|
Edward Hartt
Edward Hartt (1825-1883) was a United States Navy constructor who oversaw or participated in the construction of many prominent ironclad and tinclad naval ships used during the American Civil War. Hart was born in 1825 in Portsmouth, New Hampshire, to ship builder Samuel Hartt. Hart was also a grandson of Edmund Hartt, builder of the USS ''Constitution''. Edward Hartt became a shipbuilder himself and participated in the construction of the ironclad USS ''Monitor'' (1862) and various gunboats for Commander Joseph B. Hull in St. Louis, Missouri, during the Civil War. Hartt oversaw the construction of the tinclads USS ''St. Clair'' and ''Brilliant'', the ironclads USS ''Choctaw'' and ''Lafayette, and the monitors USS ''Neosho'' and ''Osage''. He also converted various other vessels to be tinclad as well. The Navy eventually transferred Hartt with Hull to the Philadelphia Naval Shipyard The Philadelphia Naval Shipyard was an important naval shipyard of the United States fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
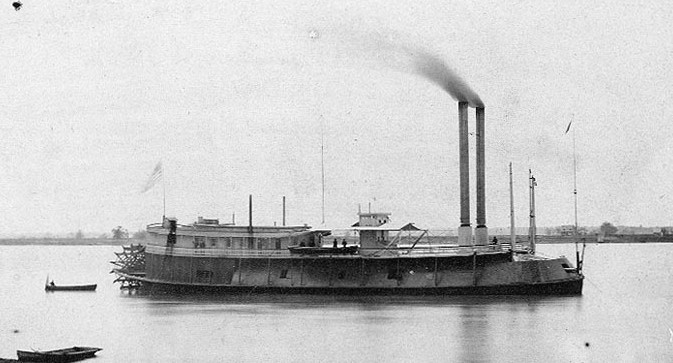
USS Brilliant (1862)
USS ''Brilliant'' was a steamer purchased by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was used by the Union Navy as a gunboat assigned to patrol Confederate waterways. ''Brilliant'', a wooden stern-wheel steamer, was built in 1862 at Brownsville, Pennsylvania, and purchased by the War Department, August 13, 1862 at St. Louis, Missouri and converted to tinclad by Edward Hartt; transferred to the Navy with the Western Flotilla October 1, 1862; and commissioned the following day. Acting Volunteer Lieutenant Charles G. Perkins in command. Assigned to the Mississippi Squadron After undergoing repairs ''Brilliant'' sailed from St. Louis, Missouri, September 25, 1862 to join the Mississippi Squadron at Cairo, Illinois. Throughout the Civil War she operated very actively on the Ohio, Cumberland, Tennessee, and Mississippi Rivers until August 2, 1865. Assisting in driving off Confederate attackers of Fort Donelson On February 3, 1863 she assisted in repelling the C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New London Navy Yard
Naval Submarine Base New London is the primary United States Navy East Coast submarine base, also known as the "Home of the Submarine Force." It is located in Groton, Connecticut directly across the Thames River from its namesake city of New London. History In 1868, the State of Connecticut gave the Navy of land along the Thames River in Groton to build a Naval Station. Due to a lack of federal funding, it was not until 1872 that two brick buildings and a T-shaped pier were constructed and officially declared a Navy Yard. In 1898, Congress approved a coaling station to be built at the Yard for refueling small naval ships traveling through the waters of New England. The Navy Yard was first used for laying up inactive ships. The Congressional appropriations were small and the Navy had little need for the yard, which was closed from 1898 to 1900 and its personnel reassigned. By 1912, oil replaced coal in warships and again the Yard was scheduled for closure and the land relinqui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philadelphia Naval Shipyard
The Philadelphia Naval Shipyard was an important naval shipyard of the United States for almost two centuries. Philadelphia's original navy yard, begun in 1776 on Front Street and Federal Street in what is now the Pennsport section of the city, was the first naval shipyard of the United States. It was replaced by a new, much larger yard developed around facilities begun in 1871 on League Island, at the confluence of the Delaware and Schuylkill rivers. The Navy Yard expansion stimulated the development over time of residential and businesses in South Philadelphia, where many shipyard workers lived. During World War II, some 40,000 workers operated on shifts around the clock to produce and repair ships at the yard for the war effort. The United States Navy ended most of its activities there in the 1990s, closing its base after recommendations by the Base Realignment and Closure commission. In 2000, the Philadelphia Industrial Development Corporation, on behalf of the city of Ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Osage (1863)
USS ''Osage'' was a single-turreted built for the Union Navy during the American Civil War. After completion in mid-1863 by Edward Hartt, the ship patrolled the Mississippi River against Confederate raids and ambushes as part of Rear Admiral David Porter's Mississippi Squadron. ''Osage'' participated in the Red River Campaign in March–May 1864, during which she supported the capture of Fort DeRussy in March and participated in the Battle of Blair's Landing in April. The ship was grounded on a sandbar for six months after the end of the campaign and badly damaged. ''Osage'', after being refloated and repaired, was transferred to the West Gulf Blockading Squadron in early 1865 for the campaign against Mobile, Alabama. During the Battle of Spanish Fort in March 1865 she struck a mine and rapidly sank. The ship was later salvaged and sold in 1867. Design and description The steam-powered gun turret of the ''Osage'' was at the bow and she had a deckhouse between the funnel and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Neosho (1863)
USS ''Neosho'', the lead ship of her class, was an ironclad river monitor laid down for the Union Navy in the summer of 1862 during the American Civil War. After completion in mid-1863, the ship spent time patrolling the Mississippi River against Confederate raids and ambushes as part of Rear Admiral David Porter's Mississippi Squadron. She participated in the Red River Campaign in March–May 1864. ''Neosho'' resumed her patrols on the Mississippi after the end of the campaign. She supported the Union Army's operations on the Cumberland River and provided fire support during the Battle of Nashville in December 1864. ''Neosho'' was decommissioned after the war and remained in reserve until sold in 1873. Design and description The steam-powered gun turret of the ''Neosho'' was at the bow. She had a single deckhouse between the funnel and the sternwheel, although another was later added between the turret and the funnel. Her pilothouse was positioned above the rear deckhouse, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Lafayette (1848)
The first USS ''Lafayette'' was a side wheel steamer, converted to an ironclad ram, in the United States Navy during the American Civil War. ''Lafayette'' was built at St. Louis, Missouri, in 1848 as ''Aleck Scott'' (often spelled ''Alick Scott''). She was purchased by the War Department as ''Fort Henry'' on 18 May 1862 for use in the western flotilla. She was converted to an ironclad ram at St. Louis by Edward Hartt. Renamed ''Lafayette'' on 8 September 1862, she was transferred to the Navy with the entire western flotilla by executive order on 1 October 1862. She was commissioned at Cairo, Illinois, 27 February 1863, with Captain Henry A. Walke in command. Service history Battle of Vicksburg, April–July 1863 The new ram joined Rear Admiral David Dixon Porter's Mississippi Squadron above Vicksburg in time for the famous dash on 16 April 1863 past the deadly batteries which protected the vital Confederate fortress. The gunboats engaged the southern guns as they shepher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Choctaw (1856)
USS ''Choctaw'' was a large (1,004-ton) steamer built for the merchant service, but acquired by the Union Navy during the second year of the American Civil War. ''Choctaw'', with her crew of 106, was outfitted by the Navy as a ram with heavy rifled guns and was used both as a gunboat and as a ram on the rivers of the Confederate States of America. Service history ''Choctaw'', a sidewheel steamer, was the first ship of the United States Navy to be named for the Choctaw Indian tribe, formerly of Alabama and Mississippi, now resident in Oklahoma. She was built for the merchant service; her keel was laid down at New Albany, Indiana, in 1853. She was launched in 1856. She was purchased by the United States Army The United States Army (USA) is the land warfare, land military branch, service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight Uniformed services of the United States, U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army o ... on 27 Septembe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ironclad
An ironclad is a steam engine, steam-propelled warship protected by Wrought iron, iron or steel iron armor, armor plates, constructed from 1859 to the early 1890s. The ironclad was developed as a result of the vulnerability of wooden warships to explosive or incendiary shell (projectile), shells. The first ironclad battleship, , was launched by the French Navy in November 1859 - narrowly pre-empting the British Royal Navy. They were first used in warfare in 1862 during the American Civil War, when ironclads operated against wooden ships and, in a historic confrontation, against each other at the Battle of Hampton Roads in Virginia. Their performance demonstrated that the ironclad had replaced the unarmored ship of the line as the most powerful warship afloat. City-class ironclad, Ironclad gunboats became very successful in the American Civil War. Ironclads were designed for several uses, including as high seas battleships, long-range cruisers, and Littoral (military), coast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph B
Joseph Ber Soloveitchik ( he, יוסף דב הלוי סולובייצ׳יק ''Yosef Dov ha-Levi Soloveychik''; February 27, 1903 – April 9, 1993) was a major American Orthodox rabbi, Talmudist, and modern Jewish philosopher. He was a scion of the Lithuanian Jewish Soloveitchik rabbinic dynasty. As a '' rosh yeshiva'' of Rabbi Isaac Elchanan Theological Seminary at Yeshiva University in New York City, The Rav, as he came to be known, ordained close to 2,000 rabbis over the course of almost half a century. Rabbinic literature sometimes refers to him as הגרי"ד, short for "The great Rabbi Yosef Dov". He served as an advisor, guide, mentor, and role-model for tens of thousands of Jews, both as a Talmudic scholar and as a religious leader. He is regarded as a seminal figure by Modern Orthodox Judaism. Heritage Joseph Ber Soloveitchik was born on February 27, 1903, in Pruzhany, Imperial Russia (later Poland, now Belarus). He came from a rabbinical dynasty dating back some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Monitor
USS ''Monitor'' was an ironclad warship built for the Union Navy during the American Civil War and completed in early 1862, the first such ship commissioned by the Navy. ''Monitor'' played a central role in the Battle of Hampton Roads on 9 March under the command of Lieutenant John L. Worden, where she fought the casemate ironclad (built on the hull of the scuttled steam frigate ) to a stalemate. The design of the ship was distinguished by its revolving turret, which was designed by American inventor Theodore Timby; it was quickly duplicated and established the monitor class and type of armored warship built for the American Navy over the next several decades. The remainder of the ship was designed by Swedish-born engineer and inventor John Ericsson, and built in only 101 days in Brooklyn, New York on the East River beginning in late 1861. ''Monitor'' presented a new concept in ship design and employed a variety of new inventions and innovations in ship building that caught ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |