|
Electrochemical Quartz Crystal Microbalance
Electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance (EQCM) is the combination of electrochemistry and quartz crystal microbalance, which was generated in the eighties. Typically, an EQCM device contains an electrochemical cells part and a QCM part. Two electrodes on both sides of the quartz crystal serve two purposes. Firstly, an alternating electric field is generated between the two electrodes for making up the oscillator. Secondly, the electrode contacting electrolyte is used as a working electrode (WE), together with a counter electrode (CE) and a reference electrode (RE), in the potentiostatic circuit constituting the electrochemistry cell. Thus, the working electrode of electrochemistry cell is the sensor of QCM. As a high mass sensitive in-situ measurement, EQCM is suitable to monitor the dynamic response of reactions at the electrode–solution interface at the applied potential. When the potential of a QCM metal electrode changes, a negative or positive mass change is monitored d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electro-impedance Spectroscopy
Dielectric spectroscopy (which falls in a subcategory of impedance spectroscopy) measures the dielectric properties of a medium as a function of frequency.Kremer F., Schonhals A., Luck W. Broadband Dielectric Spectroscopy. – Springer-Verlag, 2002. It is based on the interaction of an external field with the electric dipole moment of the sample, often expressed by permittivity. It is also an experimental method of characterizing electrochemical systems. This technique measures the impedance of a system over a range of frequencies, and therefore the frequency response of the system, including the energy storage and dissipation properties, is revealed. Often, data obtained by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) is expressed graphically in a Bode plot or a Nyquist plot. Impedance is the opposition to the flow of alternating current (AC) in a complex system. A passive complex electrical system comprises both energy dissipater (resistor) and energy storage ( capacitor) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Paramagnetic Resonance
Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) or electron spin resonance (ESR) spectroscopy is a method for studying materials that have unpaired electrons. The basic concepts of EPR are analogous to those of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), but the spins excited are those of the electrons instead of the atomic nuclei. EPR spectroscopy is particularly useful for studying metal complexes and organic radicals. EPR was first observed in Kazan State University by Soviet physicist Yevgeny Zavoisky in 1944, and was developed independently at the same time by Brebis Bleaney at the University of Oxford. Theory Origin of an EPR signal Every electron has a magnetic moment and spin quantum number s = \tfrac , with magnetic components m_\mathrm = + \tfrac or m_\mathrm = - \tfrac . In the presence of an external magnetic field with strength B_\mathrm , the electron's magnetic moment aligns itself either antiparallel ( m_\mathrm = - \tfrac ) or parallel ( m_\mathrm = + \tfrac ) to the fie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetonitrile
Acetonitrile, often abbreviated MeCN (methyl cyanide), is the chemical compound with the formula and structure . This colourless liquid is the simplest organic nitrile (hydrogen cyanide is a simpler nitrile, but the cyanide anion is not classed as organic). It is produced mainly as a byproduct of acrylonitrile manufacture. It is used as a polar aprotic solvent in organic synthesis and in the purification of butadiene. The skeleton is linear with a short distance of 1.16 Å. Acetonitrile was first prepared in 1847 by the French chemist Jean-Baptiste Dumas. Applications Acetonitrile is used mainly as a solvent in the purification of butadiene in refineries. Specifically, acetonitrile is fed into the top of a distillation column filled with hydrocarbons including butadiene, and as the acetonitrile falls down through the column, it absorbs the butadiene which is then sent from the bottom of the tower to a second separating tower. Heat is then employed in the separatin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polythiophene
Polythiophenes (PTs) are polymerized thiophenes, a sulfur heterocyclic compound, heterocycle. The parent PT is an insoluble colored solid with the formula (C4H2S)n. The rings are linked through the 2- and 5-positions. Poly(alkylthiophene)s have Alkyl, alkyl substituents at the 3- or 4-position(s). They are also colored solids, but tend to be soluble in organic solvents. PTs become Conductive polymer, conductive when oxidized. The electrical resistivity and conductivity, electrical conductivity results from the Delocalized electron, delocalization of electrons along the polymer backbone. Conductivity however is not the only interesting property resulting from electron delocalization. The optical properties of these materials respond to environmental stimuli, with dramatic color shifts in response to changes in solvent, temperature, Electric potential, applied potential, and binding to other molecules. Changes in both color and conductivity are induced by the same mechanism, tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infrared Spectroscopy
Infrared spectroscopy (IR spectroscopy or vibrational spectroscopy) is the measurement of the interaction of infrared radiation with matter by absorption, emission, or reflection. It is used to study and identify chemical substances or functional groups in solid, liquid, or gaseous forms. It can be used to characterize new materials or identify and verify known and unknown samples. The method or technique of infrared spectroscopy is conducted with an instrument called an infrared spectrometer (or spectrophotometer) which produces an infrared spectrum. An IR spectrum can be visualized in a graph of infrared light absorbance (or transmittance) on the vertical axis vs. frequency, wavenumber or wavelength on the horizontal axis. Typical units of wavenumber used in IR spectra are reciprocal centimeters, with the symbol cm−1. Units of IR wavelength are commonly given in micrometers (formerly called "microns"), symbol μm, which are related to the wavenumber in a reciprocal way. A com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultraviolet–visible Spectroscopy
UV spectroscopy or UV–visible spectrophotometry (UV–Vis or UV/Vis) refers to absorption spectroscopy or reflectance spectroscopy in part of the ultraviolet and the full, adjacent visible regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. Being relatively inexpensive and easily implemented, this methodology is widely used in diverse applied and fundamental applications. The only requirement is that the sample absorb in the UV-Vis region, i.e. be a chromophore. Absorption spectroscopy is complementary to fluorescence spectroscopy. Parameters of interest, besides the wavelength of measurement, are absorbance (A) or transmittance (%T) or reflectance (%R), and its change with time. Optical transitions Most molecules and ions absorb energy in the ultraviolet or visible range, i.e., they are chromophores. The absorbed photon excites an electron in the chromophore to higher energy molecular orbitals, giving rise to an excited state. For organic chromophores, four possible types of transitions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclic Voltammetry
Cyclic voltammetry (CV) is a type of potentiodynamic electrochemical measurement. In a cyclic voltammetry experiment, the working electrode potential is ramped linearly versus time. Unlike in linear sweep voltammetry, after the set potential is reached in a CV experiment, the working electrode's potential is ramped in the opposite direction to return to the initial potential. These cycles of ramps in potential may be repeated as many times as needed. The current at the working electrode is plotted versus the applied voltage (that is, the working electrode's potential) to give the cyclic voltammogram trace. Cyclic voltammetry is generally used to study the electrochemical properties of an analyte in solution or of a molecule that is adsorbed onto the electrode. Experimental method In cyclic voltammetry (CV), the electrode potential ramps linearly versus time in cyclical phases (Figure 2). The rate of voltage change over time during each of these phases is known as the experiment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Membrane
A membrane is a selective barrier; it allows some things to pass through but stops others. Such things may be molecules, ions, or other small particles. Membranes can be generally classified into synthetic membranes and biological membranes. Biological membranes include cell membranes (outer coverings of cells or organelles that allow passage of certain constituents); nuclear membranes, which cover a cell nucleus; and tissue membranes, such as mucosae and serosae. Synthetic membranes are made by humans for use in laboratories and industry (such as chemical plants). This concept of a membrane has been known since the eighteenth century but was used little outside of the laboratory until the end of World War II. Drinking water supplies in Europe had been compromised by the war and membrane filters were used to test for water safety. However, due to the lack of reliability, slow operation, reduced selectivity and elevated costs, membranes were not widely exploited. The first us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-assembled Monolayer
Self-assembled monolayers (SAM) of organic molecules are molecular assemblies formed spontaneously on surfaces by adsorption and are organized into more or less large ordered domains. In some cases molecules that form the monolayer do not interact strongly with the substrate. This is the case for instance of the two-dimensional supramolecular networks of e.g. perylenetetracarboxylic dianhydride (PTCDA) on gold or of e.g. porphyrins on HOPG, highly oriented pyrolitic graphite (HOPG). In other cases the molecules possess a head group that has a strong affinity to the substrate and anchors the molecule to it. Such a SAM consisting of a head group, tail and functional end group is depicted in Figure 1. Common head groups include thiols, silanes, phosphonates, etc. SAMs are created by the chemisorption of "head groups" onto a substrate from either the vapor or liquid phase followed by a slow organization of "tail groups". Initially, at small molecular density on the surface, adsorbat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
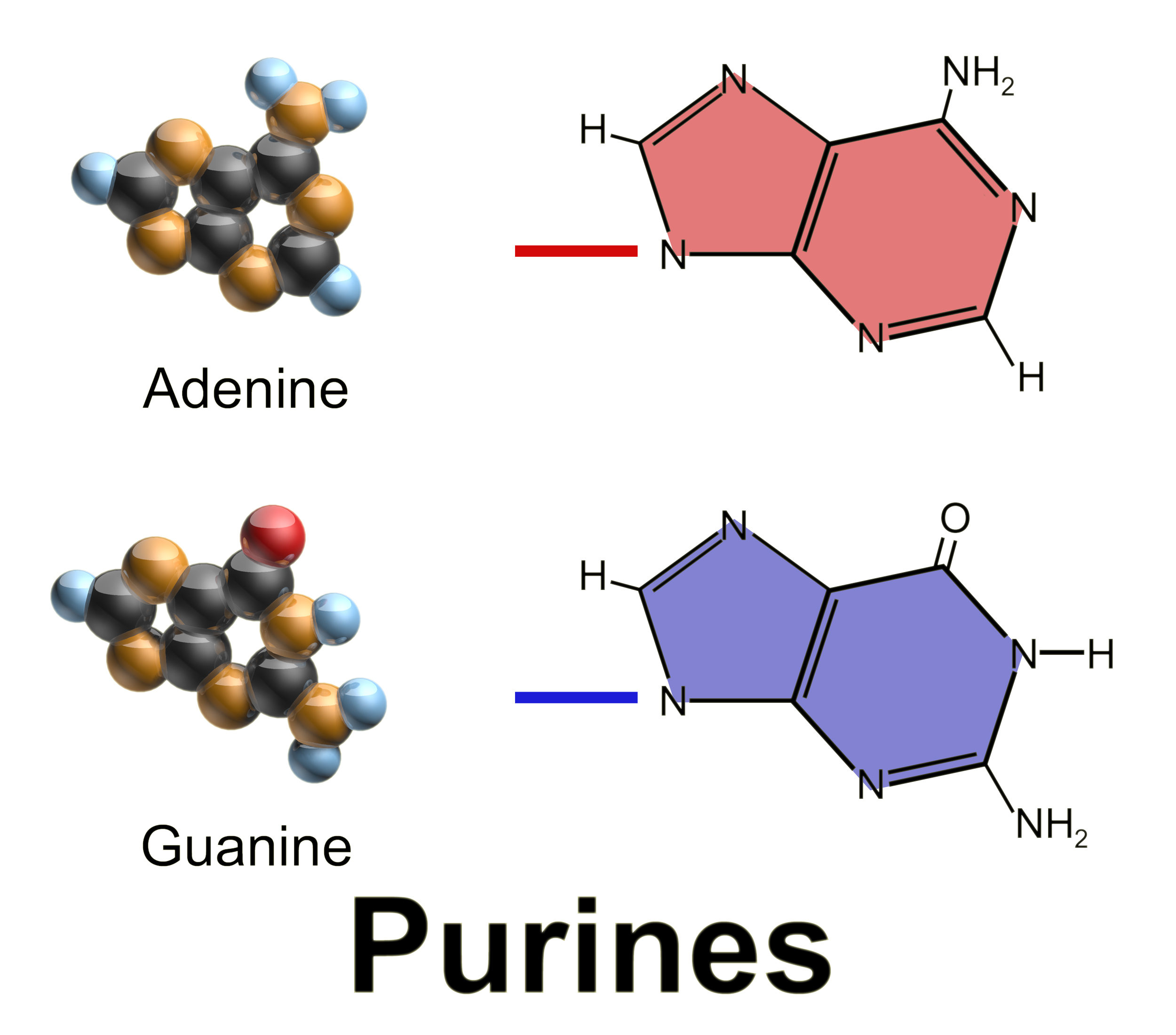
Purine
Purine is a heterocyclic compound, heterocyclic aromatic organic compound that consists of two rings (pyrimidine and imidazole) fused together. It is water-soluble. Purine also gives its name to the wider class of molecules, purines, which include substituted purines and their tautomers. They are the most widely occurring nitrogen-containing heterocycles in nature. Dietary sources Purines are found in high concentration in meat and meat products, especially internal organs such as liver and kidney. In general, plant-based diets are low in purines. High-purine plants and algae include some legumes (lentils and Black-eyed pea, black eye peas) and Spirulina (dietary supplement), spirulina. Examples of high-purine sources include: sweetbreads, Anchovies as food, anchovies, Sardines as food, sardines, liver, beef kidneys, Brain as food, brains, meat extracts (e.g., Oxo (food), Oxo, Bovril), herring, mackerel, scallops, game meats, yeast (beer, yeast extract, nutritional yeast) and g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
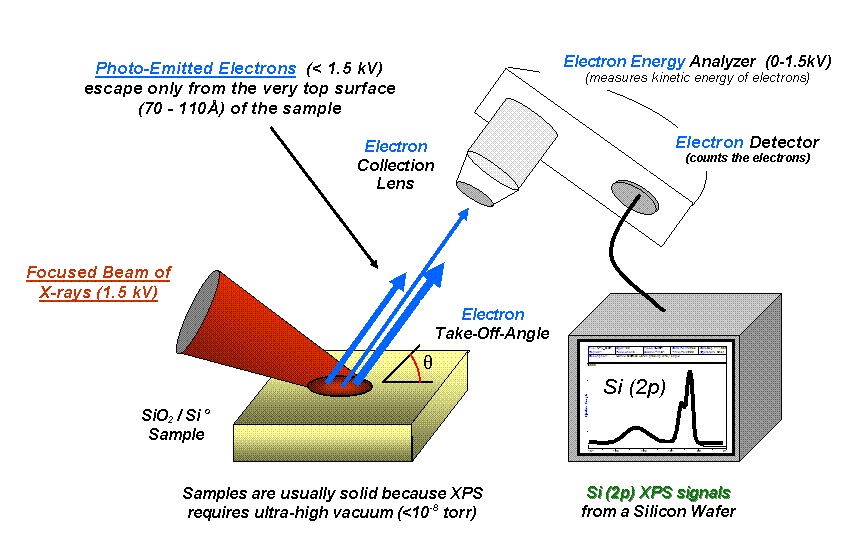
X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) is a surface-sensitive quantitative spectroscopic technique based on the photoelectric effect that can identify the elements that exist within a material (elemental composition) or are covering its surface, as well as their chemical state, and the overall electronic structure and density of the electronic states in the material. XPS is a powerful measurement technique because it not only shows what elements are present, but also what other elements they are bonded to. The technique can be used in line profiling of the elemental composition across the surface, or in depth profiling when paired with Ion beam#Ion beam etching or sputtering, ion-beam etching. It is often applied to study chemical processes in the materials in their as-received state or after cleavage, scraping, exposure to heat, reactive gasses or solutions, ultraviolet light, or during ion implantation. XPS belongs to the family of Photoemission spectroscopy, photoemission spect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |