|
Edward Pennefather
Edward Pennefather PC, KC (22 October 1774 – 6 September 1847) was an Irish barrister, Law Officer and judge of the Victorian era, who held office as Lord Chief Justice of Ireland. Early life Pennefather was born in Tipperary, the second son of William Pennefather of Knockeevan, member of the Irish House of Commons for Cashel, and his wife Ellen Moore, daughter of Edward Moore, Archdeacon of Emly and Ellen Dobson. He went to school in Clonmel and graduated from the University of Dublin. He was called to the Irish Bar in 1795. He lived at Rathsallagh House, near Dunlavin, County Wicklow. His brother Richard Pennefather (1773-1859) had a longer and more successful career as a judge: appointed a Baron of the Court of Exchequer in 1821, he served for nearly 40 years and was held in universal regard; with the general support of the profession he remained on the Bench until shortly before his death at eighty-six, by which time he was blind. Edward and Richard, "the two P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Privy Council Of Ireland
His or Her Majesty's Privy Council in Ireland, commonly called the Privy Council of Ireland, Irish Privy Council, or in earlier centuries the Irish Council, was the institution within the Dublin Castle administration which exercised formal executive power in conjunction with the chief governor of Ireland, who was viceroy of the British monarch. The council evolved in the Lordship of Ireland on the model of the Privy Council of England; as the English council advised the king in person, so the Irish council advised the viceroy, who in medieval times was a powerful Lord Deputy. In the early modern period the council gained more influence at the expense of the viceroy, but in the 18th century lost influence to the Parliament of Ireland. In the post-1800 United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, the Irish Privy Council and viceroy Lord Lieutenant had formal and ceremonial power, while policy formulation rested with a Chief Secretary directly answerable to the British cabinet. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Court Of Chancery (Ireland)
The Court of Chancery was a court which exercised equitable jurisdiction in Ireland until its abolition as part of the reform of the court system in 1877. It was the court in which the Lord Chancellor of Ireland presided. Its final sitting place was at the Four Courts in Dublin, which still stands. History The Chancery in Ireland was set up in 1232, following the model of the Court of Chancery of England. The court was abolished under the Supreme Court of Judicature Act (Ireland) 1877 and its jurisdiction transferred to the Chancery Division of the newly established High Court of Justice in Ireland, while the Lord Chancellor presided over the Court of Appeal in Ireland. In 1920, the High Court was split into separate courts for Northern Ireland and Southern Ireland under the Government of Ireland Act 1920. While the Northern Ireland court still maintains a separate Chancery Division, the Irish Free State abolished the divisions of the High Court under the Courts of Justice Ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bias
Bias is a disproportionate weight ''in favor of'' or ''against'' an idea or thing, usually in a way that is closed-minded, prejudicial, or unfair. Biases can be innate or learned. People may develop biases for or against an individual, a group, or a belief. In science and engineering, a bias is a systematic error. Statistical bias results from an unfair sampling of a population, or from an estimation process that does not give accurate results on average. Etymology The word appears to derive from Old Provençal into Old French ''biais'', "sideways, askance, against the grain". Whence comes French ''biais'', "a slant, a slope, an oblique". It seems to have entered English via the game of bowls, where it referred to balls made with a greater weight on one side. Which expanded to the figurative use, "a one-sided tendency of the mind", and, at first especially in law, "undue propensity or prejudice". Types of bias Cognitive biases A cognitive bias is a repeating or basic mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sedition
Sedition is overt conduct, such as speech and organization, that tends toward rebellion against the established order. Sedition often includes subversion of a constitution and incitement of discontent toward, or insurrection against, established authority. Sedition may include any commotion, though not aimed at direct and open violence against the laws. Seditious words in writing are seditious libel. A seditionist is one who engages in or promotes the interest of sedition. Because sedition is overt, it is typically not considered a subversive act, and the overt acts that may be prosecutable under sedition laws vary from one legal code to another. Roman origin ''Seditio'' () was the offence, in the later Roman Republic, of collective disobedience to a magistrate, including both military mutiny and civilian mob action. Leading or instigating a ''seditio'' was punishable by death. Civil ''seditio'' became frequent during the political crisis of the first century BCE, as pop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daniel O'Connell
Daniel O'Connell (I) ( ga, Dónall Ó Conaill; 6 August 1775 – 15 May 1847), hailed in his time as The Liberator, was the acknowledged political leader of Ireland's Roman Catholic majority in the first half of the 19th century. His mobilization of Catholic Ireland, down to the poorest class of tenant farmers, secured the final installment of Catholic emancipation in 1829 and allowed him to take a seat in the Parliament of the United Kingdom, United Kingdom Parliament to which he had been twice elected. At Palace of Westminster, Westminster, O'Connell championed liberal and reform causes (he was internationally renowned as an Abolitionism, abolitionist) but he failed in his declared objective for Ireland—the restoration of a separate Irish Parliament through the repeal of the Acts of Union 1800, 1800 Act of Union. Against the backdrop of a growing agrarian crisis and, in his final years, of the Great Famine (Ireland), Great Famine, O'Connell contended with dissension at home ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Peel Ministry
The second Peel ministry was formed by Sir Robert Peel in the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland in 1841. History Peel came to power for a second time after the Conservative victory in the General Election caused the Whig government of Lord Melbourne to resign. Henry Goulburn was Chancellor of the Exchequer, the future Prime Minister Lord Aberdeen Foreign Secretary and Sir James Graham Home Secretary. William Gladstone, who was yet to join the Liberal Party, became a member of the cabinet for the first time in 1843 when he was appointed President of the Board of Trade. His future rival Benjamin Disraeli was overlooked by Peel and was a sharp critic of the government. The government was brought down by Peel's decision in 1846 to support the repeal of the Corn Laws, leading to a split in the Tory party and the formation of a Whig government under Lord John Russell. Cabinet September 1841 – July 1846 Changes * October 1841: Lord FitzGerald succeeds Lord Ellen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Peel Ministry
Sir Robert Peel's first government succeeded the caretaker ministry of the Duke of Wellington. Peel was also Chancellor of the Exchequer while the Duke of Wellington served as Foreign Secretary. A young William Ewart Gladstone held office as a Junior Lord of the Treasury, his first governmental post in a ministerial career that would span for the next sixty years. The Peel ministry was a minority government, and relied on Whig support. However, this the Whigs felt disinclined to give, joining with the Irish radicals to defeat the Conservatives at every turn. After a reign of only four months, the government felt obliged to resign, whereupon the Whig leader Lord Melbourne formed his second government. Cabinet December 1834 – April 1835 List of ministers Members of the Cabinet are indicated by bold face. ;Notes References *C. Cook and B. Keith, ''British Historical Facts 1830–1900'' {{DEFAULTSORT:Peel 1 British ministries Government A governm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solicitor-General For Ireland
The Solicitor-General for Ireland was the holder of an Irish and then (from the Act of Union 1800) United Kingdom government office. The holder was a deputy to the Attorney-General for Ireland, and advised the Crown on Irish legal matters. On rare occasions, there was also a Deputy Attorney-General, who was distinct from the Solicitor-General. At least two holders of the office, Patrick Barnewall (1534–1550) and Sir Roger Wilbraham (1586-1603), played a leading role in Government, although in Barnewall's case this may be partly because he was also King's Serjeant. As with the Solicitor General for England and Wales, the Solicitor-General for Ireland was usually a barrister rather than a solicitor. The first record of a Solicitor General is in 1511, although the office may well be older than that since the records are incomplete. Early Solicitors almost always held the rank of Serjeant-at-law. In the sixteenth century a Principal Solicitor for Ireland shared the duties of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serjeant-at-law (Ireland)
This is a list of lawyers who held the rank of serjeant-at-law at the Irish Bar. Origins of the office of serjeant The first recorded serjeant was Roger Owen, who was appointed between 1261 and 1266, although the title itself was not commonly used in Ireland until about 1388; the earlier terms were "serviens", "King's Narrator" or "King's Pleader". The term Pleader was still in use in the 1470s. However, there is a reference to Richard le Blond as the King's "Serjeant pleader" in 1305 or 1306. In the early years of the office, appointment as serjeant might be temporary and might cover only a part of the country, although John de Neville was acting as Serjeant in 1295-6 "for all parts of Ireland". As a rule, they were licensed to appear in all of the Royal Courts, although John Haire in 1392 was described as "Serjeant-at-law of our Lord the King in the Common Pleas". The serjeant's duties were numerous and varied.Casey p.8 Early serjeants spent much time suing to recover Roya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attorney-General For Ireland
The Attorney-General for Ireland was an Irish and then (from the Act of Union 1800) United Kingdom government office-holder. He was senior in rank to the Solicitor-General for Ireland: both advised the Crown on Irish legal matters. With the establishment of the Irish Free State in 1922, the duties of the Attorney-General and Solicitor-General for Ireland were taken over by the Attorney General ''of'' Ireland. The office of Solicitor-General for Ireland was abolished for reasons of economy. This led to repeated complaints from the first Attorney General of Ireland, Hugh Kennedy, about the "immense volume of work" which he was now forced to deal with single-handedly. History of the Office The first record of the office of Attorney General for Ireland, some 50 years after the equivalent office was established in England, is in 1313, when Richard Manning was appointed King's Attorney (the title Attorney General was not used until the 1530s),Casey, James ''The Irish Law Officer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
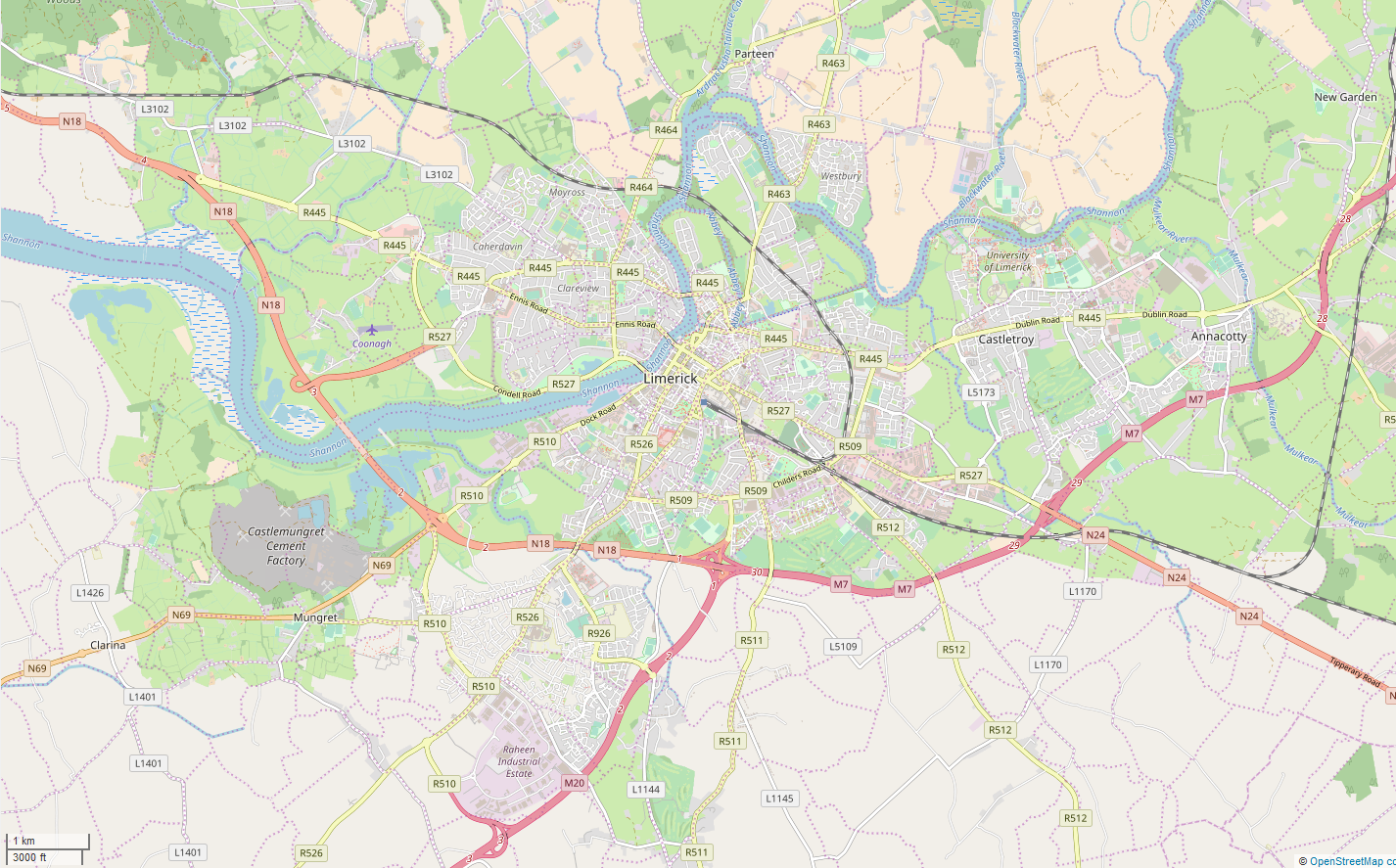
Limerick
Limerick ( ; ga, Luimneach ) is a western city in Ireland situated within County Limerick. It is in the province of Munster and is located in the Mid-West which comprises part of the Southern Region. With a population of 94,192 at the 2016 census, Limerick is the third-most populous urban area in the state, and the fourth-most populous city on the island of Ireland at the 2011 census. The city lies on the River Shannon, with the historic core of the city located on King's Island, which is bounded by the Shannon and Abbey Rivers. Limerick is also located at the head of the Shannon Estuary, where the river widens before it flows into the Atlantic Ocean. Limerick City and County Council is the local authority for the city. Geography and political subdivisions At the 2016 census, the Metropolitan District of Limerick had a population of 104,952. On 1 June 2014 following the merger of Limerick City and County Council, a new Metropolitan District of Limerick was formed within ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castleconnell
Castleconnell (, historically ''Caisleán Uí Chonaing'') is a village in County Limerick on the banks of the River Shannon. It is from Limerick city and near the boundaries of counties Clare and Tipperary. History The ruins of the ' Castle of Connell' (in fact the castle of a family named Gunning), from which the name of the village derives, was built on a rock outcrop overlooking the bend of the river. It was destroyed in a siege by the army of General Ginkel, fighting in support of the Army of William of Orange at the end of the 17th century. Even today a large chunk of the castle wall lies some fifty feet from the castle, thrown clear across the road by siege cannons. A footbridge over the Shannon - built during the 1939-1945 Emergency by the Irish Army under Captain Carley Owens - connects counties Limerick and Clare. The nearby Mountshannon House is a testament to John FitzGibbon, 1st Earl of Clare, who in the late 18th century was the Attorney-General for Ireland an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |