|
Elbow With Varying Cross Section1
The elbow is the region between the arm and the forearm that surrounds the elbow joint. The elbow includes prominent landmarks such as the olecranon, the cubital fossa (also called the chelidon, or the elbow pit), and the lateral and the medial epicondyles of the humerus. The elbow joint is a hinge joint between the arm and the forearm; more specifically between the humerus in the upper arm and the radius and ulna in the forearm which allows the forearm and hand to be moved towards and away from the body. The term ''elbow'' is specifically used for humans and other primates, and in other vertebrates forelimb plus joint is used. The name for the elbow in Latin is ''cubitus'', and so the word cubital is used in some elbow-related terms, as in ''cubital nodes'' for example. Structure Joint The elbow joint has three different portions surrounded by a common joint capsule. These are joints between the three bones of the elbow, the humerus of the upper arm, and the radius and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annotated Drawing Of An Elbow Joint
An annotation is extra information associated with a particular point in a document or other piece of information. It can be a note that includes a comment or explanation. Annotations are sometimes presented in the margin of book pages. For annotations of different digital media, see web annotation and text annotation. Literature and education Textual scholarship Textual scholarship is a discipline that often uses the technique of annotation to describe or add additional historical context to texts and physical documents to make it easier to understand. Student uses Students often highlight passages in books in order to refer back to key phrases easily, or add marginalia to aid studying. Annotated bibliographies add commentary on the relevance or quality of each source, in addition to the usual bibliographic information that merely identifies the source. Mathematical expression annotation Mathematical expressions (symbols and formulae) can be annotated with their natural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hinge-joint
A hinge joint (ginglymus or ginglymoid) is a bone joint in which the articular surfaces are molded to each other in such a manner as to permit motion only in one plane. According to one classification system they are said to be uniaxial (having one degree of freedom).Platzer, Werner (2008) ''Color Atlas of Human Anatomy', Volume 1p.28/ref> The direction which the distal bone takes in this motion is seldom in the same plane as that of the axis of the proximal bone; there is usually a certain amount of deviation from the straight line during flexion. The articular surfaces of the bones are connected by strong collateral ligaments. The best examples of ginglymoid joints are the Interphalangeal joints of the hand and those of the foot and the joint between the humerus and ulna. The knee joints and ankle joints are less typical, as they allow a slight degree of rotation or of side-to-side movement in certain positions of the limb. The knee is the largest hinge joint in the human bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Radioulnar Joint
The proximal radioulnar articulation, also known as the proximal radioulnar joint (PRUJ), is a synovial pivot joint between the circumference of the head of the radius and the ring formed by the radial notch of the ulna and the annular ligament. Structure The proximal radioulnar joint is a synovial pivot joint. It occurs between the circumference of the head of the radius and the ring formed by the radial notch of the ulna and the annular ligament. The interosseous membrane of the forearm and the annular ligament stabilise the joint. A number of nerves run close to the proximal radioulnar joint, including: *median nerve *musculocutaneous nerve *radial nerve See also * Distal radioulnar articulation * Supination Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative ... References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trochlea Of Humerus
In the human arm, the humeral trochlea is the medial portion of the articular surface of the elbow joint which articulates with the trochlear notch on the ulna in the forearm. Structure In humans and apes it is trochleariform (or trochleiform), as opposed to cylindrical in most monkeys and conical in some prosimians. It presents a deep depression between two well-marked borders; it is convex from before backward, concave from side to side, and occupies the anterior, lower, and posterior parts of the extremity. The trochlea has the capitulum located on its lateral side and the medial epicondyle on its medial. It is directly inferior to the coronoid fossa anteriorly and to the olecranon fossa posteriorly. In humans, these two fossae, the most prominent in the humerus, are occasionally transformed into a hole, the supratrochlear foramen, which is regularly present in, for example, dogs. Carrying angle When viewed from in front or behind, the trochlea looks roughly cylindrical, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equilateral Triangle
In geometry, an equilateral triangle is a triangle in which all three sides have the same length. In the familiar Euclidean geometry, an equilateral triangle is also equiangular; that is, all three internal angles are also congruent to each other and are each 60°. It is also a regular polygon, so it is also referred to as a regular triangle. Principal properties Denoting the common length of the sides of the equilateral triangle as a, we can determine using the Pythagorean theorem that: *The area is A=\frac a^2, *The perimeter is p=3a\,\! *The radius of the circumscribed circle is R = \frac *The radius of the inscribed circle is r=\frac a or r=\frac *The geometric center of the triangle is the center of the circumscribed and inscribed circles *The altitude (height) from any side is h=\frac a Denoting the radius of the circumscribed circle as ''R'', we can determine using trigonometry that: *The area of the triangle is \mathrm=\fracR^2 Many of these quantities have simple r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
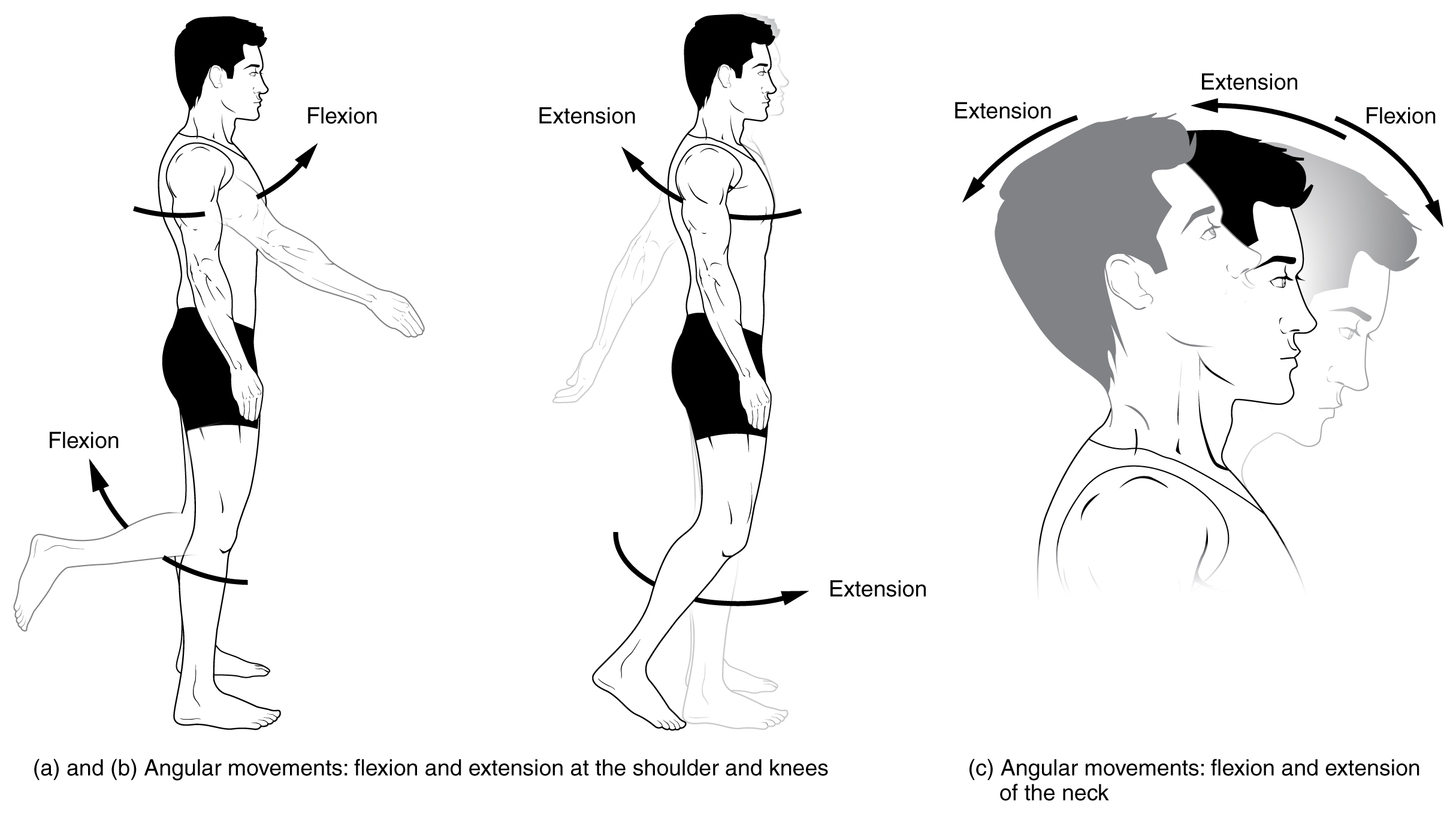
Flexion
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative to the anatomical position of the body parts involved. Anatomists and others use a unified set of terms to describe most of the movements, although other, more specialized terms are necessary for describing unique movements such as those of the hands, feet, and eyes. In general, motion is classified according to the anatomical plane it occurs in. ''Flexion'' and ''extension'' are examples of ''angular'' motions, in which two axes of a joint are brought closer together or moved further apart. ''Rotational'' motion may occur at other joints, for example the shoulder, and are described as ''internal'' or ''external''. Other terms, such as ''elevation'' and ''depression'', describe movement above or below the horizontal plane. Many anatomica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomical Position
The standard anatomical position, or standard anatomical model, is the scientifically agreed upon reference position for anatomical location terms. Standard anatomical positions are used to standardise the position of appendages of animals with respect to the main body of the organism. In medical disciplines, all references to a location on or in the body are made based upon the standard anatomical position. A straight position is assumed when describing a proximo-distal axis (towards or away from a point of attachment). This helps avoid confusion in terminology when referring to the same organism in different postures. For example, if the elbow is flexed, the hand remains distal to the shoulder even if it approaches the shoulder. Human anatomy In standard anatomical position, the human body is standing erect and at rest. Unlike the situation in other vertebrates, the limbs are placed in positions reminiscent of the supine position imposed on cadavers during autopsy. Therefo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supination
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative to the anatomical position of the body parts involved. Anatomists and others use a unified set of terms to describe most of the movements, although other, more specialized terms are necessary for describing unique movements such as those of the hands, feet, and eyes. In general, motion is classified according to the anatomical plane it occurs in. ''Flexion'' and ''extension'' are examples of ''angular'' motions, in which two axes of a joint are brought closer together or moved further apart. ''Rotational'' motion may occur at other joints, for example the shoulder, and are described as ''internal'' or ''external''. Other terms, such as ''elevation'' and ''depression'', describe movement above or below the horizontal plane. Many anatomica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pronation
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative to the anatomical position of the body parts involved. Anatomists and others use a unified set of terms to describe most of the movements, although other, more specialized terms are necessary for describing unique movements such as those of the hands, feet, and eyes. In general, motion is classified according to the anatomical plane it occurs in. ''Flexion'' and ''extension'' are examples of ''angular'' motions, in which two axes of a joint are brought closer together or moved further apart. ''Rotational'' motion may occur at other joints, for example the shoulder, and are described as ''internal'' or ''external''. Other terms, such as ''elevation'' and ''depression'', describe movement above or below the horizontal plane. Many anatomica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radial Notch
The radial notch of the ulna (lesser sigmoid cavity) is a narrow, oblong, articular depression on the lateral side of the coronoid process; it receives the circumferential articular surface of the head of the radius. It is concave from before backward, and its prominent extremities serve for the attachment of the annular ligament. Additional images File:Gray333.png, Annular ligament of radius, from above. References External links * *elbow/elbowbones/bones3at the Dartmouth Medical School The Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth is the graduate medical school of Dartmouth College in Hanover, New Hampshire. The fourth oldest medical school in the United States, it was founded in 1797 by New England physician Nathan Smith. It is o ...'s Department of Anatomy Upper limb anatomy Ulna {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proximal Radioulnar Joint
The proximal radioulnar articulation, also known as the proximal radioulnar joint (PRUJ), is a synovial pivot joint between the circumference of the head of the radius and the ring formed by the radial notch of the ulna and the annular ligament. Structure The proximal radioulnar joint is a synovial pivot joint. It occurs between the circumference of the head of the radius and the ring formed by the radial notch of the ulna and the annular ligament. The interosseous membrane of the forearm and the annular ligament stabilise the joint. A number of nerves run close to the proximal radioulnar joint, including: *median nerve *musculocutaneous nerve *radial nerve See also * Distal radioulnar articulation * Supination Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative ... References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ball-and-socket Joint
The ball-and-socket joint (or spheroid joint) is a type of synovial joint in which the ball-shaped surface of one rounded bone fits into the cup-like depression of another bone. The distal bone is capable of motion around an indefinite number of axes, which have one common center. This enables the joint to move in many directions. An enarthrosis is a special kind of spheroidal joint in which the socket covers the sphere beyond its equator.Platzer, Werner (2008) ''Color Atlas of Human Anatomy'', Volume 1p.28/ref> Examples Examples of this form of articulation are found in the hip, where the round head of the femur (ball) rests in the cup-like acetabulum (socket) of the pelvis; and in the shoulder joint, where the rounded upper extremity of the humerus (ball) rests in the cup-like glenoid fossa (socket) of the shoulder blade.And the phalanges (toes, fingers)Introduction to Joints: Synovial Joints - Ball and Socket Joints (The shoulder also includes a sternoclavicular joint Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |