|
Economic Base
Economic base analysis is a theory that posits that activities in an area divide into two categories: basic and nonbasic. Basic industries are those exporting from the region and bringing wealth from outside, while nonbasic (or service) industries support basic industries. Because export-import flows are usually not tracked at sub-national (regional) levels, it is not practical to study industry output and trade flows to and from a region. As an alternative, the concepts of basic and nonbasic are operationalized using employment data. The theory was developed by Robert Murray Haig in his work on the Regional Plan of New York in 1928. Application of the analysis The basic industries of a region are identified by comparing employment in the region to national norms. If the national norm for employment in, for example, Egyptian woodwind manufacturing is 5 percent and the region's employment is 8 percent, then 3 percent of the region's woodwind employment is basic. Once basic employme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Murray Haig
Robert Murray Haig (1887 – 1953) was an American economist regarded as an expert in public finance and taxation. The concept of Haig–Simons income bears his name. Haig graduated with a PhD in economics from Columbia University in 1914, with a thesis written under supervision of Edwin Robert Anderson Seligman Edwin Robert Anderson Seligman (1861–1939), was an American economist who spent his entire academic career at Columbia University in New York City. Seligman is best remembered for his pioneering work involving taxation and public finance. His p .... References 1887 births 1953 deaths 20th-century American economists Columbia Graduate School of Arts and Sciences alumni Columbia University faculty Georgist economists {{US-economist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regional Plan Of New York
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and the interaction of humanity and the environment (environmental geography). Geographic regions and sub-regions are mostly described by their imprecisely defined, and sometimes transitory boundaries, except in human geography, where jurisdiction areas such as national borders are defined in law. Apart from the global continental regions, there are also hydrospheric and atmospheric regions that cover the oceans, and discrete climates above the land and water masses of the planet. The land and water global regions are divided into subregions geographically bounded by large geological features that influence large-scale ecologies, such as plains and features. As a way of describing spatial areas, the concept of regions is important and widely used among the many branches of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arghul
The ''arghul'' ( ar, أرغول or يرغول), also spelled ''argul'', ''arghoul'', ''arghool'', ''argol'', or ''yarghul'', is a musical instrument in the reed family. It has been used since ancient Egyptian times and is still used as a traditional instrument in Egypt, Syria, Jordan, and Palestine. Basic characteristics ''Modern Egyptians''.) Modern Arghul, 3 ft. 2½ in. long. The arghul is a double-pipe, Single-reed woodwind instrument that consists of two tubes: a melody pipe with between five and seven holes and a longer drone (Arabic ''ardiyya'', "ground") pipe. Its tone is similar to that of a clarinet, although a bit more reed-like. Unlike the similar mijwiz, the arghul has fingering holes on only one of the instrument's pipes (the melody pipe), and the drone pipe has a detachable length that allows the player to alter the pitch of the drone. In the illustration above all three lengths are shown in use. An arghul belonging to the collection of the Conser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seattle, Washington
Seattle ( ) is a port, seaport city on the West Coast of the United States. It is the county seat, seat of King County, Washington, King County, Washington (state), Washington. With a 2020 population of 737,015, it is the largest city in both the U.S. state, state of Washington and the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The Seattle metropolitan area's population is 4.02 million, making it the List of metropolitan statistical areas, 15th-largest in the United States. Its growth rate of 21.1% between 2010 and 2020 makes it one of the nation's fastest-growing large cities. Seattle is situated on an isthmus between Puget Sound (an inlet of the Pacific Ocean) and Lake Washington. It is the northernmost major city in the United States, located about south of the Canada–United States border, Canadian border. A major gateway for trade with East Asia, Seattle is the fourth-largest port in North America in terms of container handling . The Seattle area was inhabited by Nat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
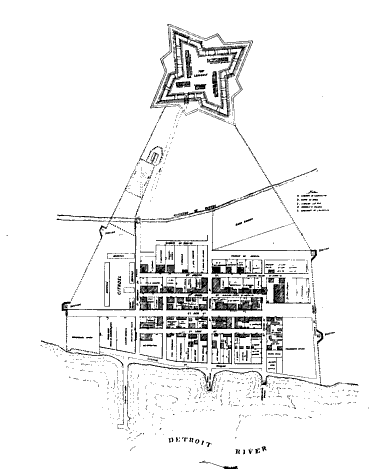
Detroit
Detroit ( , ; , ) is the largest city in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is also the largest U.S. city on the United States–Canada border, and the seat of government of Wayne County. The City of Detroit had a population of 639,111 at the 2020 census, making it the 27th-most populous city in the United States. The metropolitan area, known as Metro Detroit, is home to 4.3 million people, making it the second-largest in the Midwest after the Chicago metropolitan area, and the 14th-largest in the United States. Regarded as a major cultural center, Detroit is known for its contributions to music, art, architecture and design, in addition to its historical automotive background. '' Time'' named Detroit as one of the fifty World's Greatest Places of 2022 to explore. Detroit is a major port on the Detroit River, one of the four major straits that connect the Great Lakes system to the Saint Lawrence Seaway. The City of Detroit anchors the second-largest regional econ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicon Valley
Silicon Valley is a region in Northern California that serves as a global center for high technology and innovation. Located in the southern part of the San Francisco Bay Area, it corresponds roughly to the geographical areas San Mateo County and Santa Clara County. San Jose is Silicon Valley's largest city, the third-largest in California, and the tenth-largest in the United States; other major Silicon Valley cities include Sunnyvale, Santa Clara, Redwood City, Mountain View, Palo Alto, Menlo Park, and Cupertino. The San Jose Metropolitan Area has the third-highest GDP per capita in the world (after Zurich, Switzerland and Oslo, Norway), according to the Brookings Institution, and, as of June 2021, has the highest percentage of homes valued at $1 million or more in the United States. Silicon Valley is home to many of the world's largest high-tech corporations, including the headquarters of more than 30 businesses in the Fortune 1000, and thousands of startup com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Tiebout
Charles Mills Tiebout ( "TEE-bow") (1924–1968) was an American economist and geographer most known for his development of the Tiebout model, which suggested that there were actually non-political solutions to the free rider problem in local governance. He earned recognition in the area of local government and fiscal federalism with his widely cited 1956 paper "A Pure Theory of Local Expenditures". Tiebout graduated from Wesleyan University in 1950, and received a PhD in economics in University of Michigan in 1957. From 1954 to 1958, Tiebout served as a lecturer and assistant professor of economics at Northwestern University. From 1958 to 1962 was an assistant then associate professor of economics at UCLA. He was Professor of Economics and Geography and was co-director for the Center for Urban and Regional Studies at the University of Washington. He died suddenly on January 16, 1968, at age 43. Tiebout is frequently associated with the concept of foot voting Foot voting is expr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regional Economics
Regional economics is a sub-discipline of economics and is often regarded as one of the fields of the social sciences. It addresses the economic aspect of the regional problems that are spatially analyzable so that theoretical or policy implications can be the derived with respect to regions whose geographical scope ranges from local to global areas. Regional Economics: refer to the economics advantage of a geographical location and human activities of greatest height to contribute maximally to the general growth and prosperity of the region. Origins Regional economics has shared many traditions with regional science, whose earlier development was propelled by Walter Isard and some economists' dissatisfaction with the existing regional economic analysis. Despite such a rather critical view of regional economics, however, it is hard to be denied that the "economic" approach to regional problems was and has been the most significant one throughout the development of regional sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |