|
Edward Killwick Calver
Edward Killwick Calver (6 December 1813 – 28 October 1892) was a Captain in the Royal Navy, and hydrographic surveyor. He is particularly noted for his surveying work in the east of Britain, and as the captain of , in oceanographic voyages in 1869 and 1870. Calver was born in Southwold in Suffolk. He entered the Navy in July 1828 on board ''HMS Crocodile'' on foreign service in the East Indies, where he was active in the search for pirates. In 1832 he joined , under the command of Robert Smart, being involved in the blockade of the Dutch Coast during the Belgian Revolution, Belgian war of independence, and then cruising for slavers off the coast of Brazil. He passed his examination for Second-Master in October 1834, and carried out many surveys, both in ''Crocodile'' and ''Satellite''. His surveying work was sufficiently appreciated at home that when he returned to England in April 1836 he was appointed Assistant-Surveyor to Michael Atwell Slater who was in charge of the survey ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
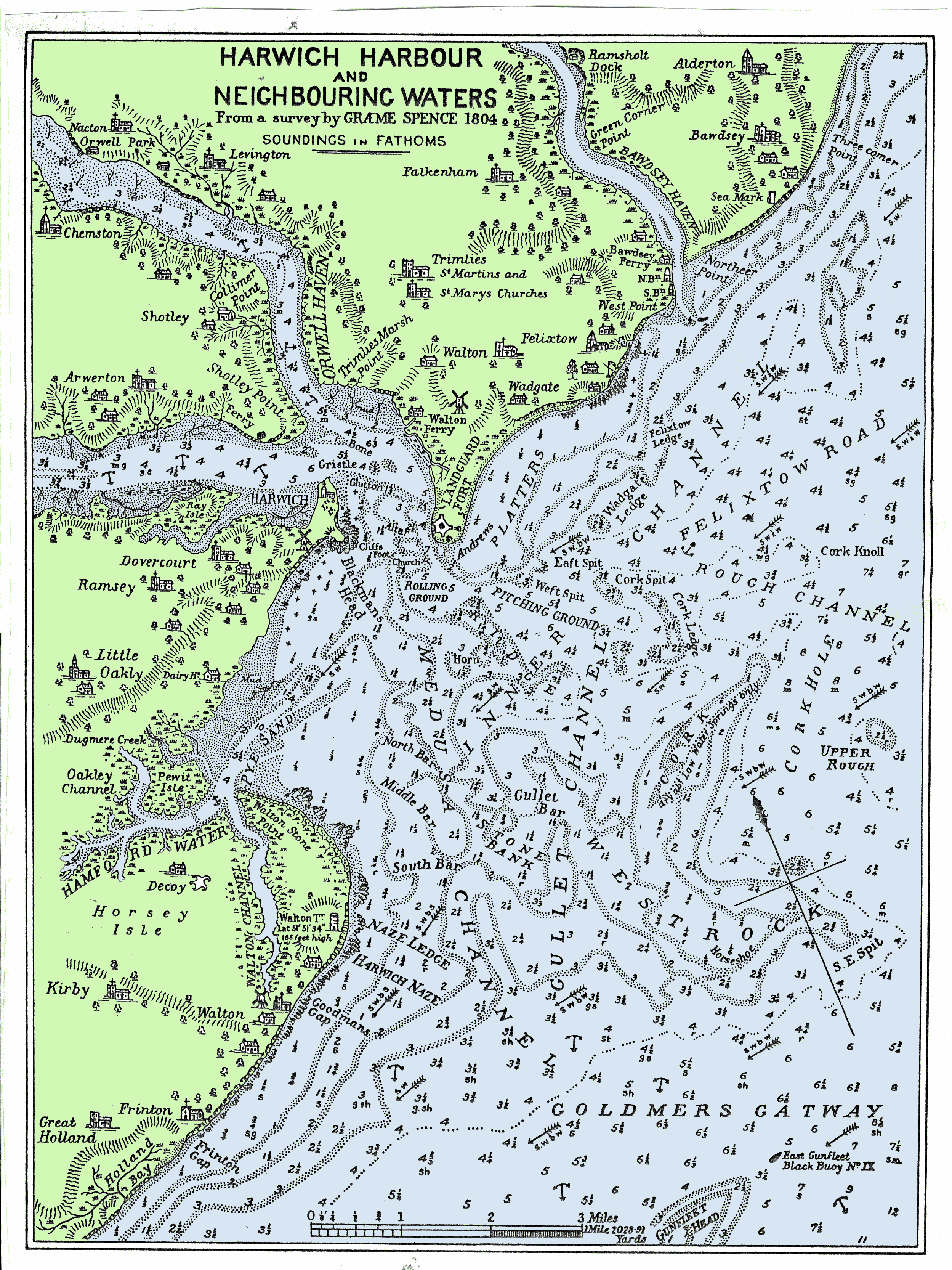
Harwich Harbour Reportofcommissi00grea 1 0033
Harwich is a town in Essex, England, and one of the Haven ports on the North Sea coast. It is in the Tendring district. Nearby places include Felixstowe to the north-east, Ipswich to the north-west, Colchester to the south-west and Clacton-on-Sea to the south. It is the northernmost coastal town in Essex. Its position on the estuaries of the Stour and Orwell rivers, with its usefulness to mariners as the only safe anchorage between the Thames and the Humber, led to a long period of civil and military maritime significance. The town became a naval base in 1657 and was heavily fortified, with Harwich Redoubt, Beacon Hill Battery, and Bath Side Battery. Harwich is the likely launch point of the '' Mayflower'', which carried English Puritans to North America, and is the presumed birthplace of ''Mayflower'' captain Christopher Jones. Harwich today is contiguous with Dovercourt and the two, along with Parkeston, are often referred to collectively as ''Harwich''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Thomas (surveyor)
George Thomas (26 February 1781 – 1850) was a Master in the Royal Navy who was one of the early surveyors of the coasts of Great Britain Early life and education Thomas was born in Southwark, son of William Thomas. At the age of eight, an orphan, he was admitted to Christ's Hospital, the first Bluecoat school. The last part of his education was in the Royal Mathematical School, where he learned the theory and practice of navigation. The mathematics master was William Wales who had revised Robertson's ''Elements of Navigation'', the standard work used at the Royal Naval Academy as well as the Royal Mathematical School. On the 2 June 1796 he was discharged to the whaling ship ''Commerce'' to serve as an apprentice for seven years. Pressed into the Royal Navy In November 1806, according to the UK National Archives, George Thomas was among a number of sailors from the American Brig ''Harry and Jane'' pressed into the Royal Navy after their ship was apprehended "trading wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel, St. Gallen a.o.). , coordinates = , largest_city = Zürich , official_languages = , englishmotto = "One for all, all for one" , religion_year = 2020 , religion_ref = , religion = , demonym = , german: Schweizer/Schweizerin, french: Suisse/Suissesse, it, svizzero/svizzera or , rm, Svizzer/Svizra , government_type = Federalism, Federal assembly-independent Directorial system, directorial republic with elements of a direct democracy , leader_title1 = Federal Council (Switzerland), Federal Council , leader_name1 = , leader_title2 = , leader_name2 = Walter Thurnherr , legislature = Fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vevey
Vevey (; frp, Vevê; german: label=former German, Vivis) is a town in Switzerland in the canton of Vaud, on the north shore of Lake Geneva, near Lausanne. The German name Vivis is no longer commonly used. It was the seat of the district of the same name until 2006, and is now part of the Riviera-Pays-d'Enhaut District. It is part of the French-speaking area of Switzerland. Vevey is home to the world headquarters of the international food and beverage company Nestlé, founded here in 1867. Milk chocolate was invented in Vevey by Daniel Peter in 1875, with the aid of Henri Nestlé. The English actor and comedian Charlie Chaplin resided in Vevey from 1952 until his death in 1977. History A piloti settlement existed here as early as the 2nd millennium BC. Under Rome, it was known as Viviscus or ''Vibiscum''. It was mentioned for the first time by the ancient Greek astronomer and philosopher Ptolemy, who gave it the name Ouikos. In the Middle Ages it was a station on the Via ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bathycrinus Gracilis
''Bathycrinus gracilis'' is a species of sea lily, a crinoid in the family Bathycrinidae Bathycrinidae is a family of echinoderms in the class Crinoidea Crinoids are marine animals that make up the class Crinoidea. Crinoids that are attached to the sea bottom by a stalk in their adult form are commonly called sea lilies, while th .... It is native to the North Atlantic. It was described by Charles Wyville Thomson. Distribution ''B. gracilis'' is found in the North Atlantic at a depth of around . References Bourgueticrinida Animals described in 1877 {{Crinoidea-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Challenger Expedition
The ''Challenger'' expedition of 1872–1876 was a scientific program that made many discoveries to lay the foundation of oceanography. The expedition was named after the naval vessel that undertook the trip, . The expedition, initiated by William Benjamin Carpenter, was placed under the scientific supervision of Sir Charles Wyville Thomson—of the University of Edinburgh and Merchiston Castle School—assisted by five other scientists, including Sir John Murray, a secretary-artist and a photographer. The Royal Society of London obtained the use of ''Challenger'' from the Royal Navy and in 1872 modified the ship for scientific tasks, equipping it with separate laboratories for natural history and chemistry. The expedition, led by Captain George Nares, sailed from Portsmouth, England, on 21 December 1872. Other naval officers included Commander John Maclear. – pages 19 and 20 list the civilian staff and naval officers and crew, along with changes that took place during the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
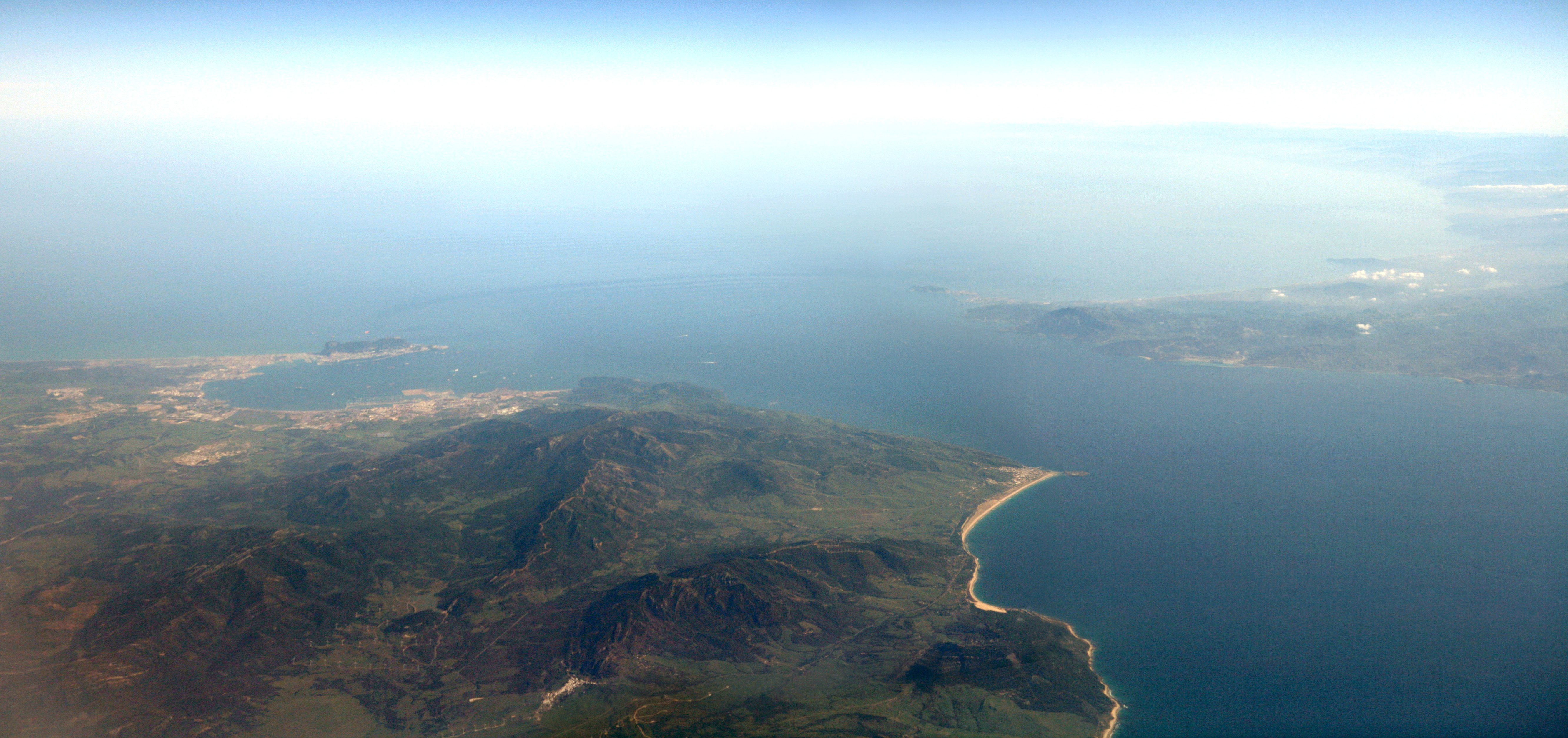
Strait Of Gibraltar
The Strait of Gibraltar ( ar, مضيق جبل طارق, Maḍīq Jabal Ṭāriq; es, Estrecho de Gibraltar, Archaic: Pillars of Hercules), also known as the Straits of Gibraltar, is a narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea and separates the Iberian Peninsula in Europe from Morocco in Africa. The two continents are separated by of ocean at the Strait's narrowest point between Point Marroquí in Spain and Point Cires in Morocco. Ferries cross between the two continents every day in as little as 35 minutes. The Strait's depth ranges between which possibly interacted with the lower mean sea level of the last major glaciation 20,000 years ago when the level of the sea is believed to have been lower by . The strait lies in the territorial waters of Morocco, Spain, and the British overseas territory of Gibraltar. Under the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea, foreign vessels and aircraft have the freedom of navigation and overflight t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isle Of Lewis
The Isle of Lewis ( gd, Eilean Leòdhais) or simply Lewis ( gd, Leòdhas, ) is the northern part of Lewis and Harris, the largest island of the Western Isles or Outer Hebrides archipelago in Scotland. The two parts are frequently referred to as if they were separate islands. The total area of Lewis is . Lewis is, in general, the lower-lying part of the island: the other part, Harris, is more mountainous. Due to its larger area and flatter, more fertile land, Lewis contains three-quarters of the population of the Western Isles, and the largest settlement, Stornoway. The island's diverse habitats are home to an assortment of flora and fauna, such as the golden eagle, red deer and seal, and are recognised in a number of conservation areas. Lewis has a Presbyterian tradition and a rich history. It was once part of the Norse Kingdom of the Isles. Today, life is very different from elsewhere in Scotland, with Sabbath observance, the Scottish Gaelic language and peat cutting retainin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faroe Islands
The Faroe Islands ( ), or simply the Faroes ( fo, Føroyar ; da, Færøerne ), are a North Atlantic island group and an autonomous territory of the Kingdom of Denmark. They are located north-northwest of Scotland, and about halfway between Norway ( away) and Iceland ( away). The islands form part of the Kingdom of Denmark, along with mainland Denmark and Greenland. The islands have a total area of about with a population of 54,000 as of June 2022. The terrain is rugged, and the subpolar oceanic climate (Cfc) is windy, wet, cloudy, and cool. Temperatures for such a northerly climate are moderated by the Gulf Stream, averaging above freezing throughout the year, and hovering around in summer and 5 °C (41 °F) in winter. The northerly latitude also results in perpetual civil twilight during summer nights and very short winter days. Between 1035 and 1814, the Faroe Islands were part of the Kingdom of Norway, which was in a personal union with Denmark from 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shetland
Shetland, also called the Shetland Islands and formerly Zetland, is a subarctic archipelago in Scotland lying between Orkney, the Faroe Islands and Norway. It is the northernmost region of the United Kingdom. The islands lie about to the northeast of Orkney, from mainland Scotland and west of Norway. They form part of the border between the Atlantic Ocean to the west and the North Sea to the east. Their total area is ,Shetland Islands Council (2012) p. 4 and the population totalled 22,920 in 2019. The islands comprise the Shetland (Scottish Parliament constituency), Shetland constituency of the Scottish Parliament. The local authority, the Shetland Islands Council, is one of the 32 council areas of Scotland. The islands' administrative centre and only burgh is Lerwick, which has been the capital of Shetland since 1708, before which time the capital was Scalloway. The archipelago has an oceanic climate, complex geology, rugged coastline, and many low, rolling hills. The lar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azoic Hypothesis
The Azoic hypothesis (sometimes referred to as the Abyssus theory) is a superseded scientific theory proposed by Edward Forbes in 1843, stating that the abundance and variety of marine life decreased with increasing depth and, by extrapolation of his own measurements, Forbes calculated that marine life would cease to exist below . Overview The theory was based upon Forbes' findings aboard , a survey ship to which he had been appointed naturalist by the ship's commander Captain Thomas Graves. With Forbes aboard, HMS ''Beacon'' set sail around the Aegean Sea on 17 April 1841, from Malta. It was at this point that Forbes began to take dredging samples at various depths of the ocean, he observed that samples from greater depths displayed a narrower diversity of creatures which were generally smaller in size. Forbes reported his findings from the Aegean Sea in his 1843 report to the British Association entitled ''Report on the Mollusca and Radiata of the Aegean Sea''. His finding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |