|
El Sueño De Arquímedes
El Sueño de Arquímedes was a Spanish science podcast and radio program which was broadcast by Radio Nacional de España (RNE) from September 2006 until June, 2007. The program was created by Ángel Rodríguez Lozano. A total of 35 programs are still available for download. In addition to El Sueño de Arquímedes, Ángel Rodríguez Lozano also hosted Vanguardia de la Ciencia, which was broadcast weekly without interruption from April 1995 until June 2007. The name of the program means "the dream of Archimedes", and alludes to Archimedes' statement that given a lever and a fixed point, he could move the world. To Ángel Rodríguez Lozano, the dream was moving the world by popularizing and sharing knowledge. Format Before the startup of El Sueño de Arquímedes, Ángel Rodríguez Lozano had been hosting Vanguardia de la Ciencia for more than a decade. When RNE asked if he would host a second popular science program, Ángel Rodríguez Lozano realised that the scheduled timing, Sun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Nacional De España
Radio Nacional de España (acronym RNE, branded rne, "National Radio of Spain") is the national state-owned public service radio broadcaster in Spain. RNE is the radio division and Televisión Española (TVE) is the television division of Radiotelevisión Española (RTVE), the public corporation which has the overall responsibility for the national broadcasting public services under a Parliament-appointed president who, in addition to being answerable to a Board of Directors, reports to an all-party committee of the national parliament, as provided for in the Public Radio and Television Law of 2006. RNE launched its first station on 19 January 1937. It is currently headquartered at Casa de la Radio at Prado del Rey in Pozuelo de Alarcón. Origins of RNE RNE officially came into existence in Salamanca on 19 January 1937, at the height of the Spanish Civil War (1936–39), and was dependent upon the recently created ' (State Delegation for Press and Propaganda). The station' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ángel Rodríguez Lozano
Ángel Rodríguez Lozano is a Spanish radio journalist and popularizer of science, best known as the creator and presenter of the program Vanguardia de la Ciencia, which was broadcast without interruption every week from April 1995 until June 2007. Before the startup of Vanguardia de la Ciencia, he participated in other programs in Radio Nacional de España. He has also contributed to other programs of popular science, ''El Mono Temático'', ''En Clave de Ciencia de Radio 5'', and ''Hora América''. From August 2006 to June 2007, he also wrote and presented the program El Sueño de Arquímedes. Ángel Rodríguez Lozano was born in 1952 in the small municipality of La Garrovilla, near Mérida in Extremadura. He is a physicist by training, and has done research work in fluid dynamics, chaos theory and non-linear phenomena at the Complutense University of Madrid. Ángel Rodríguez Lozano has stated that he enjoys popularizing science, because the effort that is required to present a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vanguardia De La Ciencia
''Vanguardia de la Ciencia'' was a Spanish science podcast and radio program which was broadcast on the shortwave band by Radio Exterior de España, one of the stations of Radio Nacional de España (RNE). The program aired weekly, without interruption, from April 1995 until June 2007. It was available for download as mp3-files from the web pages of RNE from September 2003. The program was created by Ángel Rodríguez Lozano. A total of 98 programs are still available online. In addition to ''Vanguardia de la Ciencia'', Lozano also hosted another popular science radio program and podcast, '' El Sueño de Arquímedes''. History ''Vanguardia de la Ciencia'' had a large audience worldwide. Although exact numbers of downloads and listeners are unavailable, Radio exterior de España has 80 million listeners, only surpassed by the BBC and Radio Vaticana. In addition, ''Vanguardia de la Ciencia'' was retransmitted by several radio stations in Latin America and Spain. The program was pop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archimedes
Archimedes of Syracuse (;; ) was a Greek mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and inventor from the ancient city of Syracuse in Sicily. Although few details of his life are known, he is regarded as one of the leading scientists in classical antiquity. Considered the greatest mathematician of ancient history, and one of the greatest of all time,* * * * * * * * * * Archimedes anticipated modern calculus and analysis by applying the concept of the infinitely small and the method of exhaustion to derive and rigorously prove a range of geometrical theorems. These include the area of a circle, the surface area and volume of a sphere, the area of an ellipse, the area under a parabola, the volume of a segment of a paraboloid of revolution, the volume of a segment of a hyperboloid of revolution, and the area of a spiral. Heath, Thomas L. 1897. ''Works of Archimedes''. Archimedes' other mathematical achievements include deriving an approximation of pi, defining and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
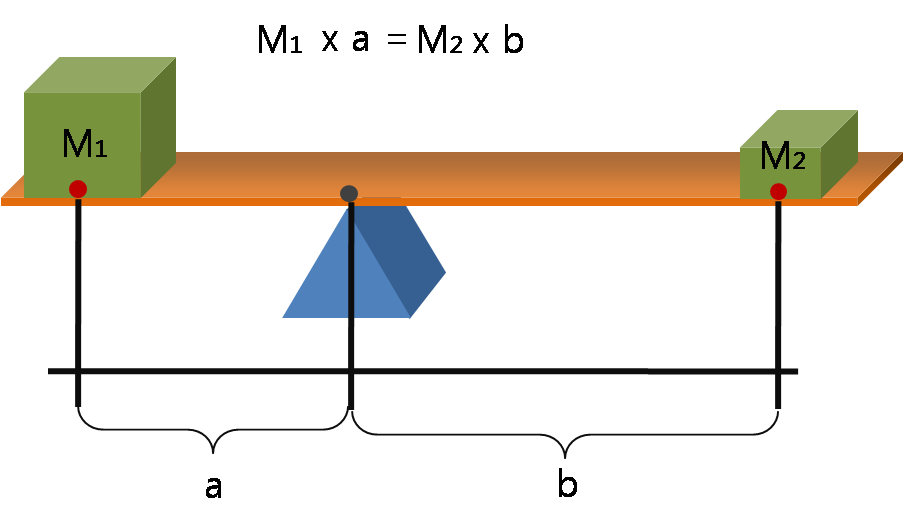
Lever
A lever is a simple machine consisting of a beam or rigid rod pivoted at a fixed hinge, or ''fulcrum''. A lever is a rigid body capable of rotating on a point on itself. On the basis of the locations of fulcrum, load and effort, the lever is divided into three types. Also, leverage is mechanical advantage gained in a system. It is one of the six simple machines identified by Renaissance scientists. A lever amplifies an input force to provide a greater output force, which is said to provide leverage. The ratio of the output force to the input force is the mechanical advantage of the lever. As such, the lever is a mechanical advantage device, trading off force against movement. Etymology The word "lever" entered English around 1300 from Old French, in which the word was ''levier''. This sprang from the stem of the verb ''lever'', meaning "to raise". The verb, in turn, goes back to the Latin ''levare'', itself from the adjective ''levis'', meaning "light" (as in "not heavy"). The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mad Scientist
The mad scientist (also mad doctor or mad professor) is a stock character of a scientist who is perceived as " mad, bad and dangerous to know" or "insane" owing to a combination of unusual or unsettling personality traits and the unabashedly ambitious, taboo or hubristic nature of their experiments. As a motif in fiction, the mad scientist may be villainous (evil genius) or antagonistic, benign, or neutral; may be insane, eccentric, or clumsy; and often works with fictional technology or fails to recognise or value common human objections to attempting to play God. Some may have benevolent intentions, even if their actions are dangerous or questionable, which can make them accidental antagonists. History Prototypes The prototypical fictional mad scientist was Victor Frankenstein, creator of his eponymous monster, who made his first appearance in 1818, in the novel ''Frankenstein, or the Modern Prometheus'' by Mary Shelley. Though the novel's title character, Victor Frankenst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Audio Podcasts
Audio most commonly refers to sound, as it is transmitted in signal form. It may also refer to: Sound *Audio signal, an electrical representation of sound *Audio frequency, a frequency in the audio spectrum *Digital audio, representation of sound in a form processed and/or stored by computers or digital electronics *Audio, audible content (media) in audio production and publishing *Semantic audio, extraction of symbols or meaning from audio *Stereophonic audio, method of sound reproduction that creates an illusion of multi-directional audible perspective *Audio equipment Entertainment *AUDIO (group), an American R&B band of 5 brothers formerly known as TNT Boyz and as B5 * ''Audio'' (album), an album by the Blue Man Group * ''Audio'' (magazine), a magazine published from 1947 to 2000 *Audio (musician), British drum and bass artist * "Audio" (song), a song by LSD Computing *, an HTML element, see HTML5 audio See also *Acoustic (other) *Audible (other) *Audio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Radio Programs
Spanish might refer to: * Items from or related to Spain: **Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain **Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries **Spanish cuisine Other places * Spanish, Ontario, Canada * Spanish River (other), the name of several rivers * Spanish Town, Jamaica Other uses * John J. Spanish (1922–2019), American politician * "Spanish" (song), a single by Craig David, 2003 See also * * * Español (other) * Spain (other) * España (other) * Espanola (other) * Hispania, the Roman and Greek name for the Iberian Peninsula * Hispanic, the people, nations, and cultures that have a historical link to Spain * Hispanic (other) * Hispanism * Spain (other) * National and regional identity in Spain * Culture of Spain * Spanish Fort (other) Spanish Fort or Old Spanish Fort may refer to: United States * Spanish Fort, Alabama, a city * Spanish Fort (Colorad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science And Technology In Spain
Science and technology in Spain relates to the set of policies, plans and programs carried out by the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation and other organizations aimed at research, development and innovation (R&D&I), as well as the reinforcement Spanish scientific and technological infrastructures and facilities such as universities and commercial laboratories. Spain has become the ninth scientific power in the world with 2.5% of the total number of scientific publications, thus surpassing Russia in the world ranking of scientific production and surpassing Switzerland and Australia in scientific quality. Regulations Science Law of 1986 Law 13/1986 on the "Promotion and General Coordination of Scientific and Technical Research" placed science for the first time on the Spanish political agenda, laying the foundations for research, as well as its financing, organization and coordination between the State and the autonomous regions. That regulation also led to the birt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science In Society
''Science In Society: An Introduction to Social Studies of Science'' () is a 2004 book by Massimiano Bucchi. The book explains how science works, what sociologists find to be of interest, and how scientific knowledge is produced. There are chapters on the relevance of science to contemporary life, Kuhn's work and its modern relevance, as well as the role of scientific communication.{{cite journal , url=http://www.sociology.org/content/2005/tier1/morrell_review.pdf , title=Book Review - Science in Society: an Introduction to Social Studies of Science , author=Morrell, Peter , journal=Electronic Journal of Sociology , year=2005 , issn=1198-3655 See also *List of books about the politics of science This is a list of notable books about the politics of science that have their own articles on Wikipedia. Environment * ''Merchants of Doubt, Merchants of Doubt: How a Handful of Scientists Obscured the Truth on Issues from Tobacco Smoke to Global ... References 2004 non-fiction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_by_Thomas_Degeorge.png)