing, nasal regurgitation, and dysphagia (patient complaint of swallowing difficulty). Other symptoms include drooling, dysarthria, dysphonia, aspiration pneumonia, depression, or nasopharyngeal regurgitation as associated symptoms. When asked where the food is getting stuck patients will often point to the cervical (neck) region as the site of the obstruction. Complications If left untreated, swallowing disorders can potentially cause aspiration pneumonia, malnutrition, or dehydration. Diagnosis Oropharyngeal dysphagia is going to be suspected ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vowels
A vowel is a syllabic speech sound pronounced without any stricture in the vocal tract. Vowels are one of the two principal classes of speech sounds, the other being the consonant. Vowels vary in quality, in loudness and also in quantity (length). They are usually voiced and are closely involved in prosodic variation such as tone, intonation and stress. The word ''vowel'' comes from the Latin word , meaning "vocal" (i.e. relating to the voice). In English, the word ''vowel'' is commonly used to refer both to vowel sounds and to the written symbols that represent them (a, e, i, o, u, and sometimes y). Definition There are two complementary definitions of vowel, one phonetic and the other phonological. *In the phonetic definition, a vowel is a sound, such as the English "ah" or "oh" , produced with an open vocal tract; it is median (the air escapes along the middle of the tongue), oral (at least some of the airflow must escape through the mouth), frictionless and continuant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
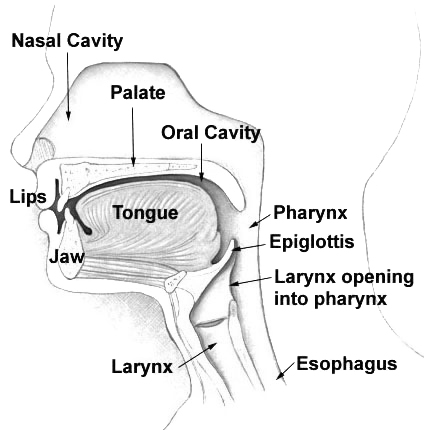
Palate
The palate () is the roof of the mouth in humans and other mammals. It separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity. A similar structure is found in crocodilians, but in most other tetrapods, the oral and nasal cavities are not truly separated. The palate is divided into two parts, the anterior, bony hard palate and the posterior, fleshy soft palate (or velum). Structure Innervation The maxillary nerve branch of the trigeminal nerve supplies sensory innervation to the palate. Development The hard palate forms before birth. Variation If the fusion is incomplete, a cleft palate results. Function When functioning in conjunction with other parts of the mouth, the palate produces certain sounds, particularly velar, palatal, palatalized, postalveolar, alveolopalatal, and uvular consonants. History Etymology The English synonyms palate and palatum, and also the related adjective palatine (as in palatine bone), are all from the Latin ''palatum'' via Old French ''palat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electropalatography
Electropalatography (EPG) is a technique used to monitor contacts between the tongue and hard palate, particularly during articulation and speech. A custom-made artificial palate is moulded to fit against a speaker's hard palate. The artificial palate contains electrodes exposed to the lingual surface. When contact occurs between the tongue surface and any of the electrodes, particularly between the lateral margins of the tongue and the borders of the hard palate, electronic signals are sent to an external processing unit. EPG provides dynamic real-time visual feedback of the location and timing of tongue contacts with the hard palate. This procedure can record details of tongue activity during speech. It can provide direct articulatory information that children can use in therapy to monitor and improve their articulation patterns. Visual feedback is very important in the success of treating deaf children. History Electropalatography was originally conceptualized and developed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palatography
Palatography is a technique used to identify which parts of the mouth are used when making different sounds. This technique is often used by linguists doing field work on little-known natural languages. A record made through palatography is called a '' palatogram''. It involves painting a coloring agent, such as a dye or a mixture of charcoal and olive oil on the tongue or the roof of a person's mouth and having that person pronounce a specific sound. A photograph is then made of the mouth roof and tongue in order to determine how the sound was articulated. The technique can also be performed electronically ( electropalatography) using a tool called a pseudo-palate, which consists of a retainer-like plate lined with electrodes that is placed on the roof of the mouth while the speaker pronounces a sound. See also * Articulatory phonetics The field of articulatory phonetics is a subfield of phonetics that studies articulation and ways that humans produce speech. Articula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tesla (unit)
The tesla (symbol: T) is the unit of magnetic flux density (also called magnetic B-field strength) in the International System of Units (SI). One tesla is equal to one weber per square metre. The unit was announced during the General Conference on Weights and Measures in 1960 and is named in honour of Serbian-American electrical and mechanical engineer Nikola Tesla, upon the proposal of the Slovenian electrical engineer France Avčin. Definition A particle, carrying a charge of one coulomb (C), and moving perpendicularly through a magnetic field of one tesla, at a speed of one metre per second (m/s), experiences a force with magnitude one newton (N), according to the Lorentz force law. That is, : \text = \dfrac. As an SI derived unit, the tesla can also be expressed in terms of other units. For example, a magnetic flux of 1 weber (Wb) through a surface of one square meter is equal to a magnetic flux density of 1 tesla.''The International System of Units (SI), 8th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dipoles
In physics, a dipole () is an electromagnetic phenomenon which occurs in two ways: *An electric dipole deals with the separation of the positive and negative electric charges found in any electromagnetic system. A simple example of this system is a pair of charges of equal magnitude but opposite sign separated by some typically small distance. (A permanent electric dipole is called an electret.) *A magnetic dipole is the closed circulation of an electric current system. A simple example is a single loop of wire with constant current through it. A bar magnet is an example of a magnet with a permanent magnetic dipole moment. Dipoles, whether electric or magnetic, can be characterized by their dipole moment, a vector quantity. For the simple electric dipole, the electric dipole moment points from the negative charge towards the positive charge, and has a magnitude equal to the strength of each charge times the separation between the charges. (To be precise: for the definition of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |