|
Edoardo Bassini
Edoardo Bassini (April 14, 1844 – July 19, 1924) was an Italian surgeon born in Pavia. In 1866 he received his medical degree from the University of Pavia, and afterwards joined the Italian Unification movement as an infantry soldier under Giuseppe Garibaldi (1807–1882). In 1867 he was seriously wounded and taken prisoner. Following his release and recovery, he traveled throughout Europe, furthering his medical studies. He learned surgical procedures in Vienna under Theodor Billroth (1829–1894), in Berlin under Bernhard von Langenbeck (1810–1887), and in Munich with Johann Nepomuk von Nussbaum (1829–1890). He also visited London, where he met with Thomas Spencer Wells (1818–1897) and Joseph Lister (1827–1912). Afterwards, he was in charge of the surgical department at the hospital La Spezia, and in 1878 became a lecturer in surgery at Parma. In 1882 he became head of surgical pathology at the University of Padua, where he later succeeded Tito Vanzetti (1809–1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portrait Of Edoardo Bassini Wellcome M0017969
A portrait is a painting, photograph, sculpture, or other artistic representation of a person, in which the face and its expressions are predominant. The intent is to display the likeness, personality, and even the mood of the person. For this reason, in photography a portrait is generally not a snapshot, but a composed image of a person in a still position. A portrait often shows a person looking directly at the painter or photographer, in order to most successfully engage the subject with the viewer. History Prehistorical portraiture Plastered human skulls were reconstructed human skulls that were made in the ancient Levant between 9000 and 6000 BC in the Pre-Pottery Neolithic B period. They represent some of the oldest forms of art in the Middle East and demonstrate that the prehistoric population took great care in burying their ancestors below their homes. The skulls denote some of the earliest sculptural examples of portraiture in the history of art. Historical portraitu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Padua
The University of Padua ( it, Università degli Studi di Padova, UNIPD) is an Italian university located in the city of Padua, region of Veneto, northern Italy. The University of Padua was founded in 1222 by a group of students and teachers from Bologna. Padua is the second-oldest university in Italy and the world's fifth-oldest surviving university. In 2010, the university had approximately 65,000 students. In 2021, it was ranked second "best university" among Italian institutions of higher education with more than 40,000 students according to Censis institute, and among the best 200 universities in the world according to ARWU. History The university is conventionally said to have been founded in 1222 when a large group of students and professors left the University of Bologna in search of more academic freedom ('Libertas scholastica'). The first subjects to be taught were law and theology. The curriculum expanded rapidly, and by 1399 the institution had divided in two: a ''Univ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bartolomeo Panizza
Bartolomeo Panizza (August 17, 1785 – April 17, 1867) was an Italian anatomist born in Vicenza. He received a medical degree in surgery from Padua, and furthered his studies at Bologna and Pavia. In 1809 he became a professor at the University of Pavia, and in 1835 a member of the ''Academia nazionale delle scienze'' (National Academy of Science). Panizza was a student and associate to famed anatomist Antonio Scarpa (1752-1832). He was the first physician to attribute the vision function to the posterior cortex. He published his findings in an 1855 treatise titled "''Osservazioni sul nervo ottico''" (Observations on the Optic Nerve). At the time, his discovery was largely ignored, and it would be several years until the importance of Panizza's findings were realized. In 1833 he described the "foramen of Panizza", defined as a hole with a valve that connects the left and right aorta in the crocodilian heart. He is also remembered for studies involving the lymphatic system of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camillo Golgi
Camillo Golgi (; 7 July 184321 January 1926) was an Italian biologist and pathologist known for his works on the central nervous system. He studied medicine at the University of Pavia (where he later spent most of his professional career) between 1860 and 1868 under the tutelage of Cesare Lombroso. Inspired by pathologist Giulio Bizzozero, he pursued research in the nervous system. His discovery of a staining technique called black reaction (sometimes called Golgi's method or Golgi's staining in his honour) in 1873 was a major breakthrough in neuroscience. Several structures and phenomena in anatomy and physiology are named for him, including the Golgi apparatus, the Golgi tendon organ and the Golgi tendon reflex. Golgi and the Spanish biologist Santiago Ramón y Cajal were jointly given the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1906 "in recognition of their work on the structure of the nervous system". Biography Camillo Golgi was born on 7 July 1843 in the village of Corteno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tomba Di Edoardo Bassini 1
''Tomba!'' is a 1997 platform-adventure game developed by Whoopee Camp and published by Sony Computer Entertainment for the PlayStation. It was released in Japan in 1997 and in other territories the following year. The game centers on the eponymous feral child as he attempts to recover his grandfather's bracelet from an evil race of anthropomorphic pigs. Creator Tokuro Fujiwara developed ''Tomba!'' after leaving Capcom in 1995, founding Whoopee Camp as director, producer and lead designer. He chose the game's 2D side-scrolling perspective for the format's straightforward nature, and created a non-linear "event" system to differentiate the game from other platforming titles. ''Tomba!'' was received positively by critics, with praise for its controls, visuals, and varied gameplay objectives. However, the game's audio received a more mixed reception. Despite the game's lackluster commercial performance, it was followed by a sequel in 1999, '' Tomba! 2: The Evil Swine Return''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eucalyptus
''Eucalyptus'' () is a genus of over seven hundred species of flowering trees, shrubs or mallees in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae. Along with several other genera in the tribe Eucalypteae, including '' Corymbia'', they are commonly known as eucalypts. Plants in the genus ''Eucalyptus'' have bark that is either smooth, fibrous, hard or stringy, leaves with oil glands, and sepals and petals that are fused to form a "cap" or operculum over the stamens. The fruit is a woody capsule commonly referred to as a "gumnut". Most species of ''Eucalyptus'' are native to Australia, and every state and territory has representative species. About three-quarters of Australian forests are eucalypt forests. Wildfire is a feature of the Australian landscape and many eucalypt species are adapted to fire, and resprout after fire or have seeds which survive fire. A few species are native to islands north of Australia and a smaller number are only found outside the continent. Eucalypts have been grow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbolic Acid
Phenol (also called carbolic acid) is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile. The molecule consists of a phenyl group () bonded to a hydroxy group (). Mildly acidic, it requires careful handling because it can cause chemical burns. Phenol was first extracted from coal tar, but today is produced on a large scale (about 7 billion kg/year) from petroleum-derived feedstocks. It is an important industrial commodity as a precursor to many materials and useful compounds. It is primarily used to synthesize plastics and related materials. Phenol and its chemical derivatives are essential for production of polycarbonates, epoxies, Bakelite, nylon, detergents, herbicides such as phenoxy herbicides, and numerous pharmaceutical drugs. Properties Phenol is an organic compound appreciably soluble in water, with about 84.2 g dissolving in 1000 mL (0.895 M). Homogeneous mixtures of phenol and water at phenol to wate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiseptic
An antiseptic (from Greek ἀντί ''anti'', "against" and σηπτικός ''sēptikos'', "putrefactive") is an antimicrobial substance or compound that is applied to living tissue/skin to reduce the possibility of infection, sepsis, or putrefaction. Antiseptics are generally distinguished from ''antibiotics'' by the latter's ability to safely destroy bacteria within the body, and from ''disinfectants'', which destroy microorganisms found on non-living objects. Antibacterials include antiseptics that have the proven ability to act against bacteria. Microbicides which destroy virus particles are called viricides or antivirals. Antifungals, also known as antimycotics, are pharmaceutical fungicides used to treat and prevent mycosis (fungal infection). Surgery The widespread introduction of antiseptic surgical methods was initiated by the publishing of the paper ''Antiseptic Principle of the Practice of Surgery'' in 1867 by Joseph Lister, which was inspired by Louis Pasteur's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prosthesis
In medicine, a prosthesis (plural: prostheses; from grc, πρόσθεσις, prósthesis, addition, application, attachment), or a prosthetic implant, is an artificial device that replaces a missing body part, which may be lost through trauma, disease, or a condition present at birth (congenital disorder). Prostheses are intended to restore the normal functions of the missing body part. Amputee rehabilitation is primarily coordinated by a physiatrist as part of an inter-disciplinary team consisting of physiatrists, prosthetists, nurses, physical therapists, and occupational therapists. Prostheses can be created by hand or with computer-aided design (CAD), a software interface that helps creators design and analyze the creation with computer-generated 2-D and 3-D graphics as well as analysis and optimization tools. Types A person's prosthesis should be designed and assembled according to the person's appearance and functional needs. For instance, a person may need a transra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
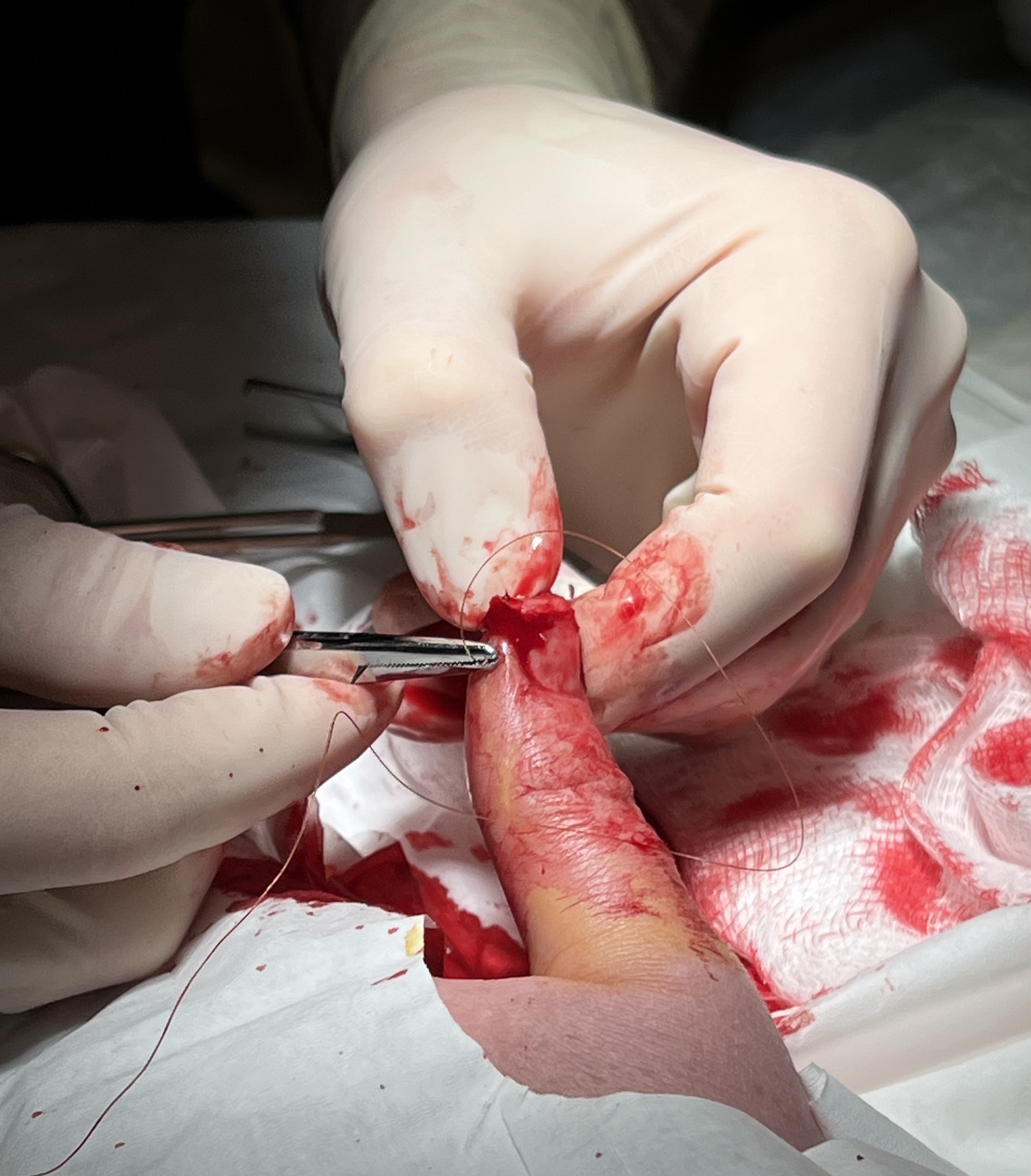
Surgical Sutures
A surgical suture, also known as a stitch or stitches, is a medical device used to hold body tissues together and approximate wound edges after an injury or surgery. Application generally involves using a needle with an attached length of thread. There are numerous types of suture which differ by needle shape and size as well as thread material and characteristics. Selection of surgical suture should be determined by the characteristics and location of the wound or the specific body tissues being approximated. In selecting the needle, thread, and suturing technique to use for a specific patient, a medical care provider must consider the tensile strength of the specific suture thread needed to efficiently hold the tissues together depending on the mechanical and shear forces acting on the wound as well as the thickness of the tissue being approximated. One must also consider the elasticity of the thread and ability to adapt to different tissues, as well as the memory of the threa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hernia
A hernia is the abnormal exit of tissue or an organ (anatomy), organ, such as the bowel, through the wall of the cavity in which it normally resides. Various types of hernias can occur, most commonly involving the abdomen, and specifically the groin. Groin hernias are most commonly of the inguinal hernia, inguinal type but may also be femoral hernia, femoral. Other types of hernias include Hiatal hernia, hiatus, incisional hernia, incisional, and umbilical hernias. Symptoms are present in about 66% of people with groin hernias. This may include pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen, especially with coughing, exercise, or Urination, urinating or Defecation, defecating. Often, it gets worse throughout the day and improves when lying down. A bulge may appear at the site of hernia, that becomes larger when bending down. Groin hernias occur more often on the right than left side. The main concern is Strangulation (bowel), bowel strangulation, where the blood supply to part of the bowe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomy
Anatomy () is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having its beginnings in prehistoric times. Anatomy is inherently tied to developmental biology, embryology, comparative anatomy, evolutionary biology, and phylogeny, as these are the processes by which anatomy is generated, both over immediate and long-term timescales. Anatomy and physiology, which study the structure and function (biology), function of organisms and their parts respectively, make a natural pair of related disciplines, and are often studied together. Human anatomy is one of the essential basic research, basic sciences that are applied in medicine. The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic scale, macroscopic and microscopic scale, microscopic. Gross anatomy, Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |