|
Edward Nicolls
Sir Edward Nicolls ( – 5 February 1865) was an Anglo-Irish officer of the Royal Marines. Known as "Fighting Nicolls", he had a distinguished military career. According to his obituary in ''The Times'', he was "in no fewer than 107 actions, in various parts of the world", and had "his left leg broken and his right leg severely injured, was shot through the body and right arm, had received a severe sabre cut in the head, was bayoneted in the chest, and had lost the sight of an eye." Nicolls was born in Coleraine, Ireland, in a family with a military tradition; his father was surveyor of excise in Coleraine, and his maternal grandfather was a rector. Nicolls spent his life as an intensely devout Ulster Protestant. He had two years of school in Greenwich, but enlisted in the Royal Navy at the age of 11. In 1795, at the age of 16, he received his first commission in the Royal Marines and soon began service with shipborne detachments of marines. During the N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Fitzwilliam Owen
Vice Admiral William Fitzwilliam Owen (17 September 1774 – 3 November 1857), was a British naval officer and explorer. He is best known for his exploration of the west and east African coasts, discovery of the Seaflower Channel off the coast of Sumatra and for surveying the Canadian Great Lakes. The illegitimate son of Captain William Owen he was orphaned at the age of four, however, his father's friend Rear-Admiral Sir Thomas Rich, kept an eye on both William and his elder brother Edward. In 1788 at age 13 he embarked as a midshipman in Rich's ship, , and from that time the Royal Navy was his life. Self-willed and boisterous, he had not infrequent difficulties early in his naval career. He served at home and on ships in the East Indies. He was commissioned as a lieutenant in 1797. In 1801 he took command of the fireship . In late 1801 the hired armed cutter ''King George'', under the command of a Mr. Yawkins, served under Nelson at his failed attack on Boulogne. On ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against France. The modern Royal Navy traces its origins to the early 16th century; the oldest of the UK's armed services, it is consequently known as the Senior Service. From the middle decades of the 17th century, and through the 18th century, the Royal Navy vied with the Dutch Navy and later with the French Navy for maritime supremacy. From the mid 18th century, it was the world's most powerful navy until the Second World War. The Royal Navy played a key part in establishing and defending the British Empire, and four Imperial fortress colonies and a string of imperial bases and coaling stations secured the Royal Navy's ability to assert naval superiority globally. Owing to this historical prominence, it is common, even among non-Britons, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commandant Of Ascension Island
The Administrator of Ascension is the head of government and representative of the Governor of St Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha in Ascension Island. The role of the Administrator includes that of chairing the territory's Island Council which consists of five or seven elected members. The Administrator of Ascension is formally referred to as "His Honour" or "Her Honour." As a part of the British overseas territory of Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha the head of state is Charles III Charles III (Charles Philip Arthur George; born 14 November 1948) is King of the United Kingdom and the 14 other Commonwealth realms. He was the longest-serving heir apparent and Prince of Wales and, at age 73, became the oldest person t ..., with the Governor appointed by the British government to act as her local representative. However, as Ascension Island is away from Saint Helena, an Administrator is appointed as the Governor's representative on the Island. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Nicolls' Outpost
The Treaty of Nicolls' Outpost is a little-known (because never ratified) treaty between Great Britain and the Red Stick Creek and other refugee Native Americans. Under it, Britain was to recognize the Native Americans as subjects of the Crown, and defend them and their territory from the United States. The treaty was the product of a March 10, 1815 meeting at Nicolls' Outpost, a small fortification built by Colonel Edward Nicolls just south of the U.S. (Georgia) border (in modern Chattahoochee, Florida). Attending, besides Nicolls, were four other British officers, Capt. George Woodbine, Capt. Joseph Ross, Henry Ross, and William Hambly, about to depart after the conclusion of the War of 1812 in early 1815. Representing the Native Americans were Neamathla, Francis the Prophet, Peter McQueen, Thomas Perryman, his son William Perryman, and more than thirty others, the whole of what was about to become a new ethnicity, the Seminoles. In the Treaty the Native Americans promised a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
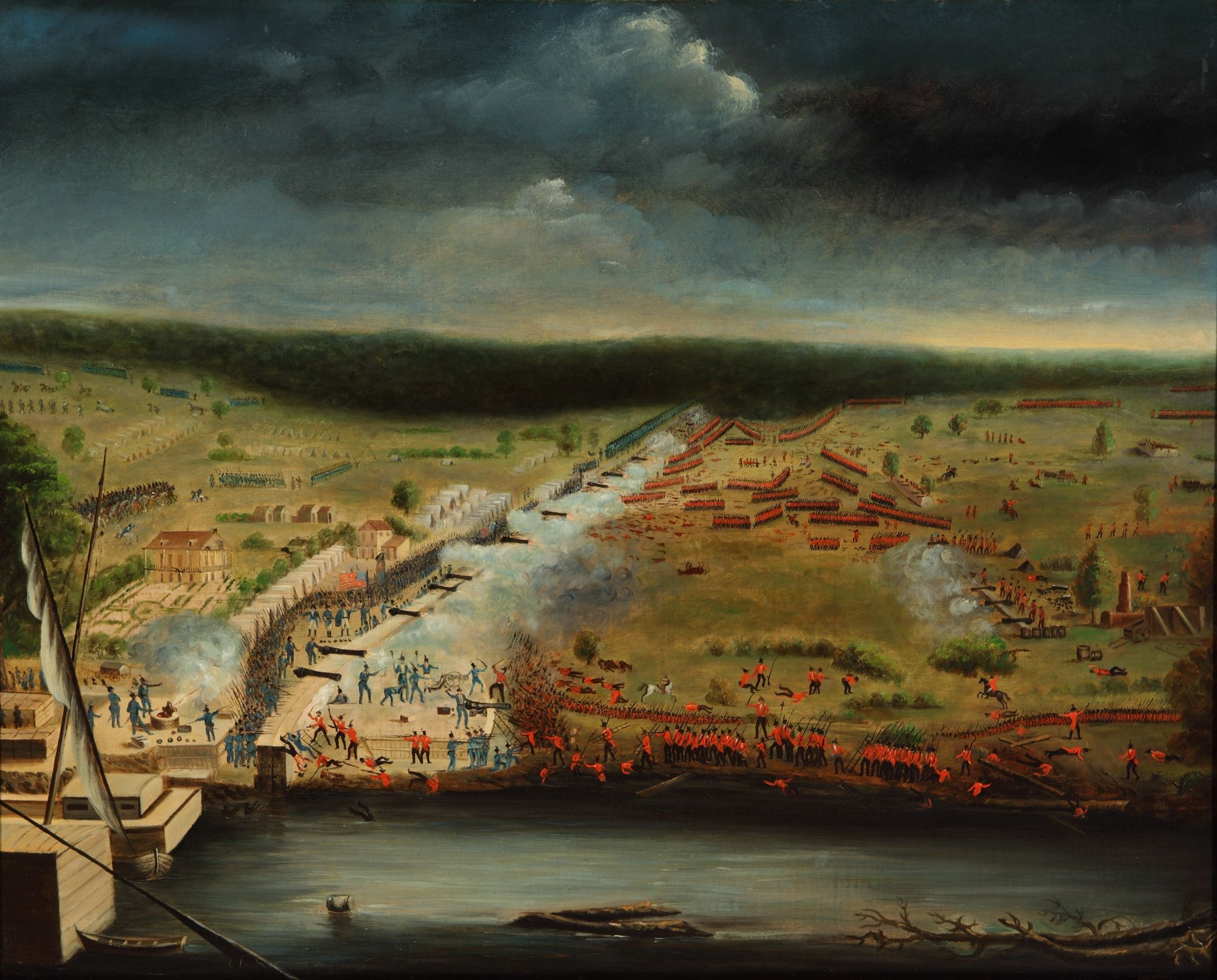
Battle Of New Orleans
The Battle of New Orleans was fought on January 8, 1815 between the British Army under Major General Sir Edward Pakenham and the United States Army under Brevet Major General Andrew Jackson, roughly 5 miles (8 km) southeast of the French Quarter of New Orleans, in the current suburb of Chalmette, Louisiana. The battle was the climax of the five-month Gulf Campaign (September 1814 to February 1815) by Britain to try to take New Orleans, West Florida, and possibly Louisiana Territory which began at the First Battle of Fort Bowyer. Britain started the New Orleans campaign on December 14, 1814, at the Battle of Lake Borgne and numerous skirmishes and artillery duels happened in the weeks leading up to the final battle. The battle took place 15 days after the signing of the Treaty of Ghent, which formally ended the War of 1812, on December 24, 1814, though it would not be ratified by the United States (and therefore did not take effect) until February 16, 1815, as new ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
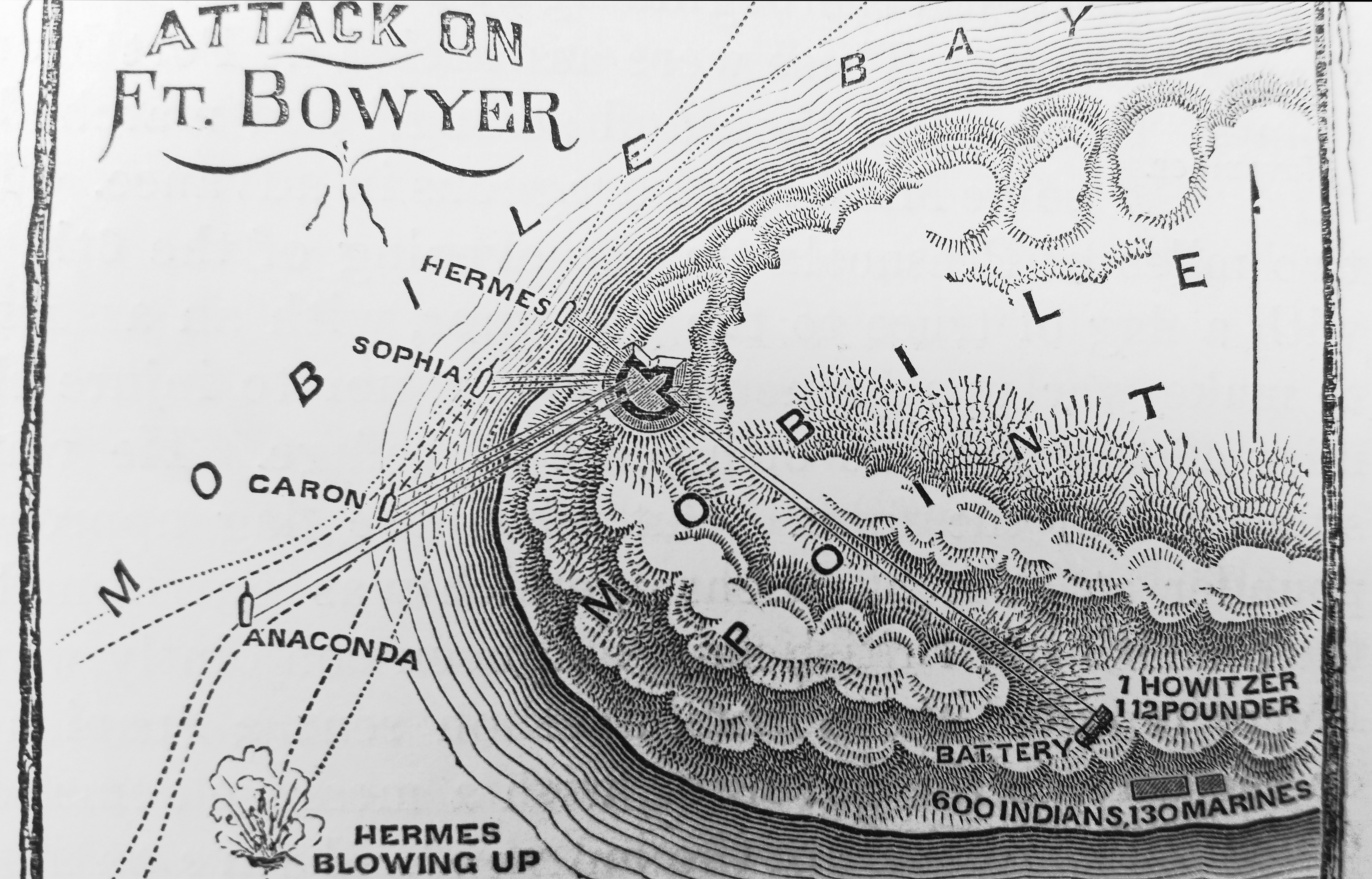
Fort Bowyer
Fort Bowyer was a short-lived earthen and stockade fortification that the United States Army erected in 1813 on Mobile Point, near the mouth of Mobile Bay in what is now Baldwin County, Alabama, but then was part of the Mississippi Territory. The British twice attacked the fort during the War of 1812. The first attack took place in September 1814; unsuccessful, it led to the British changing their strategy and attacking New Orleans. The second attack, following the Battle of New Orleans, was successful. It took place in February 1815, after the Treaty of Ghent had been signed but before the news had reached that part of America. Between 1819 and 1834 the United States built a new masonry fortification, Fort Morgan, on the site of Fort Bowyer. Construction Mobile had been a Spanish possession before the beginning of the Patriot War, but Congress had declared it American territory after the War of 1812 started. After Spanish forces evacuated Mobile in April 1813, the American ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corps Of Colonial Marines
The Corps of Colonial Marines were two different British Marine units raised from former black slaves for service in the Americas, at the behest of Alexander Cochrane. The units were created at two separate periods: 1808-1810 during the Napoleonic Wars; and then again during the War of 1812; both units being disbanded once the military threat had passed. Apart from being created in each case by Cochrane, they had no connection with each other. The first Corps was a small unit that served in the Caribbean from 1808 to 12 October 1810, recruited from former slaves to address the shortage of military manpower in the Caribbean. The locally-recruited men were less susceptible to tropical illnesses than were troops sent from Britain. The Corps followed the practice of the British Army's West India Regiments in recruiting former slaves as soldiers. In the previous year, the Mutiny Act of 1807 emancipated all slaves in the British Army and, as a result, subsequently enlisted slaves we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apalachicola River
The Apalachicola River is a river, approximately 160 mi (180 km) long in the state of Florida. The river's large watershed, known as the ACF River Basin, drains an area of approximately into the Gulf of Mexico. The distance to its farthest head waters in northeast Georgia is approximately 500 miles (800 km). Its name comes from the Apalachicola people, who used to live along the river. Description The river is formed on the state line between Florida and Georgia, near the town of Chattahoochee, Florida, approximately northeast of Panama City, by the confluence of the Flint and Chattahoochee rivers. The actual confluence is contained within the Lake Seminole reservoir formed by the Jim Woodruff Dam. It flows generally south through the forests of the Florida Panhandle, past Bristol. In northern Gulf County, it receives the Chipola River from the west. It flows into Apalachicola Bay, an inlet of the Gulf of Mexico, at Apalachicola, Florida. The lower of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
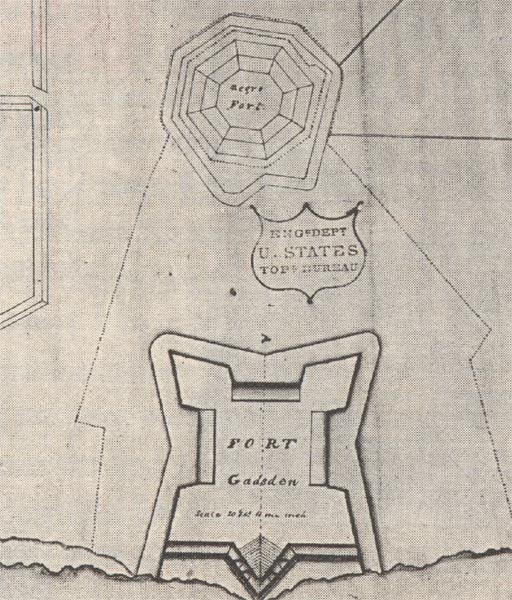
Prospect Bluff Historic Sites
Prospect Bluff Historic Sites (until 2016 known as Fort Gadsden Historic Site, and sometimes written as Fort Gadsden Historic Memorial) is located in Franklin County, Florida, on the Apalachicola River, SW of Sumatra, Florida. The site contains the ruins of two forts. The earlier and larger one was built by the British in 1814, during the War of 1812. They allowed the members of the disbanded Corps of Colonial Marines, made up largely of fugitive slaves, and Creek tribesmen to occupy it after the British evacuated Florida in 1815, deliberately leaving their munitions behind. At that point, since the British had not named it, Americans started referring to it as Negro Fort. It was destroyed in a river attack from U.S. forces in 1816. Fort Gadsden was built in 1818 within the former walls of the former Negro Fort. The site has been known by several other names at various times, including Prospect Bluff, British post, Nicholls' Fort, Blount's Fort, Fort Blount, African Fort, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Florida
Spanish Florida ( es, La Florida) was the first major European land claim and attempted settlement in North America during the European Age of Discovery. ''La Florida'' formed part of the Captaincy General of Cuba, the Viceroyalty of New Spain, and the Spanish Empire during Spanish colonization of the Americas. While its boundaries were never clearly or formally defined, the territory was initially much larger than the present-day state of Florida, extending over much of what is now the southeastern United States, including all of present-day Florida plus portions of Georgia, Alabama, Mississippi, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Louisiana. Spain's claim to this vast area was based on several wide-ranging expeditions mounted during the 16th century. A number of missions, settlements, and small forts existed in the 16th and to a lesser extent in the 17th century; they were eventually abandoned due to pressure from the expanding English and French colonial settlements, the col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperance Movement In Ireland
The Temperance movement in Ireland was an influential movement dedicated to lowering consumption of alcohol that involved both Protestant and Catholic religious leaders. In Ireland, a Catholic priest Theobald Mathew persuaded thousands of people to sign the pledge, therefore, establishing the Teetotal Abstinence Society in 1838. Many years later, in 1898, James Cullen founded the Pioneer Total Abstinence Association in response of the fading influence of the original temperance pledge. In 1829, the Presbyterian minister Rev. John Edgar initiated a temperance movement, by ''pouring his stock of whiskey out his window''.Peter Fryer (1965) ''Mrs Grundy: Studies in English Prudery'': 141-44. Corgi Also, many Orange lodges are "temperance lodges" and abstain from drinking. These particular lodges are more common in rural areas where the religious ethos of the organisation is more to the fore. References Ireland Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Native Americans In The United States
Native Americans, also known as American Indians, First Americans, Indigenous Americans, and other terms, are the Indigenous peoples of the mainland United States ( Indigenous peoples of Hawaii, Alaska and territories of the United States are generally known by other terms). There are 574 federally recognized tribes living within the US, about half of which are associated with Indian reservations. As defined by the United States Census, "Native Americans" are Indigenous tribes that are originally from the contiguous United States, along with Alaska Natives. Indigenous peoples of the United States who are not listed as American Indian or Alaska Native include Native Hawaiians, Samoan Americans, and the Chamorro people. The US Census groups these peoples as " Native Hawaiian and other Pacific Islanders". European colonization of the Americas, which began in 1492, resulted in a precipitous decline in Native American population because of new diseases, wars, ethni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |