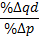|
Elasticity Of Complementarity
Elasticity of complementarity (Hamermesh, 1993) is the percentage responsiveness of relative factor prices to a 1 percent change in relative inputs. Mathematical definition Given the production function f(x_1,x_2) then the elasticity of complementarity is defined as : c = \frac = \frac . The inverse of elasticity of complementarity is elasticity of substitution Elasticity of substitution is the ratio of percentage change in capital-labour ratio with the percentage change in Marginal Rate of Technical Substitution. In a competitive market, it measures the percentage change in the two inputs used in respons .... References *Hamermesh, Daniel S., ''Labor Demand'', Princeton University Press, Princeton NJ, 1993, Elasticity (economics) {{economics-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Percent Change
In any quantitative science, the terms relative change and relative difference are used to compare two quantities while taking into account the "sizes" of the things being compared, i.e. dividing by a ''standard'' or ''reference'' or ''starting'' value. The comparison is expressed as a ratio and is a unitless number. By multiplying these ratios by 100 they can be expressed as percentages so the terms percentage change, percent(age) difference, or relative percentage difference are also commonly used. The terms "change" and "difference" are used interchangeably. Relative change is often used as a quantitative indicator of quality assurance and quality control for repeated measurements where the outcomes are expected to be the same. A special case of percent change (relative change expressed as a percentage) called ''percent error'' occurs in measuring situations where the reference value is the accepted or actual value (perhaps theoretically determined) and the value being compared ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elasticity (economics)
In economics, elasticity measures the percentage change of one economic variable in response to a percentage change in another. If the price elasticity of the demand of something is -2, a 10% increase in price causes the demand quantity to fall by 20%. Introduction Elasticity is an important concept in neoclassical economic theory, and enables in the understanding of various economic concepts, such as the incidence of indirect taxation, marginal concepts relating to the theory of the firm, distribution of wealth, and different types of goods relating to the theory of consumer choice. An understanding of elasticity is also important when discussing welfare distribution, in particular consumer surplus, producer surplus, or government surplus. Elasticity is present throughout many economic theories, with the concept of elasticity appearing in several main indicators. These include price elasticity of demand, price elasticity of supply, income elasticity of demand, elastic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elasticity Of Substitution
Elasticity of substitution is the ratio of percentage change in capital-labour ratio with the percentage change in Marginal Rate of Technical Substitution. In a competitive market, it measures the percentage change in the two inputs used in response to a percentage change in their prices.Bergstrom, Ted (2015)''Lecture Notes on Elasticity of Substitution'' p. 5. Viewed June 17, 2016. It gives a measure of the curvature of an isoquant, and thus, the substitutability between inputs (or goods), i.e. how easy it is to substitute one input (or good) for the other. History of the concept John Hicks introduced the concept in 1932. Joan Robinson independently discovered it in 1933 using a mathematical formulation that was equivalent to Hicks's, though that was not implemented at the time.Chirinko, Robert (2006)''Sigma: The Long and Short of It'' '' Journal of Macroeconomics. '' 2: 671-86. Definition The general definition of the elasticity of X with respect to Y is E^X_Y = \frac, which redu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |