|
Edmund Davall
Edmund Davall (24 November 1762 in London ã 26 September 1798 in Orbe) was a Switzerland, Swiss-English botanist.London, England, Church of England Baptisms, Marriages and Burials, 1538-1812. Baptism: 3 Dec 1762 - St Lawrence Jewry, London, England. Ancestry.com. Life He was born in England. His parents were Edmund Davall (1737-1784) and Charlotte Thomasset (1728-1788) both of Swiss origin.. He returned with her to Switzerland on the death of his father in 1788, and took up residence at Orbe, Canton de Vaud. Upon his arrival in Orbe, Edmund created a Jardin botanique, botanical garden, which he took care of personally. In 1787, he discovered different plants with Albrecht von Haller (1758-1823), which is classified in the nomenclature of Jean Louis Antoine Reynier (1762-1824). It is his neighbor Charles Victor de Bonstetten (1745-1832), the last bailiff of Nyon and member of the Groupe de Coppet , who encouraged him to get in touch with Jakob Samuel Wyttenbach (1748-1830), pasto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a major settlement for two millennia. The City of London, its ancient core and financial centre, was founded by the Romans as '' Londinium'' and retains its medieval boundaries.See also: Independent city ôÏ National capitals The City of Westminster, to the west of the City of London, has for centuries hosted the national government and parliament. Since the 19th century, the name "London" has also referred to the metropolis around this core, historically split between the counties of Middlesex, Essex, Surrey, Kent, and Hertfordshire, which largely comprises Greater London, governed by the Greater London Authority.The Greater London Authority consists of the Mayor of London and the London Assembly. The London Mayor is distinguished fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Forster The Elder
Edward Forster the Elder (11 February 1730 ã 20 April 1812) was an English banker and antiquary. Life Forster was the son of Thomas Forster, and brother of Benjamin Forster, born on 11 February 1730. He was educated at Felsted School. He then visited the Netherlands and his relative Benjamin Furly. In 1764 Forster settled at Walthamstow. He was a member of the Mercers' Company, a director of the London Docks, governor of the Royal Exchange, and, for nearly thirty years, of the Russia Company, in which capacity he gave an annual ministerial dinner. When consulted by Pitt as to a forced paper currency he was offered a baronetcy. He is stated to have been the introducer of bearded wheat from Smyrna. He died at Hoe Street, Walthamstow, 20 April 1812. Joseph Addison, Jonathan Swift, and Jean-Jacques Rousseau were his favourite authors, and Thomas Gray, Richard Gough and Michael Tyson were among his personal friends. One of his letters (''Epistolarium Forsterianum'', i. 205ã2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
18th-century British Botanists
The 18th century lasted from January 1, 1701 ( MDCCI) to December 31, 1800 ( MDCCC). During the 18th century, elements of Enlightenment thinking culminated in the American, French, and Haitian Revolutions. During the century, slave trading and human trafficking expanded across the shores of the Atlantic, while declining in Russia, China, and Korea. Revolutions began to challenge the legitimacy of monarchical and aristocratic power structures, including the structures and beliefs that supported slavery. The Industrial Revolution began during mid-century, leading to radical changes in human society and the environment. Western historians have occasionally defined the 18th century otherwise for the purposes of their work. For example, the "short" 18th century may be defined as 1715ã1789, denoting the period of time between the death of Louis XIV of France and the start of the French Revolution, with an emphasis on directly interconnected events. To historians who expand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People From Orbe
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of property, or legal responsibility. The defining features of personhood and, consequently, what makes a person count as a person, differ widely among cultures and contexts. In addition to the question of personhood, of what makes a being count as a person to begin with, there are further questions about personal identity and self: both about what makes any particular person that particular person instead of another, and about what makes a person at one time the same person as they were or will be at another time despite any intervening changes. The plural form "people" is often used to refer to an entire nation or ethnic group (as in "a people"), and this was the original meaning of the word; it subsequently acquired its use as a plural form of per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientists From London
A scientist is a person who conducts scientific research to advance knowledge in an area of the natural sciences. In classical antiquity, there was no real ancient analog of a modern scientist. Instead, philosophers engaged in the philosophical study of nature called natural philosophy, a precursor of natural science. Though Thales (circaã624-545 BC) was arguably the first scientist for describing how cosmic events may be seen as natural, not necessarily caused by gods,Frank N. Magill''The Ancient World: Dictionary of World Biography'', Volume 1 Routledge, 2003 it was not until the 19th century that the term ''scientist'' came into regular use after it was coined by the theologian, philosopher, and historian of science William Whewell in 1833. In modern times, many scientists have advanced degrees in an area of science and pursue careers in various sectors of the economy such as academia, industry, government, and nonprofit environments.'''' History The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1798 Deaths
Events JanuaryãJune * January – Eli Whitney contracts with the U.S. federal government for 10,000 muskets, which he produces with interchangeable parts. * January 4 – Constantine Hangerli enters Bucharest, as Prince of Wallachia. * January 22 – A coup d'ûˋtat is staged in the Netherlands ( Batavian Republic). Unitarian Democrat Pieter Vreede ends the power of the parliament (with a conservative-moderate majority). * February 10 – The Pope is taken captive, and the Papacy is removed from power, by French General Louis-Alexandre Berthier. * February 15 – U.S. Representative Roger Griswold (Fed-CT) beats Congressman Matthew Lyon (Dem-Rep-VT) with a cane after the House declines to censure Lyon earlier spitting in Griswold's face; the House declines to discipline either man.''Harper's Encyclopaedia of United States History from 458 A. D. to 1909'', ed. by Benson John Lossing and, Woodrow Wilson (Harper & Brothers, 1910) p171 * March &nd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1762 Births
Year 176 ( CLXXVI) was a leap year starting on Sunday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Proculus and Aper (or, less frequently, year 929 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 176 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * November 27 – Emperor Marcus Aurelius grants his son Commodus the rank of ''Imperator'', and makes him Supreme Commander of the Roman legions. * December 23 ã Marcus Aurelius and Commodus enter Rome after a campaign north of the Alps, and receive a triumph for their victories over the Germanic tribes. * The Equestrian Statue of Marcus Aurelius is made. It is now kept at Museo Capitolini in Rome (approximate date). Births * Fa Zheng, Chinese nobleman and adviser (d. 220) * Liu Bian, Chinese emperor of the Han Dynasty ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edmond Davall
Edmond Davall (Orbe, 1793 - Lausanne, 1860) was a Swiss botanist and politician. He was son of the English-Swiss botanist Edmund Davall Edmund Davall (24 November 1762 in London ã 26 September 1798 in Orbe) was a Switzerland, Swiss-English botanist.London, England, Church of England Baptisms, Marriages and Burials, 1538-1812. Baptism: 3 Dec 1762 - St Lawrence Jewry, London, Engl .... Sources * Cûˋdric ROSSIER, mûˋmoire de licence de l'Universitûˋ de Lausanne, septembre 2003. * "Edmond Davall : approche biographique de lãhomme et du forestier", Cûˋdric ROSSIER, in Revue historique vaudoise, 2005. * J. Barbey, ô¨Les forestiers D.ô£, in Journal forestier suisse, 1953, 391ã395. 1793 births 1860 deaths People from Orbe 19th-century Swiss botanists {{Switzerland-politician-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Davallia
'' Davallia'' (deersfoot fern, hare's foot fern, shinobu fern, rabbit foot fern, ball fern) is a genus of about 40 species of fern. In the Pteridophyte Phylogeny Group classification of 2016 (PPG I), it is the only genus in the family Davalliaceae, which is placed in the suborder Polypodiineae, order Polypodiales. Alternatively, the family may be placed in a very broadly defined family Polypodiaceae ''sensu lato'' as the subfamily Davallioideae. The family is sister to the largest family of ferns, Polypodiaceae, and shares some morphological characters with it.Karl U. Kramer. 1990. "Davalliaceae". pages 74-80. In: Klaus Kubitzki (general editor); Karl U. Kramer and Peter S. Green (volume editors) ''The Families and Genera of Vascular Plants'' volume I. Springer-Verlag: Berlin;Heidelberg, Germany. Species are epiphytic ferns, with fronds arising from long aerial rhizomes which grow on and over thick bark on trees or on rock crevices. Description Usually epiphytic or epipe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linnean Society
The Linnean Society of London is a learned society dedicated to the study and dissemination of information concerning natural history, evolution, and taxonomy. It possesses several important biological specimen, manuscript and literature collections, and publishes academic journals and books on plant and animal biology. The society also awards a number of prestigious medals and prizes. A product of the 18th-century enlightenment, the Society is the oldest extant biological society in the world and is historically important as the venue for the first public presentation of the theory of evolution by natural selection on 1 July 1858. The patron of the society was Queen Elizabeth II. Honorary members include: King Charles III of Great Britain, Emeritus Emperor Akihito of Japan, King Carl XVI Gustaf of Sweden (both of latter have active interests in natural history), and the eminent naturalist and broadcaster Sir David Attenborough. History Founding The Linnean Society wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Edward Smith (botanist)
__NOTOC__ Sir James Edward Smith (2 December 1759 ã 17 March 1828) was an English botanist and founder of the Linnean Society. Early life and education Smith was born in Norwich in 1759, the son of a wealthy wool merchant. He displayed a precocious interest in the natural world. During the early 1780s he enrolled in the medical course at the University of Edinburgh where he studied chemistry under Joseph Black and natural history under John Walker. He then moved to London in 1783 to continue his studies. Smith was a friend of Sir Joseph Banks, who was offered the entire collection of books, manuscripts and specimens of the Swedish natural historian and botanist Carl Linnaeus following the death of his son Carolus Linnaeus the Younger. Banks declined the purchase, but Smith bought the collection for the bargain price of ôÈ1,000. The collection arrived in London in 1784, and in 1785 Smith was elected Fellow of the Royal Society. Academic career Between 1786 and 1788 Smit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
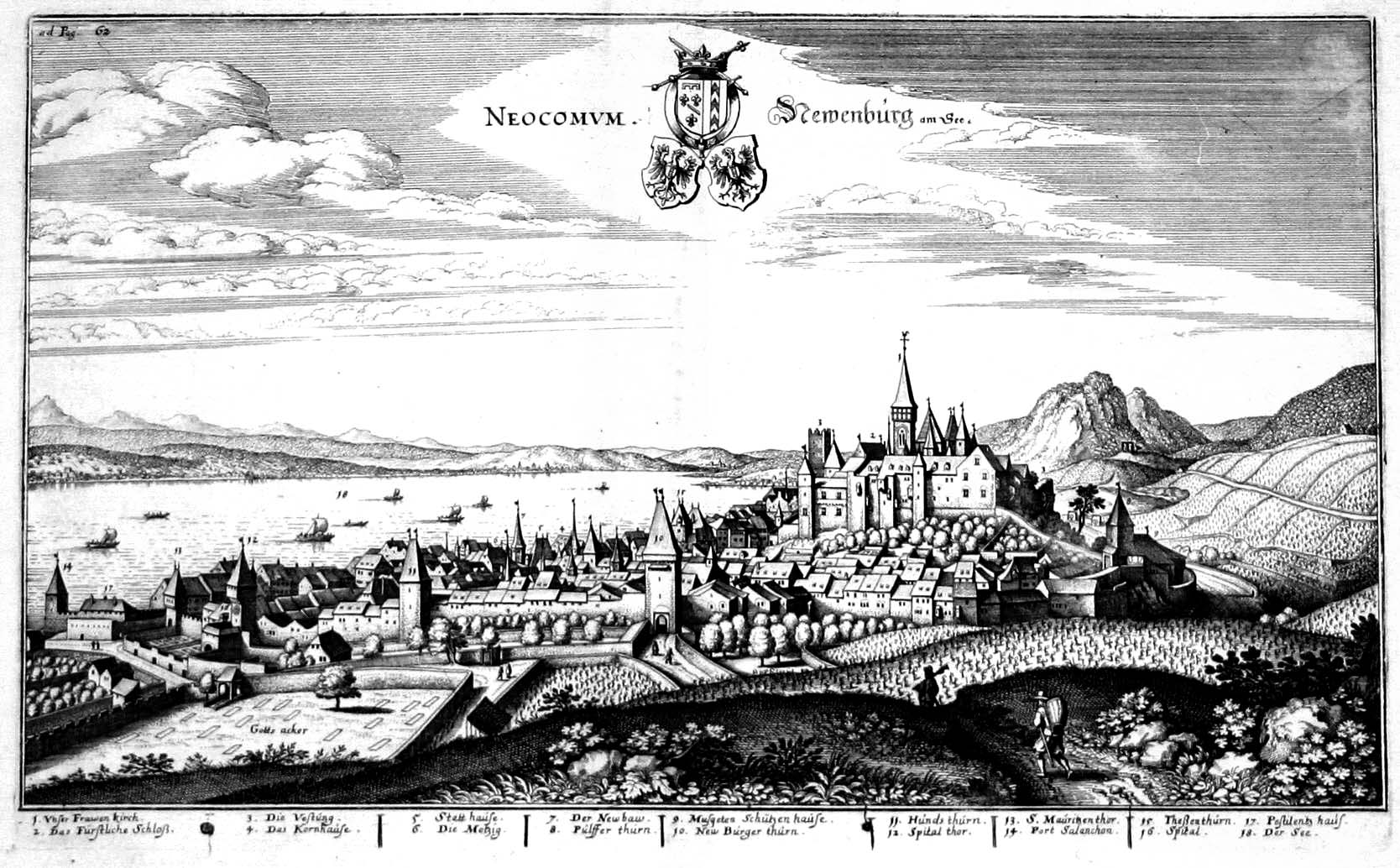
NeuchûÂtel
, neighboring_municipalities= Auvernier, Boudry, Chabrey (VD), Colombier, Cressier, Cudrefin (VD), Delley-Portalban (FR), Enges, Fenin-Vilars-Saules, Hauterive, Saint-Blaise, Savagnier , twintowns = Aarau (Switzerland), BesanûÏon (France), Sansepolcro (Italy) NeuchûÂtel (, , ; german: Neuenburg) is the capital of the Swiss canton of NeuchûÂtel, situated on the shoreline of Lake NeuchûÂtel. Since the fusion in 2021 of the municipalities of NeuchûÂtel, Corcelles-Cormondrû´che, Peseux, and Valangin, the city has approximately 45,000 inhabitants (80,000 in the metropolitan area). The city is sometimes referred to historically by the German name ; both the French and German names mean "New Castle". It was originally part of the Kingdom of Burgundy, then part of the Holy Roman Empire and later under Prussian control from 1707 until 1848, with an interruption during the Napoleonic Wars from 1802 to 1814. In 1848, NeuchûÂtel became a republic and a canton of Switzerland. Neuchû ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_1938.jpg)



.jpg)