|
Edith Kaplan
Edith F. Kaplan (February 16, 1924 – September 3, 2009) was an American psychologist. She was a pioneer of neuropsychological tests and did most of her work at the Boston VA Hospital. Kaplan is known for her promotion of clinical neuropsychology as a specialty area in psychology. She examined brain-behavioral relationships in aphasia, apraxia, developmental issues in clinical neuropsychology, as well as normal and abnormal aging. Kaplan helped develop a new method of assessing brain function with neuropsychological assessment, called " The Boston Process Approach." As a graduate student Kaplan worked with Heinz Werner, and then collaborated further with Norman Geschwind and Harold Goodglass. Personal history Kaplan was born in Brooklyn, New York. She earned her bachelor's degree at Brooklyn College, then did her graduate work at Clark University in Worcester, with a dissertation focusing on the development of word meanings and apraxia in children. Kaplan was a Professor in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychologist
A psychologist is a professional who practices psychology and studies mental states, perceptual, cognitive, emotional, and social processes and behavior. Their work often involves the experimentation, observation, and interpretation of how individuals relate to each other and to their environments. Psychologists usually acquire a bachelor's degree in psychology, followed by a master's degree or doctorate in psychology. Unlike psychiatric physicians and psychiatric nurse-practitioners, psychologists usually cannot prescribe medication, but depending on the jurisdiction, some psychologists with additional training can be licensed to prescribe medications; qualification requirements may be different from a bachelor's degree and master's degree. Psychologists receive extensive training in psychological testing, scoring, interpretation, and reporting, while psychiatrists are not usually trained in psychological testing. Psychologists are also trained in, and often specialise in, on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baycrest Centre For Geriatric Care
Baycrest Health Sciences is a research and teaching hospital for the elderly in the North York district of Toronto, Ontario, Canada. It is fully affiliated with the University of Toronto. Baycrest was originally founded in 1918 as the Toronto Jewish Old Folks Home in a semi-detached Victorian house at 29 Cecil Street in Downtown Toronto. History Slova Greenberg, president of the Ezras Noshem Society, identified the need to provide health care for elderly Jewish people in Toronto in 1913. The "Toronto Jewish Old Folks Home" opened at 29 Cecil Street, Toronto in 1918. The original location on Cecil street was demolished in 1954 and is now home to the United Steelworkers Larry Sefton Hall (c. 1972 at 25 Cecil Street) and Toronto Labour Lyceum (c. 1971 33 Cecil Street). In 1954, the new "Jewish Home for the Aged" moved to Bathurst Street. It expanded to a new building in 1968 at Baycrest's present location at 3560 Bathurst Street in North York. The entire Bathurst Street complex b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemispatial Neglect
Hemispatial neglect is a neuropsychological condition in which, after damage to one hemisphere of the brain (e.g. after a stroke), a deficit in attention and awareness towards the side of space opposite brain damage (contralesional space) is observed. It is defined by the inability of a person to process and perceive stimuli towards the contralesional side of the body or environment. Hemispatial neglect is very commonly contralateral to the damaged hemisphere, but instances of ipsilesional neglect (on the same side as the lesion) have been reported. Presentation Hemispatial neglect results most commonly from strokes and brain unilateral injury to the right cerebral hemisphere, with rates in the critical stage of up to 80% causing visual neglect of the left-hand side of space. Neglect is often produced by massive strokes in the middle cerebral artery region and is variegated, so that most sufferers do not exhibit all of the syndrome's traits. Right-sided spatial neglect is rare bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harcourt Assessment
Harcourt Assessment was a company that published and distributed educational and psychological assessment tools and therapy resources and provided educational assessment and data management services for national, state, district and local assessments. On January 30, 2008, Harcourt Assessment was merged into Pearson PLC, Pearson's Pearson Assessment & Information, Assessment & Information group after being acquired from Reed Elsevier for $950 million. History Harcourt Assessment's history dates to the early part of the 20th century. Although the company name derives from Harcourt Trade Publishers, Harcourt Brace & Company, which was established in 1919, the corporate heritage goes back to 1905 and the founding of World Book Company. Many of the educational products produced by Harcourt Assessment originated at World Book. The psychological assessments originated at The Psychological Corporation, which was founded in 1921. Harcourt Brace & Company (1919) Alfred Harcourt and Donald B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
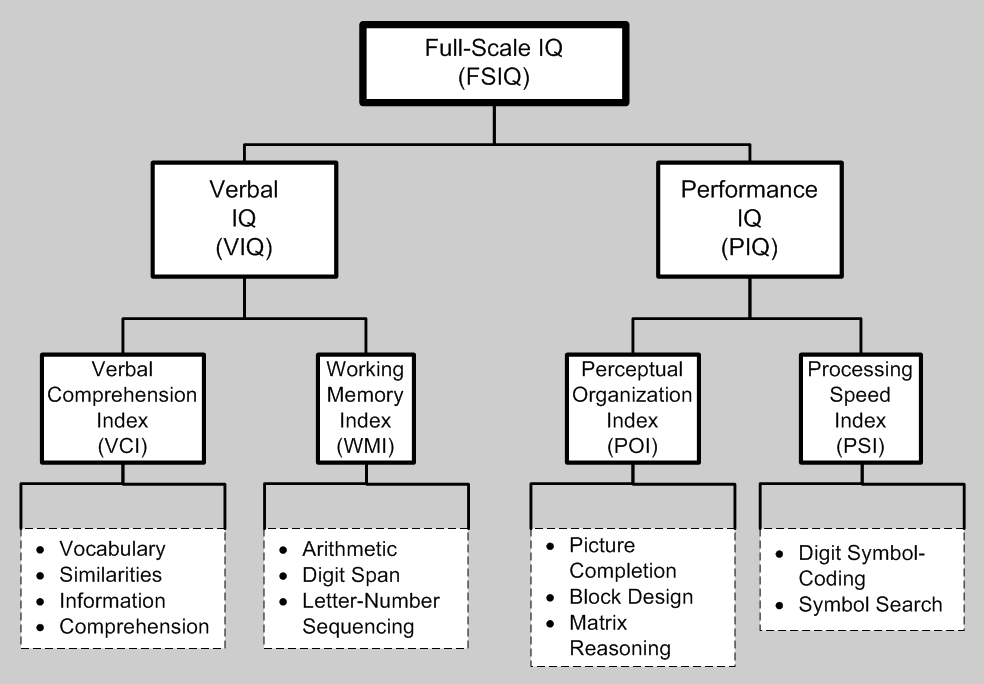
Wechsler Intelligence Scale For Children
The Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children (WISC) is an individually administered intelligence test for children between the ages of 6 and 16. The Fifth Edition (WISC-V; Wechsler, 2014) is the most recent version. The WISC-V takes 45 to 65 minutes to administer. It generates a Full Scale IQ (formerly known as an intelligence quotient or IQ score) that represents a child's general intellectual ability. It also provides five primary index scores, namely Verbal Comprehension Index, Visual Spatial Index, Fluid Reasoning Index, Working Memory Index, and Processing Speed Index. These indices represent a child's abilities in discrete cognitive domains. Five ancillary composite scores can be derived from various combinations of primary or primary and secondary subtests. Five complementary subtests yield three complementary composite scores to measure related cognitive abilities. Technical papers by the publishers support other indices such as VECI, EFI, and GAI (Raiford et al., 2015). Va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
California Verbal Learning Test
The California Verbal Learning Test (CVLT)Delis, D. C., Kramer, J. H., Kaplan, E., & Ober, B. A. (1987). ''CVLT, California Verbal Learning Test: Adult Version: Manual''. Psychological Corporation. is one of the most widely used neuropsychological tests in North America. As an instrument, it represents a relatively new approach to clinical psychology and the cognitive science of memory. It measures episodic verbal learning and memory, and demonstrates sensitivity to a range of clinical conditions.Elwood, R. W. (1995). The California Verbal Learning Test: psychometric characteristics and clinical application. ''Neuropsychology Review'', ''5''(3), 173–201. The test does this by attempting to link memory deficits with impaired performance on specific tasks. It assesses encoding, recall and recognition in a single modality of item presentation (auditory-verbal). The CVLT is considered to be a more sensitive measure of episodic memory than other verbal learning tests. It was designe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boston Naming Test
The Boston Naming Test (BNT), introduced in 1983 by Edith Kaplan, Harold Goodglass and Sandra Weintraub, is a widely used neuropsychological assessment tool to measure confrontational word retrieval in individuals with aphasia or other language disturbance caused by stroke, Alzheimer's disease, or other dementing disorder. A common and debilitating feature is anomic aphasia, an impairment in the ability to name objects. The BNT contains 60 line drawings graded in difficulty. Patients with anomia often have greater difficulties with the naming of not only difficult and low frequency objects but also easy and high frequency objects. Naming difficulties may be rank ordered along a continuum. Items are rank ordered in terms of their ability to be named, which is correlated with their frequency. This type of picture-naming test is also useful in the examination of children with learning disabilities and the evaluation of brain-injured adults. Instructions for administration The 60-item ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lesion
A lesion is any damage or abnormal change in the tissue of an organism, usually caused by disease or trauma. ''Lesion'' is derived from the Latin "injury". Lesions may occur in plants as well as animals. Types There is no designated classification or naming convention for lesions. Since lesions can occur anywhere in the body and the definition of a lesion is so broad, the varieties of lesions are virtually endless. Generally, lesions may be classified by their patterns, their sizes, their locations, or their causes. They can also be named after the person who discovered them. For example, Ghon lesions, which are found in the lungs of those with tuberculosis, are named after the lesion's discoverer, Anton Ghon. The characteristic skin lesions of a varicella zoster virus infection are called '' chickenpox''. Lesions of the teeth are usually called dental caries. Location Lesions are often classified by their tissue types or locations. For example, a "skin lesion" or a " bra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale
The Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS) is an IQ test designed to measure intelligence and cognitive ability in adults and older adolescents. The original WAIS (Form I) was published in February 1955 by David Wechsler, as a revision of the Wechsler–Bellevue Intelligence Scale, released in 1939. It is currently in its fourth edition (''WAIS-IV'') released in 2008 by Pearson, and is the most widely used IQ test, for both adults and older adolescents, in the world. History The WAIS is founded on Wechsler's definition of intelligence, which he defined as "... the global capacity of a person to act purposefully, to think rationally, and to deal effectively with his environment." He believed that intelligence was made up of specific elements that could be isolated, defined, and subsequently measured. However, these individual elements were not entirely independent, but were all interrelated. His argument, in other words, is that general intelligence is composed of various speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intelligence Tests
An intelligence quotient (IQ) is a total score derived from a set of standardized tests or subtests designed to assess human intelligence. The abbreviation "IQ" was coined by the psychologist William Stern for the German term ''Intelligenzquotient'', his term for a scoring method for intelligence tests at University of Breslau he advocated in a 1912 book. Historically, IQ was a score obtained by dividing a person's mental age score, obtained by administering an intelligence test, by the person's chronological age, both expressed in terms of years and months. The resulting fraction (quotient) was multiplied by 100 to obtain the IQ score. For modern IQ tests, the raw score is transformed to a normal distribution with mean 100 and standard deviation 15. This results in approximately two-thirds of the population scoring between IQ 85 and IQ 115 and about 2.5 percent each above 130 and below 70. Scores from intelligence tests are estimates of intelligence. Unlike, for example, d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |