|
Elastic-rebound Theory
__NOTOC__ In geology, the elastic-rebound theory is an explanation for how energy is released during an earthquake. As the Earth's crust deforms, the rocks which span the opposing sides of a fault are subjected to shear stress. Slowly they deform, until their internal rigidity is exceeded. Then they separate with a rupture along the fault; the sudden movement releases accumulated energy, and the rocks snap back almost to their original shape. The previously solid mass is divided between the two slowly moving plates, the energy released through the surroundings in a seismic wave. Theory After the great 1906 San Francisco earthquake, geophysicist Harry Fielding Reid examined the displacement of the ground surface along the San Andreas Fault in the 50 years before the earthquake.Reid, H.F., ''The Mechanics of the Earthquake, The California Earthquake of April 18, 1906; Report of the State Investigation Commission,'' Vol.2, Carnegie Institution of Washington, Washington, D.C. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
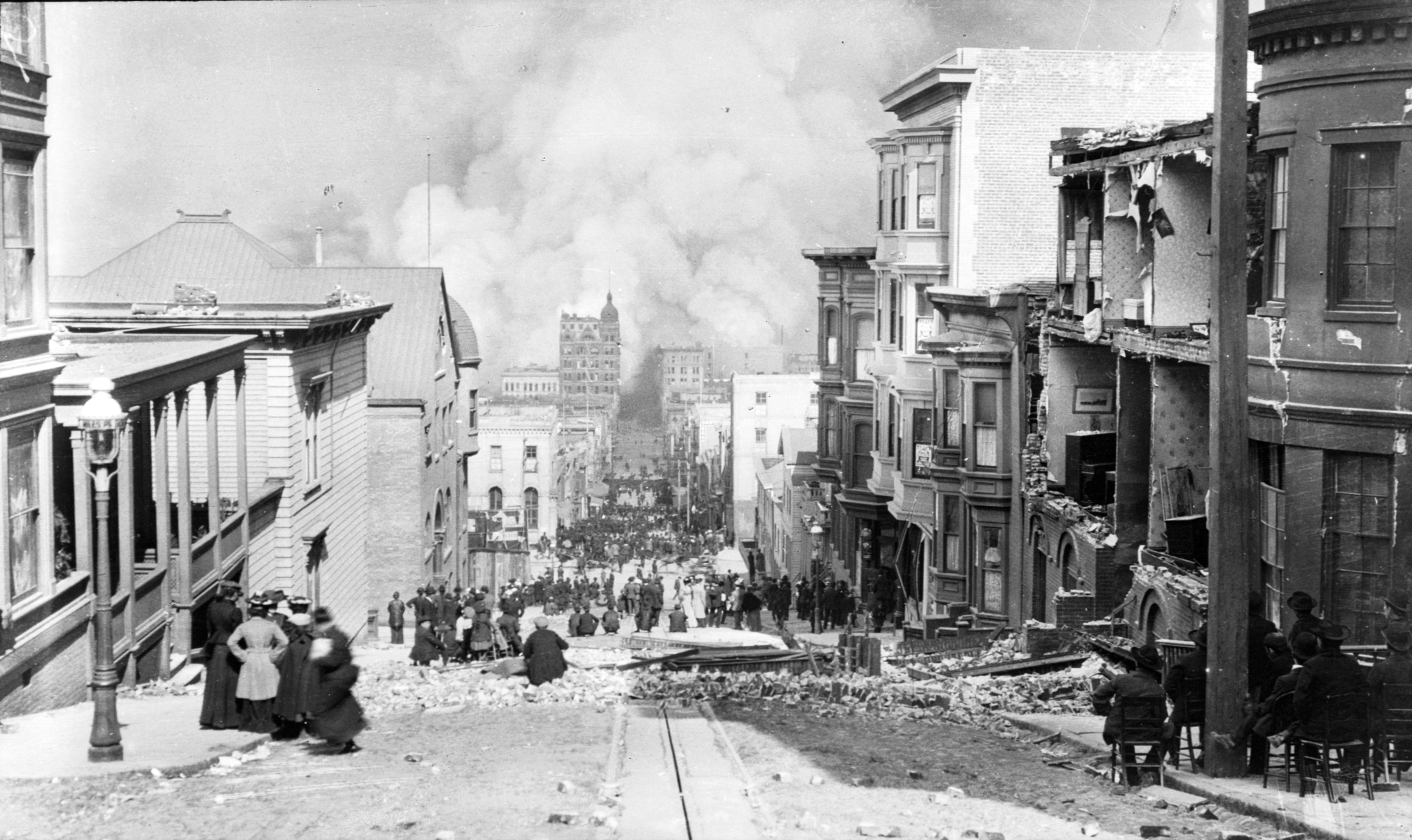
1906 San Francisco Earthquake
At 05:12 AM Pacific Time Zone, Pacific Standard Time on Wednesday, April 18, 1906, the coast of Northern California was struck by a major earthquake with an estimated Moment magnitude scale, moment magnitude of 7.9 and a maximum Mercalli intensity scale, Mercalli intensity of XI (''Extreme''). High-intensity shaking was felt from Eureka, California, Eureka on the North Coast (California), North Coast to the Salinas Valley, an agricultural region to the south of the San Francisco Bay Area. Devastating fires soon broke out in San Francisco and lasted for several days. More than 3,000 people died and over 80% of the city was destroyed. The event is remembered as the List of disasters in the United States by death toll, deadliest earthquake in the history of the United States. The death toll remains the greatest loss of life from a natural disaster in California's history and high on the list of worst American disasters. Tectonic setting The San Andreas Fault is a continental tran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
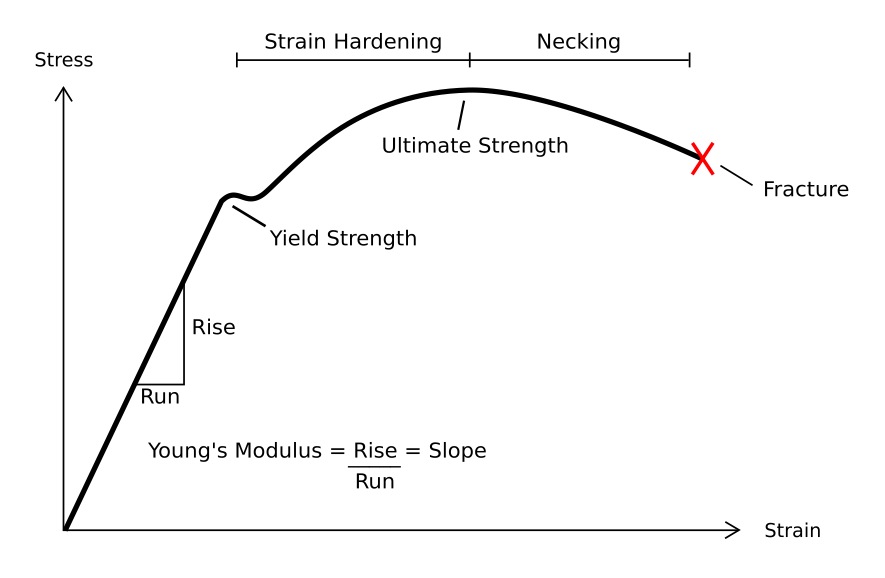
Tensile Strength
Ultimate tensile strength (also called UTS, tensile strength, TS, ultimate strength or F_\text in notation) is the maximum stress that a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before breaking. In brittle materials, the ultimate tensile strength is close to the yield point, whereas in ductile materials, the ultimate tensile strength can be higher. The ultimate tensile strength is usually found by performing a tensile test and recording the engineering stress versus strain. The highest point of the stress–strain curve is the ultimate tensile strength and has units of stress. The equivalent point for the case of compression, instead of tension, is called the compressive strength. Tensile strengths are rarely of any consequence in the design of ductile members, but they are important with brittle members. They are tabulated for common materials such as alloys, composite materials, ceramics, plastics, and wood. Definition The ultimate tensile strength ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elastic Deformation
In engineering, deformation (the change in size or shape of an object) may be ''elastic'' or ''plastic''. If the deformation is negligible, the object is said to be ''rigid''. Main concepts Occurrence of deformation in engineering applications is based on the following background concepts: * ''Displacements'' are any change in position of a point on the object, including whole-body translations and rotations ( rigid transformations). * ''Deformation'' are changes in the relative position between internals points on the object, excluding rigid transformations, causing the body to change shape or size. * ''Strain'' is the ''relative'' ''internal'' deformation, the dimensionless change in shape of an infinitesimal cube of material relative to a reference configuration. Mechanical strains are caused by mechanical stress, ''see stress-strain curve''. The relationship between stress and strain is generally linear and reversible up until the yield point and the deformation is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fault Trace
A fault trace describes the intersection of a Fault (geology), geological fault with the Earth's surface, which leaves a visible disturbance on the surface, usually looking like a crack in the surface with jagged rock structures protruding outward. The term also applies to a line plotted on a geological map to represent a fault. These fractures tend to occur when a Slope stability, slip surface expands from a fault core, especially during an earthquake. This tends to occur with fault displacement, in which surfaces on both sides of a fault, known as fault blocks, separate horizontally or vertically. Traces caused by different faults Fault (geology), Faults, at the broadest level, can be differentiated by the relative motion between their fault blocks. Horizontal motion is indicative of what is known as a Strike-slip Fault, strike-slip fault and does not usually show much vertical separation. This is when the motion along the fault is parallel to the fault trace, usually cause ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Global Positioning System
The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a satellite-based hyperbolic navigation system owned by the United States Space Force and operated by Mission Delta 31. It is one of the global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) that provide geolocation and time information to a GPS receiver anywhere on or near the Earth where there is an unobstructed line of sight to four or more GPS satellites. It does not require the user to transmit any data, and operates independently of any telephone or Internet reception, though these technologies can enhance the usefulness of the GPS positioning information. It provides critical positioning capabilities to military, civil, and commercial users around the world. Although the United States government created, controls, and maintains the GPS system, it is freely accessible to anyone with a GPS receiver. Overview The GPS project was started by the U.S. Department of Defense in 1973. The first prototype spacecraft was launched in 1978 an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strain (materials Science)
In mechanics, strain is defined as relative deformation, compared to a position configuration. Different equivalent choices may be made for the expression of a strain field depending on whether it is defined with respect to the initial or the final configuration of the body and on whether the metric tensor or its dual is considered. Strain has dimension of a length ratio, with SI base units of meter per meter (m/m). Hence strains are dimensionless and are usually expressed as a decimal fraction or a percentage. Parts-per notation is also used, e.g., parts per million or parts per billion (sometimes called "microstrains" and "nanostrains", respectively), corresponding to μm/m and nm/m. Strain can be formulated as the spatial derivative of displacement: \boldsymbol \doteq \cfrac\left(\mathbf - \mathbf\right) = \boldsymbol'- \boldsymbol, where is the identity tensor. The displacement of a body may be expressed in the form , where is the reference position of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Andreas Fault
The San Andreas Fault is a continental Fault (geology)#Strike-slip faults, right-lateral strike-slip transform fault that extends roughly through the U.S. state of California. It forms part of the tectonics, tectonic boundary between the Pacific plate and the North American plate. Traditionally, for scientific purposes, the fault has been classified into three main segments (northern, central, and southern), each with different characteristics and a different degree of earthquake risk. The average slip rate along the entire fault ranges from per year. In the north, the fault terminates offshore near Eureka, California, at the Mendocino triple junction, where three tectonic plates meet. The Cascadia subduction zone intersects the San Andreas fault at the Mendocino triple junction. It has been hypothesized that a major earthquake along the Cascadia subduction zone could trigger a rupture along the San Andreas Fault. In the south, the fault terminates near Bombay Beach, Califor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harry Fielding Reid
Harry Fielding Reid (May 18, 1859 – June 18, 1944) was an American geophysicist. He was notable for his contributions to glaciology and seismology, particularly his theory of elastic rebound that related faults to earthquakes. He was a professor of dynamical geology and geography at Johns Hopkins University. Early life Harry Fielding Reid was born in Baltimore, the fourth of seven children of Andrew and Fanny Brooke Gwathmey Reid. Reid's mother was a descendant of Betty Washington Lewis, sister of George Washington; his father was a successful sugar merchant. The younger Reid's early education took him for at least one year to Switzerland; he is also known to have attended and graduated from the Pennsylvania Military Academy. In 1877 Reid enrolled at the newly founded Johns Hopkins University, from which he earned a A.B. in 1880 as part of the second graduating class. During the following year, he entered the Hopkins Ph.D. program, which was then revolutionizing American ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
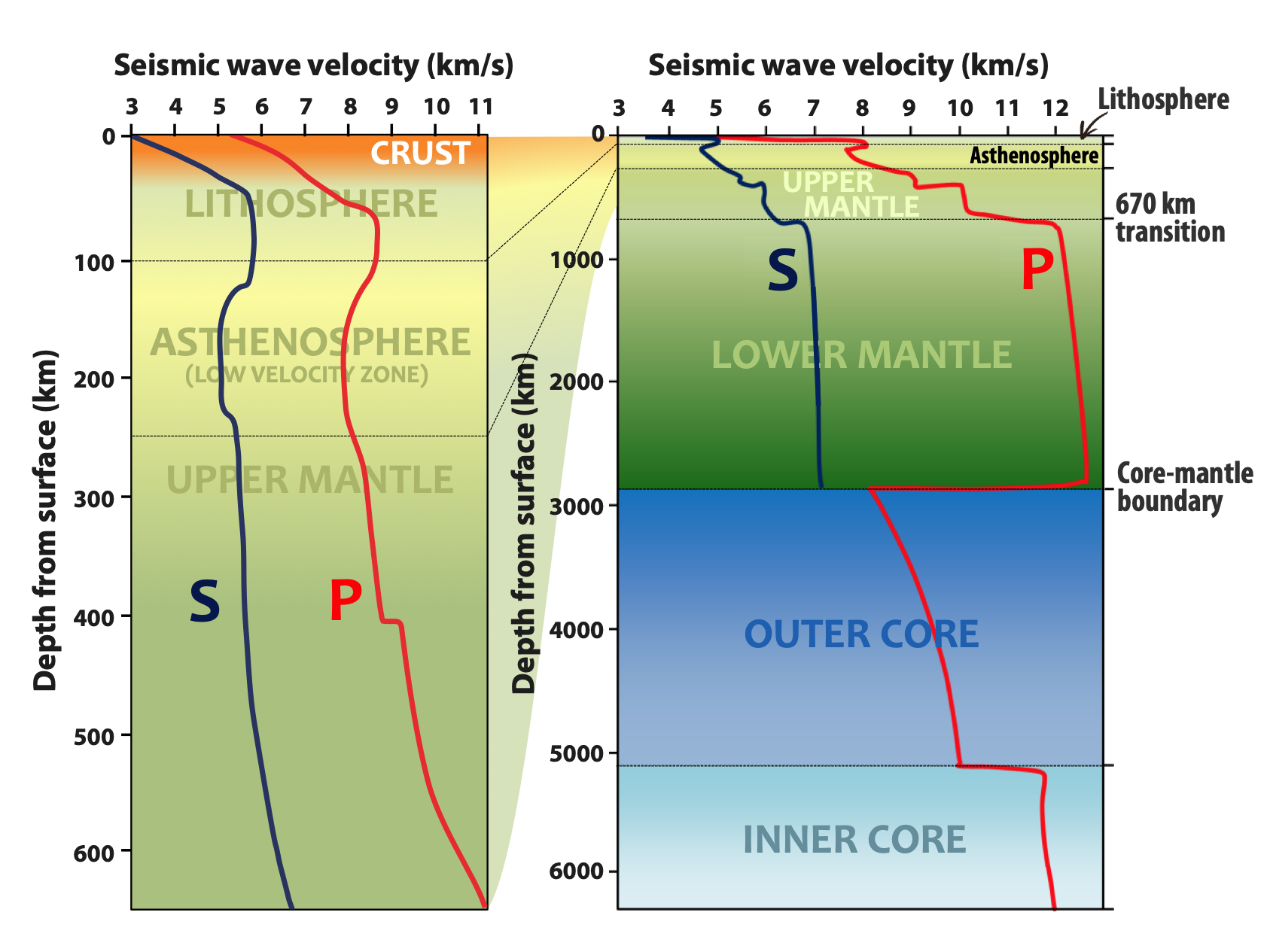
Seismic Wave
A seismic wave is a mechanical wave of acoustic energy that travels through the Earth or another planetary body. It can result from an earthquake (or generally, a quake), volcanic eruption, magma movement, a large landslide and a large man-made explosion that produces low-frequency acoustic energy. Seismic waves are studied by seismologists, who record the waves using seismometers, hydrophones (in water), or accelerometers. Seismic waves are distinguished from seismic noise (ambient vibration), which is persistent low-amplitude vibration arising from a variety of natural and anthropogenic sources. The propagation velocity of a seismic wave depends on density and elasticity of the medium as well as the type of wave. Velocity tends to increase with depth through Earth's crust and mantle, but drops sharply going from the mantle to Earth's outer core. Earthquakes create distinct types of waves with different velocities. When recorded by a seismic observatory, their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology
Geology (). is a branch of natural science concerned with the Earth and other astronomical objects, the rocks of which they are composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth sciences, including hydrology. It is integrated with Earth system science and planetary science. Geology describes the structure of the Earth on and beneath its surface and the processes that have shaped that structure. Geologists study the mineralogical composition of rocks in order to get insight into their history of formation. Geology determines the relative ages of rocks found at a given location; geochemistry (a branch of geology) determines their absolute ages. By combining various petrological, crystallographic, and paleontological tools, geologists are able to chronicle the geological history of the Earth as a whole. One aspect is to demonstrate the age of the Earth. Geology provides evidence for plate tectonics, the ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strain (mechanics)
In mechanics, strain is defined as relative deformation, compared to a position configuration. Different equivalent choices may be made for the expression of a strain field depending on whether it is defined with respect to the initial or the final configuration of the body and on whether the metric tensor or its dual is considered. Strain has dimension of a length ratio, with SI base units of meter per meter (m/m). Hence strains are dimensionless and are usually expressed as a decimal fraction or a percentage. Parts-per notation is also used, e.g., parts per million or parts per billion (sometimes called "microstrains" and "nanostrains", respectively), corresponding to μm/m and nm/m. Strain can be formulated as the spatial derivative of displacement: \boldsymbol \doteq \cfrac\left(\mathbf - \mathbf\right) = \boldsymbol'- \boldsymbol, where is the identity tensor. The displacement of a body may be expressed in the form , where is the reference position of material ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |