|
Edward Fortunatus
Edward Fortunatus (or in German Eduard Fortunat) of Baden (17 September 1565 – 8 June 1600) was Margrave of Baden-Rodemachern and Baden-Baden. Life and work Born in London, Edward was the son of Christopher II, Margrave of Baden-Rodemachern and Swedish Princess Cecilia Vasa. He received his name from Queen Elizabeth I of England, who was his godmother. He spent his first year at Hampton Court Palace, England. When his father died in 1575, he became the Margrave of Baden-Rodemachern. His guardian, Duke William V of Bavaria, gave him a Catholic upbringing and in 1584 he converted from Lutheranism to Catholicism, as his mother had already done. The strife between Catholics and Protestants divided Edward's family, and on 18 November 1589 he hosted a colloquy in the Town Hall at Baden to discuss the relative claims of Catholicism (represented by Johann Pistorius), Lutheranism (represented by Andreä and Jacob Heerbrand), and Calvinism, represented by Schyrius, but it caused o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Zähringen
The House of Zähringen (german: Zähringer) was a dynasty of Swabian nobility. The family's name derived from Zähringen Castle near Freiburg im Breisgau. The Zähringer in the 12th century used the title of Duke of Zähringen, in compensation for having conceded the title of Duke of Swabia to the Staufer in 1098. The Zähringer were granted the special title of Rector of Burgundy in 1127, and they continued to use both titles until the extinction of the ducal line in 1218. The territories and fiefs held by the Zähringer were known as the 'Duchy of Zähringen' (), but it was not seen as a duchy in equal standing with the old stem duchies. The Zähringer attempted to expand their territories in Swabia and Burgundy into a fully recognized duchy, but their expansion was halted in the 1130s due to their feud with the Welfs. Pursuing their territorial ambitions, the Zähringer founded numerous cities and monasteries on either side of the Black Forest, as well as in the western S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernest Frederick, Margrave Of Baden-Durlach
Ernest Frederick of Baden-Durlach (born 17 October 1560 in Durlach – died 14 April 1604 in Remchingen) ruled the northern part of the Margraviate of Baden-Durlach. He came to power when he came of age in 1584. He founded the first Gymnasium ''Illustrie'' in the margraviate. His conversion from the Lutheranism to Calvinism and his occupation of Upper Baden caused serious conflicts – even with the Emperor – the consequences of which damaged Lower Baden and ultimately also led to losses of territory. Life Ernest Frederick was the eldest son of the Margrave Charles II of Baden-Durlach and Anna of Veldenz. From 1577 onwards, he received his education at the court of his guardian, the Lutheran Duke Louis III of Württemberg. The regency 1577–1584 After his father's death, a regency council was formed, consisting of his mother Anna, Elector Palatine Louis VI, Elector Palatine (until 1583), Duke Philip Louis of Neuburg and Duke Louis "the Pious" of Württemberg. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William, Margrave Of Baden-Baden
Margrave William of Baden-Baden (30 July 1593 – 22 May 1677) was the ruler of Baden-Baden between 1621 and 1677. Life Born in Baden-Baden, he was the eldest son of Margrave Edward Fortunatus of Baden and Maria of Eicken. He was Geheimrat, Generalfeldmarschall and Imperial ''Kammerrichter'' of Speyer, which gave him his nickname: ''Wilhelm der Kammerrichter''. Wilhelm was also a Knight in the Order of the Golden Fleece. He raised his grandson and successor Ludwig Wilhelm. Wilhelm only received the Regency of Baden after the victory of Johann Tserclaes, Count of Tilly in the Battle of Wimpfen over Georg Friedrich, Margrave of Baden-Durlach, whose brother Ernst Friedrich had occupied Baden-Baden in 1594. During the Regency of Wilhelm, Baden suffered from a terrible witch-hunt. Between 1626 and 1631, some 244 people, mostly women, were charged and 231 were condemned and burned in the Baden-Baden witch trials.Martin Burkart: Hexen und Hexenprozesse in Baden. Durmersheim 2009. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anna Maria Lukretia
Anna may refer to: People Surname and given name * Anna (name) Mononym * Anna the Prophetess, in the Gospel of Luke * Anna (wife of Artabasdos) (fl. 715–773) * Anna (daughter of Boris I) (9th–10th century) * Anna (Anisia) (fl. 1218 to 1221) * Anna of Poland, Countess of Celje (1366–1425) * Anna of Cilli (1386–1416) * Anna, Grand Duchess of Lithuania (died 1418) * Anne of Austria, Landgravine of Thuringia (1432–1462) * Anna of Nassau-Dillenburg (died 1514) * Anna, Duchess of Prussia (1576–1625) * Anna of Russia (1693–1740) * Anna, Lady Miller (1741–1781) * Anna Russell, Duchess of Bedford (1783–1857) * Anna, Lady Barlow (1873–1965) * Anna (feral child) (1932–1942) * Anna (singer) (born 1987) Places Australia * Hundred of Anna, a cadastral district in South Australia Iran * Anna, Fars, a village in Fars Province * Anna, Kohgiluyeh and Boyer-Ahmad, a village in Kohgiluyeh and Boyer-Ahmad Province Russia * Anna, Voronezh Oblast, an urban locality in Voron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Stångebro
The Battle of Stångebro, or the Battle of Linköping, took place at Linköping, Sweden, on 25 September 1598 (O.S.) and effectively ended the personal union between Sweden and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, that had existed since 1592. In the battle, an army of c. 8,000–12,000 commanded by Duke Charles defeated a mixed force of c. 5,000–8,000 consisting of an invading army of mercenaries in the king's employ and diverse but poorly co-ordinated supporting Swedish noblemen's forces commanded by King of both Sweden and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth Sigismund III Vasa, who was acting to maintain and restore his personal union against anti-Catholic forces in Lutheran Sweden. The Swedish king's general Constantin fought at the western bridge. The battle was the beginning of the seven decades long Polish–Swedish Wars, which eventually destroyed the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, at the time, arguably the largest nation state in Europe and also led to fall of Sw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles IX Of Sweden
Charles IX, also Carl ( sv, Karl IX; 4 October 1550 – 30 October 1611), reigned as King of Sweden from 1604 until his death. He was the youngest son of King Gustav I () and of his second wife, Margaret Leijonhufvud, the brother of King Eric XIV and of King John III, and the uncle of Sigismund, who became king both of Sweden and of Poland. By his father's will Charles received, by way of appanage, the Duchy of Södermanland, which included the provinces of Närke and Värmland; but he did not come into actual possession of them till after the fall of Eric and the succession to the throne of John in 1568. Both Charles and one of his predecessors, Eric XIV (), took their regnal numbers according to a fictitious history of Sweden. He was actually the third Swedish king called Charles. He came into the throne by championing the Protestant cause during the increasingly tense times of religious strife between competing sects of Christianity. Just under a decade after his death, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
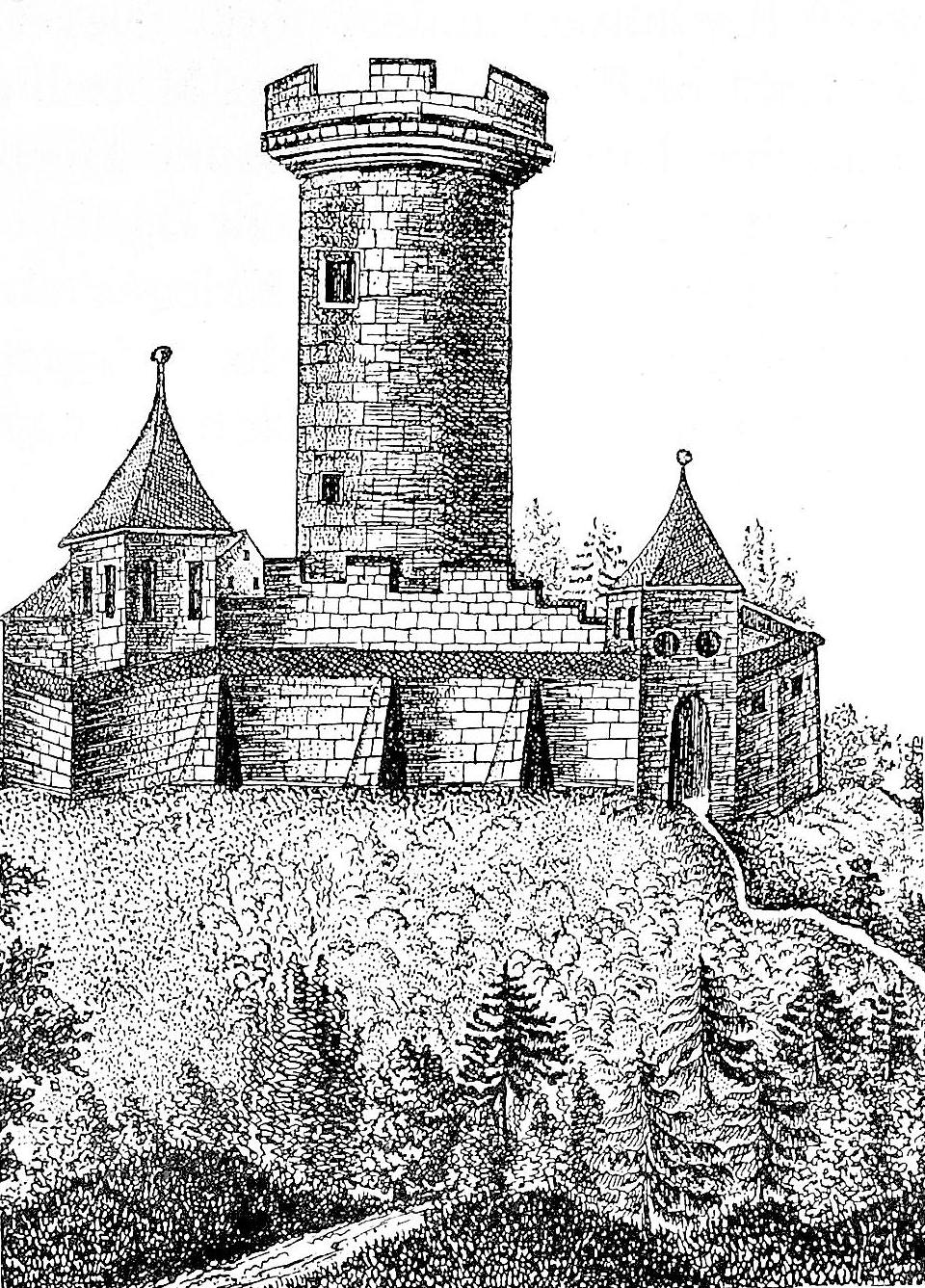
Yburg
The Yburg is a ruined hilltop castle atop the Yberg, on the western edge of the Black Forest near Baden-Baden, in southwestern Germany. History In 1190, Herman V, Margrave of Baden-Baden inherited the rights to the villages of Steinbach and Sinzheim. As the Yburg would have secured the Margraviate of Baden's new southwest border, it can be assumed that they built it at this time. The surrounding territory increasingly came under Baden's influence from mid-13th century on; Eberstein Castle was constructed nearby, Hohenbaden Castle was enlarged, and Steinbach was fortified and given the status of a township. Until 1369, the Yburg was administered by the Röder von Rodeck family, who served the House of Baden as civil servants. In the 15th century, under Margrave Bernhard I, a bailiff resided at Yburg, and it is likely the castle received its eastern annex for their residence. The Yburg was destroyed in 1525 during the German Peasants' War. In 1535, the Margraviate of Baden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kohlhammer Verlag
W. Kohlhammer Verlag GmbH, or Kohlhammer Verlag, is a German publishing house headquartered in Stuttgart. History Kohlhammer Verlag was founded in Stuttgart on 30 April 1866 by . Kohlhammer had taken over the businesses of his late father-in-law, a 120-year-old printer and a profitable . The printing business, operating out of the back of a commercial building at 14 Urbanstrasse, became W. Kohlhammer Verlag and was funded by proceeds from the bathhouse until it was closed in 1890. Kohlhammer purchased the ''Deutsche Feuerwehrzeitung'' in 1882 and printed that publication until 1923. In 1872 Kohlhammer started a weekly newspaper, the ''Neue Deutsche Familienblatt'' that by 1914 had a circulation of 185,000. Contemporary Employees of Kohlhammer joined those of other Stuttgart-based companies in early 2016 to petition the mayor to abate traffic congestion hindering their operations inside the city. In 2017, Kohlhammer Verlag employed about 400 people in Stuttgart, Würzburg and Aug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Pestalozzi
Paul may refer to: *Paul (given name), a given name (includes a list of people with that name) *Paul (surname), a list of people People Christianity *Paul the Apostle (AD c.5–c.64/65), also known as Saul of Tarsus or Saint Paul, early Christian missionary and writer *Pope Paul (other), multiple Popes of the Roman Catholic Church *Saint Paul (other), multiple other people and locations named "Saint Paul" Roman and Byzantine empire *Lucius Aemilius Paullus Macedonicus (c. 229 BC – 160 BC), Roman general *Julius Paulus Prudentissimus (), Roman jurist *Paulus Catena (died 362), Roman notary *Paulus Alexandrinus (4th century), Hellenistic astrologer *Paul of Aegina or Paulus Aegineta (625–690), Greek surgeon Royals *Paul I of Russia (1754–1801), Tsar of Russia *Paul of Greece (1901–1964), King of Greece Other people *Paul the Deacon or Paulus Diaconus (c. 720 – c. 799), Italian Benedictine monk *Paul (father of Maurice), the father of Maurice, Byzan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Magic
Black magic, also known as dark magic, has traditionally referred to the use of supernatural powers or magic for evil and selfish purposes, specifically the seven magical arts prohibited by canon law, as expounded by Johannes Hartlieb in 1456. During his period of scholarship, A. E. Waite provided a comprehensive account of black magic practices, rituals and traditions in ''The Book of Ceremonial Magic'' (1911). It is also sometimes referred to as the "left-hand path". In modern times, some find that the definition of black magic has been convoluted by people who define magic or ritualistic practices that they disapprove of as black magic. The seven ''Artes prohibitae'' of black magic The seven ''artes prohibitae'' or ''artes magicae'', arts prohibited by canon law, as expounded by Johannes Hartlieb in 1456, their sevenfold partition reflecting that of the artes liberales and artes mechanicae, were: #necromancy #geomancy #hydromancy #aeromancy #pyromancy #chiromancy #scap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alchemy
Alchemy (from Arabic: ''al-kīmiyā''; from Ancient Greek: χυμεία, ''khumeía'') is an ancient branch of natural philosophy, a philosophical and protoscientific tradition that was historically practiced in China, India, the Muslim world, and Europe. In its Western form, alchemy is first attested in a number of pseudepigraphical texts written in Greco-Roman Egypt during the first few centuries AD.Principe, Lawrence M. The secrets of alchemy'. University of Chicago Press, 2012, pp. 9–14. Alchemists attempted to purify, mature, and perfect certain materials. Common aims were chrysopoeia, the transmutation of "base metals" (e.g., lead) into "noble metals" (particularly gold); the creation of an elixir of immortality; and the creation of panaceas able to cure any disease. The perfection of the human body and soul was thought to result from the alchemical ''magnum opus'' ("Great Work"). The concept of creating the philosophers' stone was variously connected with all of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |