|
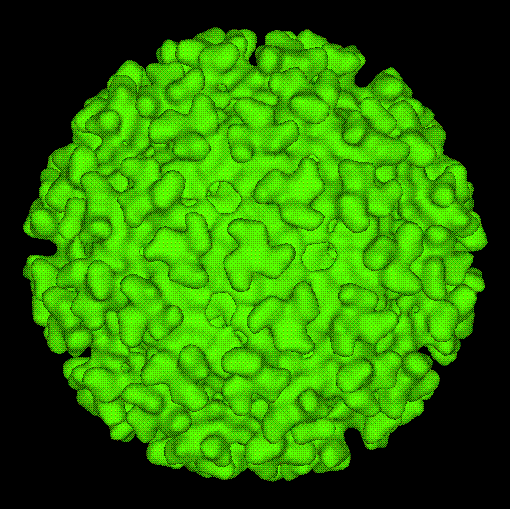
Eilat Virus
''Eilat virus'' (EILV) is a unique ''Alphavirus'' which is known mainly for its host range restriction generally to insects (primarily to mosquitoes) by means of RNA replication. The virus is found in the Negev desert. It is incapable of infecting vertebrate cells, differentiating it from other alphaviruses. Virology The ''Eilat virus'' is from the family ''Togaviridae'', genus ''Alphavirus''. Alphaviruses are miniature spherical shaped (around 70 nm in diameter) enveloped viruses which consist of a positive sense (5' to 3') RNA genome, which encompasses two ORF's (Open Reading Frame which is an incessant stretch of codons that do not contain a stop codon). Four nonstructural proteins are encoded on two thirds of the genome (5' end), which include nsP1, nsP2, nsP3, nsP4. While five structural proteins ( sPs; Capsid, E1, E2, E3, and 6K) are encoded on the one third part of the genome ( 3' portion). By receptor-mediated endocytosis alphaviruses gain entry into a host cell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alphavirus
''Alphavirus'' is a genus of RNA viruses, the sole genus in the ''Togaviridae'' family. Alphaviruses belong to group IV of the Baltimore classification of viruses, with a positive-sense, single-stranded RNA genome. There are 32 alphaviruses, which infect various vertebrates such as humans, rodents, fish, birds, and larger mammals such as horses, as well as invertebrates. Alphaviruses that could infect both vertebrates and arthropods are referred dual-host alphaviruses, while insect-specific alphaviruses such as Eilat virus and Yada yada virus are restricted to their competent arthropod vector. Transmission between species and individuals occurs mainly via mosquitoes, making the alphaviruses a member of the collection of arboviruses – or arthropod-borne viruses. Alphavirus particles are enveloped, have a 70 nm diameter, tend to be spherical (although slightly pleomorphic), and have a 40 nm isometric nucleocapsid. Genome The alphaviruses are small, spherical, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Texas Medical Branch
The University of Texas Medical Branch (UTMB) is a public academic health science center in Galveston, Texas. It is part of the University of Texas System. UTMB includes the oldest medical school in Texas, and has about 11,000 employees. In February 2019, it received an endowment of $560 million. Established in 1891 as the University of Texas Medical Department, UTMB has grown from one building, 23 students and 13 faculty members to more than 70 buildings, more than 2,500 students and more than 1,000 faculty. It has four schools, three institutes for advanced study, a comprehensive medical library, four on-site hospitals (including an affiliated Shriners Hospital for Children), a network of clinics that provide primary and specialized medical care and numerous research facilities. UTMB's primary missions are health sciences education, medical research (it is home to the Galveston National Laboratory) and health care services. Its emergency department at John Sealy Hospital is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mosquito-borne Disease
Mosquito-borne diseases or mosquito-borne illnesses are diseases caused by bacteria, viruses or parasites transmitted by mosquitoes. Nearly 700 million people get a mosquito-borne illness each year resulting in over 725,000 deaths. Diseases transmitted by mosquitoes include malaria, dengue, West Nile virus, chikungunya, yellow fever, filariasis, tularemia, dirofilariasis, Japanese encephalitis, Saint Louis encephalitis, Western equine encephalitis, Eastern equine encephalitis, Venezuelan equine encephalitis, Ross River fever, Barmah Forest fever, La Crosse encephalitis, and Zika fever, as well as newly detected Keystone virus and Rift Valley fever. There is no evidence as of April 2020 that COVID-19 can be transmitted by mosquitoes, and it is extremely unlikely this could occur. Types Protozoa The female mosquito of the genus ''Anopheles'' may carry the malaria parasite. Four different species of protozoa cause malaria: ''Plasmodium falciparum'', ''Plasmodium malariae'', ''P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or hair, and three middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles (including birds) from which they diverged in the Carboniferous, over 300 million years ago. Around 6,400 extant species of mammals have been described divided into 29 orders. The largest orders, in terms of number of species, are the rodents, bats, and Eulipotyphla (hedgehogs, moles, shrews, and others). The next three are the Primates (including humans, apes, monkeys, and others), the Artiodactyla ( cetaceans and even-toed ungulates), and the Carnivora (cats, dogs, seals, and others). In terms of cladistics, which reflects evolutionary history, mammals are the only living members of the Synapsida (synapsids); this clade, together with Saur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area and 20% of its land area.Sayre, April Pulley (1999), ''Africa'', Twenty-First Century Books. . With billion people as of , it accounts for about of the world's human population. Africa's population is the youngest amongst all the continents; the median age in 2012 was 19.7, when the worldwide median age was 30.4. Despite a wide range of natural resources, Africa is the least wealthy continent per capita and second-least wealthy by total wealth, behind Oceania. Scholars have attributed this to different factors including geography, climate, tribalism, colonialism, the Cold War, neocolonialism, lack of democracy, and corruption. Despite this low concentration of wealth, recent economic expansion and the large and young population make Afr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabian Peninsula, Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Anatolia, Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Province), East Thrace (European part of Turkey), Egypt, Iran, the Levant (including Syria (region), Ash-Shām and Cyprus), Mesopotamia (modern-day Iraq), and the Socotra Governorate, Socotra Archipelago (a part of Yemen). The term came into widespread usage as a replacement of the term Near East (as opposed to the Far East) beginning in the early 20th century. The term "Middle East" has led to some confusion over its changing definitions, and has been viewed by some to be discriminatory or too Eurocentrism, Eurocentric. The region includes the vast majority of the territories included in the closely associated definition of Western Asia (including Iran), but without the South Caucasus, and additionally includes all of Egypt (not just the Sina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venezuelan Equine Encephalitis Virus
Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus is a mosquito-borne viral pathogen that causes Venezuelan equine encephalitis or encephalomyelitis (VEE). VEE can affect all equine species, such as horses, donkeys, and zebras. After infection, equines may suddenly die or show progressive central nervous system disorders. Humans also can contract this disease. Healthy adults who become infected by the virus may experience flu-like symptoms, such as high fevers and headaches. People with weakened immune systems and the young and the elderly can become severely ill or die from this disease. The virus that causes VEE is transmitted primarily by mosquitoes that bite an infected animal and then bite and feed on another animal or human. The speed with which the disease spreads depends on the subtype of the VEE virus and the density of mosquito populations. Enzootic subtypes of VEE are diseases endemic to certain areas. Generally these serotypes do not spread to other localities. Enzootic subtypes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Equine Encephalitis Virus
The Western equine encephalomyelitis virus is the causative agent of relatively uncommon viral disease ''Western equine encephalomyelitis'' (WEE). An alphavirus of the family ''Togaviridae'', the WEE virus is an arbovirus (arthropod-borne virus) transmitted by mosquitoes of the genera ''Culex'' and ''Culiseta''. WEE is a recombinant virus between two other alphaviruses, an ancestral Sindbis virus-like virus, and an ancestral Eastern equine encephalitis virus-like virus. There have been under 700 confirmed cases in the U.S. since 1964. This virus contains an envelope that is made up of glycoproteins and nucleic acids. The virus is transmitted to people and horses by bites from infected mosquitoes ('' Culex tarsalis'' and '' Aedes taeniorhynchus'') and birds during wet, summer months. According to the CDC, geographic occurrence for this virus is worldwide, and tends to be more prevalent in places in and around swampy areas where human populations tend to be limited. In the U.S. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sindbis Virus
''Sindbis virus'' (SINV) is a member of the ''Togaviridae'' family, in the ''Alphavirus'' genus. The virus was first isolated in 1952 in Cairo, Egypt. The virus is transmitted by mosquitoes (''Culex'' and Culiseta). SINV is linked to Pogosta diseaseKurkela S, Manni T, Vaheri A, Vapalahti OCausative agent of Pogosta disease isolated from blood and skin lesions Emerg Infect Dis erial on the Internet Published 2004 May. (accessed 2007-10-16) (Finland), Ockelbo disease ( Sweden) and Karelian fever (Russia). In humans, the symptoms include arthralgia, rash and malaise. Sindbis virus is widely and continuously found in insects and vertebrates in Eurasia, Africa, and Oceania. Clinical infection and disease in humans however has almost only been reported from Northern Europe (Finland, Sweden, Russian Karelia), where SINV is endemic and where large outbreaks occur intermittently. Cases are occasionally reported in Australia, China, and South Africa. SINV is an arbovirus, it is arthro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intergenic Region
An intergenic region is a stretch of DNA sequences located between genes. Intergenic regions may contain functional elements and junk DNA. ''Inter''genic regions should not be confused with ''intra''genic regions (or introns), which are non-coding regions that are found ''within'' genes, especially within the genes of eukaryotic organisms. Properties and functions Intergenic regions may contain a number of functional DNA sequences such as promoters and regulatory elements, enhancers, spacers, and (in eukaryotes) centromeres. They may also contain origins of replication, scaffold attachment regions, and transposons and viruses. Non-functional DNA elements such as pseudogenes and repetitive DNA, both of which are types of junk DNA, can also be found in intergenic regions—although they may also be located within genes in introns. As all scientific knowledge is ultimately tentative—and in principle subject to revision given better evidence—it is possible s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |