|
Edward Bury
Edward Bury (22 October 1794 – 25 November 1858) was an English locomotive manufacturer. Born in Salford, Lancashire, he was the son of a timber merchant and was educated at Chester. Career By 1823 he was a partner in Gregson and Bury's steam sawmill at Toxteth Park, Liverpool, but in 1826 he set himself up as an iron-founder and engineer. His original premises were in Tabley Street near the Liverpool and Manchester Railway's workshops. He hoped to supply locomotives to that line, but opposition from the L&M Engineer, George Stephenson, thwarted this. Clarence Foundry & Steam Engine Works He moved his works to new premises in Love Lane, Liverpool, on the Leeds and Liverpool Canal and near the Clarence Dock, hence the name 'Clarence Foundry and Steam Engine Works'. Around this time he recruited as his manager James Kennedy, who had gained locomotive building experience working for George Stephenson and Mather, Dixon and Company. The first locomotive built by Edward Bury and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salford, Greater Manchester
Salford () is a city and the largest settlement in the City of Salford metropolitan borough in Greater Manchester, England. In 2011, Salford had a population of 103,886. It is also the second and only other city in the metropolitan county after neighbouring Manchester. Salford is located in a meander of the River Irwell which forms part of its boundary with Manchester. The former County Borough of Salford, which also included Broughton, Pendleton and Kersal, was granted city status in 1926. In 1974 the wider Metropolitan Borough of the City of Salford was established with responsibility for a significantly larger region. Historically in Lancashire, Salford was the judicial seat of the ancient hundred of Salfordshire. It was granted a charter by Ranulf de Blondeville, 6th Earl of Chester, in about 1230, making Salford a free borough of greater cultural and commercial importance than its neighbour Manchester.. The Industrial Revolution of the late 18th and early 19th centu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liverpool
Liverpool is a City status in the United Kingdom, city and metropolitan borough in Merseyside, England. With a population of in 2019, it is the List of English districts by population, 10th largest English district by population and its ESPON metropolitan areas in the United Kingdom, metropolitan area is the fifth largest in the United Kingdom, with a population of 2.24 million. On the eastern side of the Mersey Estuary, Liverpool historically lay within the ancient Hundred (county division), hundred of West Derby (hundred), West Derby in the county of Lancashire. It became a Borough status in the United Kingdom, borough in 1207, a City status in the United Kingdom, city in 1880, and a county borough independent of the newly-created Lancashire County Council in 1889. Its Port of Liverpool, growth as a major port was paralleled by the expansion of the city throughout the Industrial Revolution. Along with general cargo, freight, and raw materials such as coal and cotton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
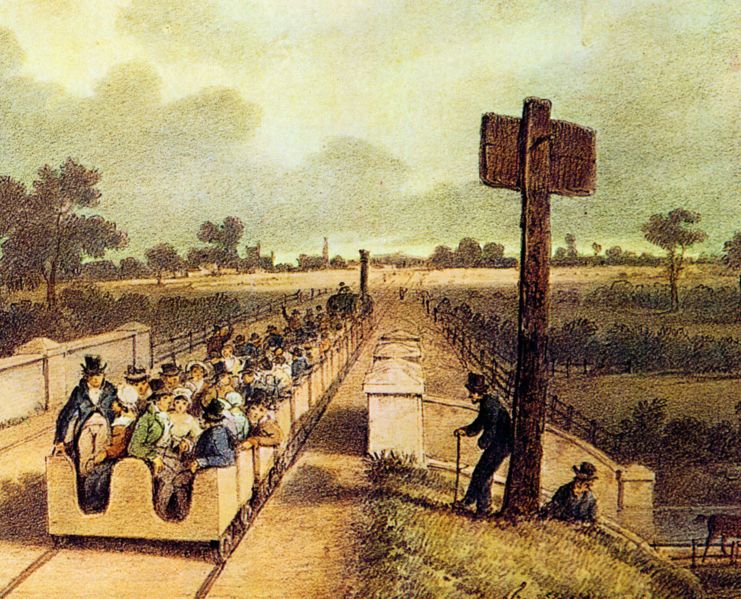
Liverpool & Manchester Railway
The Liverpool and Manchester Railway (L&MR) was the first inter-city railway in the world. It opened on 15 September 1830 between the Lancashire towns of Liverpool and Manchester in England. It was also the first railway to rely exclusively on locomotives driven by steam power, with no horse-drawn traffic permitted at any time; the first to be entirely double track throughout its length; the first to have a true signalling system; the first to be fully timetabled; and the first to carry mail. Trains were hauled by company steam locomotives between the two towns, though private wagons and carriages were allowed. Cable haulage of freight trains was down the steeply-graded Wapping Tunnel to Liverpool Docks from Edge Hill junction. The railway was primarily built to provide faster transport of raw materials, finished goods and passengers between the Port of Liverpool and the cotton mills and factories of Manchester and surrounding towns. Designed and built by George Steph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
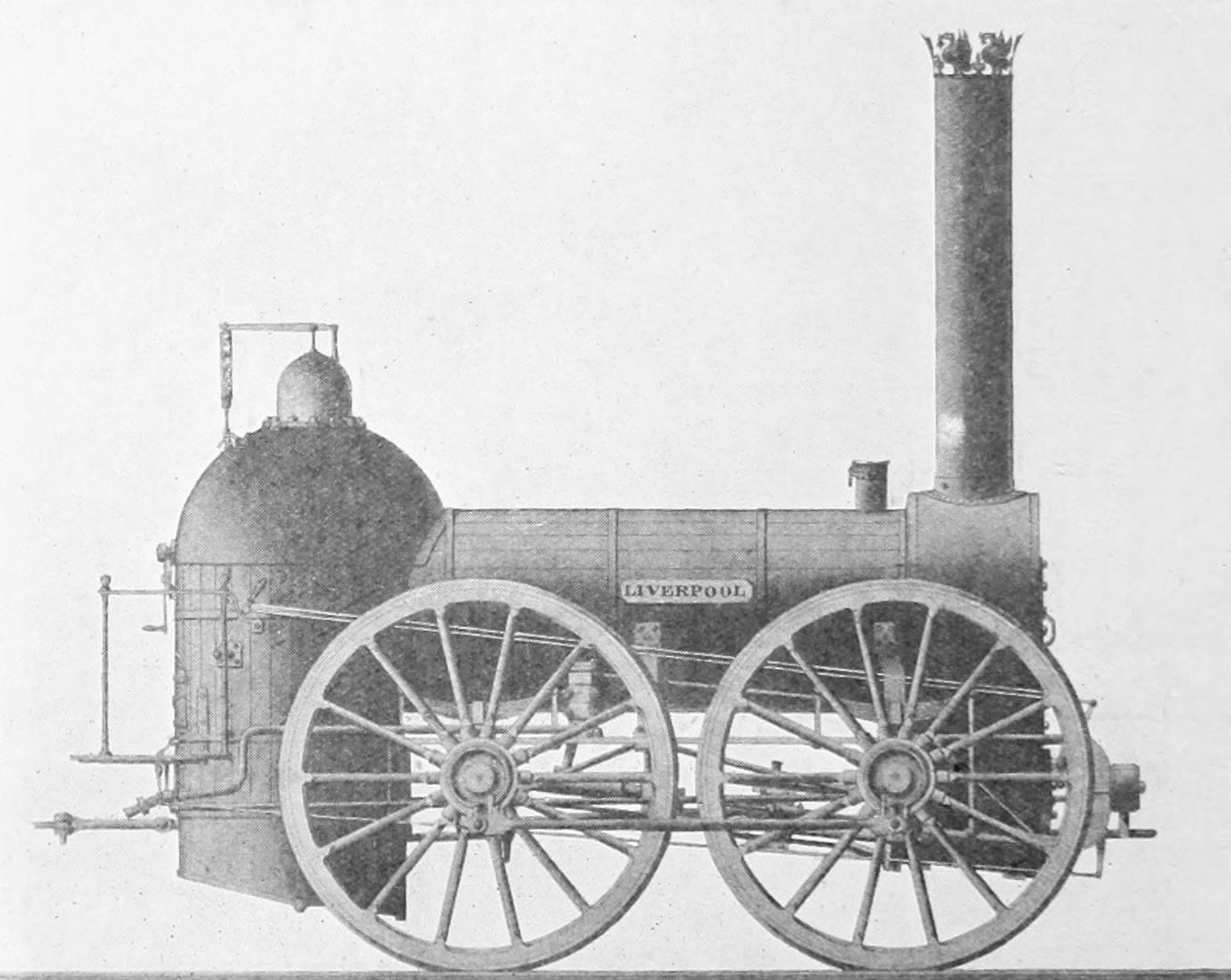
Liverpool (1840 Locomotive)
Liverpool is a city and metropolitan borough in North West England. With a population of 486,100 in 2021, it is located within the county of Merseyside and is the principal city of the wider Liverpool City Region. Its metropolitan area is the fifth largest in the United Kingdom, with a population of 2.24 million. On the eastern side of the Mersey Estuary, Liverpool historically lay within the ancient hundred of West Derby in the county of Lancashire. It became a Borough status in the United Kingdom, borough in 1207, a City status in the United Kingdom, city in 1880, and a county borough independent of the newly-created Lancashire County Council in 1889. Its Port of Liverpool, growth as a major port was paralleled by the expansion of the city throughout the Industrial Revolution. Along with general cargo, freight, and raw materials such as coal and cotton, merchants were involved in the Atlantic slave trade, slave trade. In the 19th century, Liverpool was a major port ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bury 0-4-0 "Liverpool", 1830
Bury may refer to: *The burial of human remains *-bury, a suffix in English placenames Places England * Bury, Cambridgeshire, a village * Bury, Greater Manchester, a town, historically in Lancashire ** Bury (UK Parliament constituency) (1832–1950) ***Bury and Radcliffe (UK Parliament constituency) (1950–1983) ***Bury North (UK Parliament constituency), from 1983 ***Bury South (UK Parliament constituency), from 1983 ** County Borough of Bury, 1846–1974 ** Metropolitan Borough of Bury, from 1974 ** Bury Rural District, 1894–1933 * Bury, Somerset, a hamlet * Bury, West Sussex, a village and civil parish ** Bury (UK electoral ward) * Bury St Edmunds, a town in Suffolk, commonly referred to as Bury * New Bury, a suburb of Farnworth in the Bolton district of Greater Manchester Elsewhere * Bury, Hainaut, Belgium, a village in the commune of Péruwelz, Wallonia * Bury, Quebec, Canada, a municipality * Bury, Oise, France, a commune Sports * Bury (professional wrestling), a slang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolton And Leigh Railway
The Bolton and Leigh Railway (B&LR) was the first public railway in Lancashire, it opened for goods on 1 August 1828 preceding the Liverpool and Manchester Railway (L&MR) by two years. Passengers were carried from 1831. The railway operated independently until 1845 when it became part of the Grand Junction Railway. Background Bolton was situated on the Manchester, Bolton and Bury Canal and Leigh straddled a major east–west canal route, to the west ran the Leeds and Liverpool Canal and joined to it in the center of Leigh was the Bridgewater Canal running east. The canals provided freight routes to both Liverpool and Manchester. The canals of the time were the major freight routes being faster and able to transport greater loads than the carriers using the turnpike road system. But, unfortunately, these canal routes were slow, becoming congested, and increasingly more expensive as demand from the rapidly expanding businesses in the area increased. The waterways had a virtua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
0-6-0
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of no leading wheels, six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles and no trailing wheels. This was the most common wheel arrangement used on both tender and tank locomotives in versions with both inside and outside cylinders. In the United Kingdom, the Whyte notation of wheel arrangement was also often used for the classification of electric and diesel-electric locomotives with side-rod coupled driving wheels. Under the UIC classification, popular in Europe, this wheel arrangement is written as C if the wheels are coupled with rods or gears, or Co if they are independently driven, the latter usually being electric and diesel-electric locomotives. Overview History The 0-6-0 configuration was the most widely used wheel arrangement for both tender and tank steam locomotives. The type was also widely used for diesel switchers (shunters). Because they lack leading and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Bury And Company
Bury, Curtis and Kennedy was a steam locomotive manufacturer in Liverpool, England. Edward Bury established the works in 1826, under the name Edward Bury and Company. He employed James Kennedy as foreman; Kennedy later became a partner. About 1828, the firm moved to bigger premises in Love Lane, Liverpool, known as the Clarence Foundry. Locomotives Their first engine was built in 1830. Called ''Dreadnought'', it ran on the Liverpool and Manchester Railway. It was objected to because it was on six wheels and was sold to the Bolton & Leigh Railway. The second, the four-coupled ''Liverpool'', later in 1830, used a cranked driving axle, and was also objected to (by George Stephenson) because the 6 ft diameter wheels were too big. The Bury type However, they refined their designs and the resulting and locomotives quickly became a standard which was emulated by many other manufacturers, becoming known as the "Bury type". Distinguishing features of these engines were inside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mather, Dixon And Company
Mather, Dixon and Company was an engineering firm in Liverpool, England. It was established in 1826 at the Bath Street Foundry to build marine and stationary steam engines. Production of steam locomotives began in 1827. Products Early years The first engine was a small four-coupled tank locomotive in 1827, in addition to a steam traverser and two mobile cranes. These were for their own use, their main business being marine and stationary engines. Contracts from Edward Bury and Company They received contracts from Edward Bury and Company for three engines for the Petersburg Railroad. Two were four coupled and the other was a four-wheeled single, completed in 1833. The following year a number of orders were fulfilled for tank engines among other equipment. Six wheeled engines In 1836 they had four designs for six wheeled engines: , , and , which they built initially for display purposes. Standard and broad gauge locomotives Between 1836 and 1839 they supplied engines for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Kennedy (engineer)
James Kennedy (13 January 1797 – 25 September 1886) was a Scottish locomotive and marine engineer. He was born in the village of Gilmerton near Edinburgh, Scotland. Career Early years He was apprenticed at the age of 13 to a millwright near Dalkeith, where he remained for five years. He spent some years working as a millwright, working with winding and pumping engines at several places before moving to Laverock Hall (now Larkhall) near Hamilton, where he was employed to erect pumping and winding engines of his own design. Robert Stephenson and Company In Liverpool to supervise the installation of a marine engine, he met George Stephenson, who was then establishing his locomotive works, Robert Stephenson and Company, at Newcastle-upon-Tyne. Stephenson appointed Kennedy manager in 1824. While in this post, Kennedy constructed two pairs of stationary winding engines and planned the first three locomotives for the opening of the Stockton and Darlington Railway in 1825. Bury, Cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clarence Dock (Liverpool)
Clarence Dock was a dock on the River Mersey, England, and part of the Port of Liverpool. Situated in the northern dock system in Vauxhall, it was connected to Trafalgar Dock. History Designed by Jesse Hartley, the dock opened on 16 September 1830. Clarence Dock was named after William, Duke of Clarence, who became William IV. It was built as a self-contained steamship dock facility. This was to avoid the risk of fire to wooden-hulled sailing vessels then using the other docks. The dock was the principal berth for the Irish ferry ships. During the Irish famine in the 1840s over 1.3 million Irish people travelled through the dock. After many weeks or months, many took a ship to America from Waterloo Dock, there being fewer direct sailings to America from Ireland at this time. However many thousands made their home in Liverpool. Others moved to London and other British towns and cities in search of work. The dock closed in 1928, and in 1929 was filled in when the site was rede ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


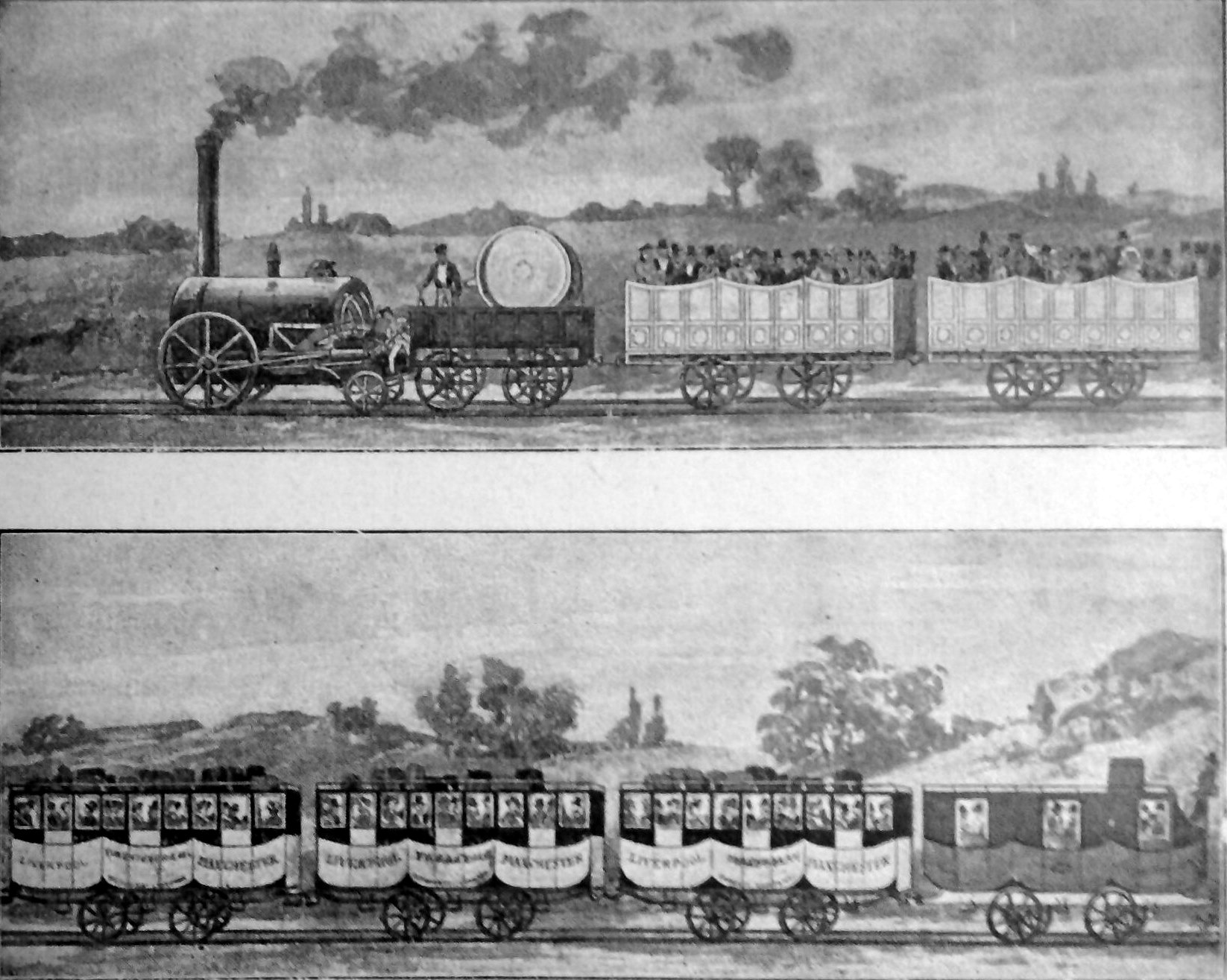

.jpg)

