|
Electro-oxidation
Electro-oxidation (EO), also known as anodic oxidation or electrochemical oxidation, is a technique used for wastewater treatment, mainly for industrial effluents, and is a type of advanced oxidation process (AOP). The most general layout comprises two electrodes, operating as anode and cathode, connected to a power source. When an energy input and sufficient supporting electrolyte are provided to the system, strong oxidizing species are formed, which interact with the contaminants and degrade them. The refractory compounds are thus converted into reaction intermediates and, ultimately, into water and CO2 by complete mineralization. Electro-oxidation has recently grown in popularity thanks to its ease of set-up and effectiveness in treating harmful and recalcitrant organic pollutants, which are typically difficult to degrade with conventional wastewater remediation processes. Also, it does not require any external addition of chemicals (contrarily to other processes like in-situ c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electro-oxidation Apparatus
Electro-oxidation (EO), also known as anodic oxidation or electrochemical oxidation, is a technique used for wastewater treatment, mainly for industrial effluents, and is a type of advanced oxidation process (AOP). The most general layout comprises two electrodes, operating as anode and cathode, connected to a power source. When an energy input and sufficient supporting electrolyte are provided to the system, strong oxidizing species are formed, which interact with the contaminants and degrade them. The refractory compounds are thus converted into reaction intermediates and, ultimately, into water and CO2 by complete mineralization. Electro-oxidation has recently grown in popularity thanks to its ease of set-up and effectiveness in treating harmful and recalcitrant organic pollutants, which are typically difficult to degrade with conventional Wastewater treatment, wastewater remediation processes. Also, it does not require any external addition of chemicals (contrarily to other proc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
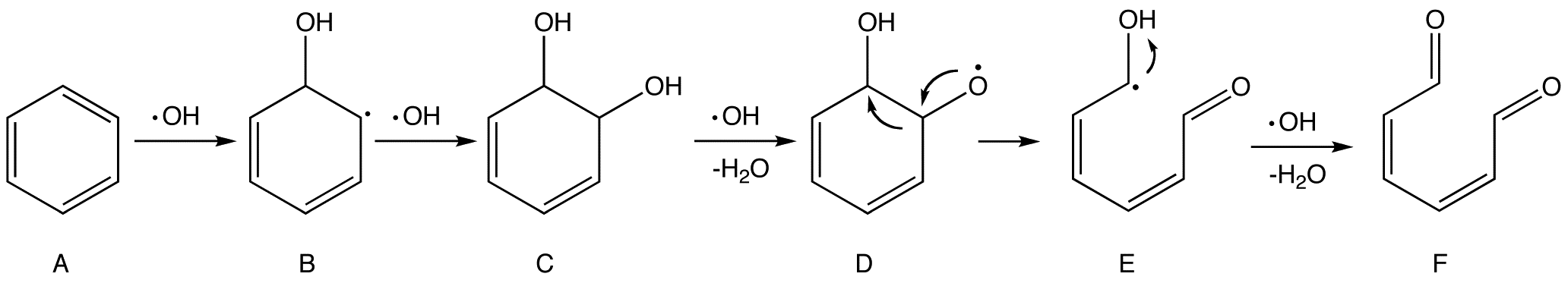
Advanced Oxidation Process
Advanced oxidation processes (AOPs), in a broad sense, are a set of chemical treatment procedures designed to remove organic (and sometimes inorganic) materials in water and wastewater by oxidation through reactions with hydroxyl radicals (·OH). In real-world applications of wastewater treatment, however, this term usually refers more specifically to a subset of such chemical processes that employ ozone (O3), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and/or UV light. One such type of process is called in situ chemical oxidation. Description AOPs rely on in-situ production of highly reactive hydroxyl radicals (·OH). These reactive species are the strongest oxidants that can be applied in water and can oxidize virtually any compound present in the water matrix, often at a diffusion-controlled reaction speed. Consequently, ·OH reacts unselectively once formed and contaminants will be quickly and efficiently fragmented and converted into small inorganic molecules. Hydroxyl radicals are produced wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wastewater Treatment
Wastewater treatment is a process used to remove contaminants from wastewater and convert it into an effluent that can be returned to the water cycle. Once returned to the water cycle, the effluent creates an acceptable impact on the environment or is reused for various purposes (called water reclamation). The treatment process takes place in a wastewater treatment plant. There are several kinds of wastewater which are treated at the appropriate type of wastewater treatment plant. For domestic wastewater (also called municipal wastewater or sewage), the treatment plant is called a sewage treatment plant. For industrial wastewater, treatment either takes place in a separate industrial wastewater treatment plant, or in a sewage treatment plant (usually after some form of pre-treatment). Further types of wastewater treatment plants include agricultural wastewater treatment plants and leachate treatment plants. Processes commonly used in wastewater treatment include phase sepa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Compound
In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon-hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The study of the properties, reactions, and syntheses of organic compounds comprise the discipline known as organic chemistry. For historical reasons, a few classes of carbon-containing compounds (e.g., carbonate salts and cyanide salts), along with a few other exceptions (e.g., carbon dioxide, hydrogen cyanide), are not classified as organic compounds and are considered inorganic. Other than those just named, little consensus exists among chemists on precisely which carbon-containing compounds are excluded, making any rigorous definition of an organic compound elusive. Although organic compounds make up only a small percentage of Earth's crust, they are of central importance because all known life is based on organic compounds. Living t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reduction Potential
Redox potential (also known as oxidation / reduction potential, ''ORP'', ''pe'', ''E_'', or E_) is a measure of the tendency of a chemical species to acquire electrons from or lose electrons to an electrode and thereby be reduced or oxidised respectively. Redox potential is expressed in volts (V). Each species has its own intrinsic redox potential; for example, the more positive the reduction potential (reduction potential is more often used due to general formalism in electrochemistry), the greater the species' affinity for electrons and tendency to be reduced. Measurement and interpretation In aqueous solutions, redox potential is a measure of the tendency of the solution to either gain or lose electrons when it is subjected to change by introduction of a new species. A solution with a higher (more positive) reduction potential than the new species will have a tendency to gain electrons from the new species (i.e. to be reduced by oxidizing the new species) and a solution with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxygen Evolution
Oxygen evolution is the process of generating molecular oxygen (O2) by a chemical reaction, usually from water. Oxygen evolution from water is effected by oxygenic photosynthesis, electrolysis of water, and thermal decomposition of various oxides. The biological process supports aerobic life. When relatively pure oxygen is required industrially, it is isolated by distillation of liquified air. Oxygen evolution in nature Photosynthetic oxygen evolution is the fundamental process by which oxygen is generated in earth's biosphere. The reaction is part of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis in cyanobacteria and the chloroplasts of green algae and plants. It utilizes the energy of light to split a water molecule into its protons and electrons for photosynthesis. Free oxygen, generated as a by-product of this reaction, is released into the atmosphere. Water oxidation is catalyzed by a manganese-containing cofactor contained in photosystem II known as the oxygen-evolving ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Oxygen Demand
In environmental chemistry, the chemical oxygen demand (COD) is an indicative measure of the amount of oxygen that can be consumed by reactions in a measured solution. It is commonly expressed in mass of oxygen consumed over volume of solution which in SI units is milligrams per litre ( mg/ L). A COD test can be used to easily quantify the amount of organics in water. The most common application of COD is in quantifying the amount of oxidizable pollutants found in surface water (e.g. lakes and rivers) or wastewater. COD is useful in terms of water quality by providing a metric to determine the effect an effluent will have on the receiving body, much like biochemical oxygen demand (BOD). Overview The basis for the COD test is that nearly all organic compounds can be fully oxidized to carbon dioxide with a strong oxidizing agent under acidic conditions. The amount of oxygen required to oxidize an organic compound to carbon dioxide, ammonia, and water is given by: :\mbox_n\mbox_a\mb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotonically Decreasing
In mathematics, a monotonic function (or monotone function) is a function between ordered sets that preserves or reverses the given order. This concept first arose in calculus, and was later generalized to the more abstract setting of order theory. In calculus and analysis In calculus, a function f defined on a subset of the real numbers with real values is called ''monotonic'' if and only if it is either entirely non-increasing, or entirely non-decreasing. That is, as per Fig. 1, a function that increases monotonically does not exclusively have to increase, it simply must not decrease. A function is called ''monotonically increasing'' (also ''increasing'' or ''non-decreasing'') if for all x and y such that x \leq y one has f\!\left(x\right) \leq f\!\left(y\right), so f preserves the order (see Figure 1). Likewise, a function is called ''monotonically decreasing'' (also ''decreasing'' or ''non-increasing'') if, whenever x \leq y, then f\!\left(x\right) \geq f\!\left(y\ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equivalent Weight
In chemistry, equivalent weight (also known as gram equivalent) is the mass of one equivalent, that is the mass of a given substance which will combine with or displace a fixed quantity of another substance. The equivalent weight of an element is the mass which combines with or displaces 1.008 gram of hydrogen or 8.0 grams of oxygen or 35.5 grams of chlorine. These values correspond to the atomic weight divided by the usual valence; for oxygen as example that is 16.0 g / 2 = 8.0 g. For acid–base reactions, the equivalent weight of an acid or base is the mass which supplies or reacts with one mole of hydrogen cations (). For redox reactions, the equivalent weight of each reactant supplies or reacts with one mole of electrons (e−) in a redox reaction. Equivalent weight has the units of mass, unlike atomic weight, which is now used as a synonym for relative atomic mass and is dimensionless. Equivalent weights were originally determined by experiment, but (insofar as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faraday Constant
In physical chemistry, the Faraday constant, denoted by the symbol and sometimes stylized as ℱ, is the electric charge per mole of elementary charges. It is named after the English scientist Michael Faraday. Since the 2019 redefinition of SI base units, which took effect on 20 May 2019, the Faraday constant has the exactly defined value given by the product of the elementary charge ''e'' and Avogadro constant ''N''A: : : :. Derivation The Faraday constant can be thought of as the conversion factor between the mole (used in chemistry) and the coulomb (used in physics and in practical electrical measurements), and is therefore of particular use in electrochemistry. Because 1 mole contains exactly entities, and 1 coulomb contains exactly elementary charges, the Faraday constant is given by the quotient of these two quantities: :. One common use of the Faraday constant is in electrolysis calculations. One can divide the amount of charge (the current integrated over time) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Oxygen Demand
In environmental chemistry, the chemical oxygen demand (COD) is an indicative measure of the amount of oxygen that can be consumed by reactions in a measured solution. It is commonly expressed in mass of oxygen consumed over volume of solution which in SI units is milligrams per litre ( mg/ L). A COD test can be used to easily quantify the amount of organics in water. The most common application of COD is in quantifying the amount of oxidizable pollutants found in surface water (e.g. lakes and rivers) or wastewater. COD is useful in terms of water quality by providing a metric to determine the effect an effluent will have on the receiving body, much like biochemical oxygen demand (BOD). Overview The basis for the COD test is that nearly all organic compounds can be fully oxidized to carbon dioxide with a strong oxidizing agent under acidic conditions. The amount of oxygen required to oxidize an organic compound to carbon dioxide, ammonia, and water is given by: :\mbox_n\mbox_a\mb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


.jpg)