|
Eco-communalism
The Global Scenario Group (GSG) was an international, interdisciplinary body convened in 1995 by the Tellus Institute and the Stockholm Environment Institute (SEI) to develop scenarios for world development in the twenty-first century. Further development of the Great Transition scenarios has been carried on by the Great Transition Initiative (GTI). The GSG's underlying scenario development work was rooted in the long-range integrated scenario analysis that Tellus Institute and Stockholm Environment Institute had undertaken through the PoleStar Project and its PoleStar System. Initially conceived in 1991 as a tool for integrated sustainability planning and long-range scenario analysis, the PoleStar System was inspired by the 1987 Brundtland Commission report ''Our Common Future'', which first put the concept of sustainable development on the international agenda. The work of the Global Scenario Group was widely adopted in high-level intergovernmental settings. The scenarios i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Transition
Great Transition is used by the Great Transition Initiative and its predecessor, the Global Scenario Group (GSG), to describe a vision of a just and sustainable global future. The term was originally coined by Kenneth E. Boulding in ''The Meaning of the 20th Century – The Great Transition'' (1964) and describes the shift from pre-modern to post-modern culture, and the four possible courses of action that these organizations believe will allow humanity to successfully manage the Great Transition. Elements of the Great Transition vision include egalitarian social and ecological values, increased inter-human connectivity, improved quality of life, and a healthy planet, as well as the absence of poverty, war, and environmental destruction. The Great Transition concept was cited by Prime Minister of Bhutan Jigme Thinley, Josh Ryan-Collins of the New Economics Foundation, and the Capital Institute. It was used as a theme for the 2011 SmartCSOs conference on strategies for Civil Socie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Transition Initiative
Great Transition is used by the Great Transition Initiative and its predecessor, the Global Scenario Group (GSG), to describe a vision of a just and sustainable global future. The term was originally coined by Kenneth E. Boulding in ''The Meaning of the 20th Century – The Great Transition'' (1964) and describes the shift from pre-modern to post-modern culture, and the four possible courses of action that these organizations believe will allow humanity to successfully manage the Great Transition. Elements of the Great Transition vision include egalitarian social and ecological values, increased inter-human connectivity, improved quality of life, and a healthy planet, as well as the absence of poverty, war, and environmental destruction. The Great Transition concept was cited by Prime Minister of Bhutan Jigme Thinley, Josh Ryan-Collins of the New Economics Foundation, and the Capital Institute. It was used as a theme for the 2011 SmartCSOs conference on strategies for Civil Socie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post-capitalism
Post-capitalism is a state in which the economic systems of the world can no longer be described as forms of capitalism. Various individuals and political ideologies have speculated on what would define such a world. According to classical Marxist and social evolutionary theories, post-capitalist societies may come about as a result of spontaneous evolution as capitalism becomes obsolete. Others propose models to intentionally replace capitalism. The most notable among them are socialism, anarchism, nationalism and degrowth. History In 1993, Peter Drucker outlined a possible evolution of capitalistic society in his book '' Post-Capitalist Society''. The book stated that knowledge, rather than capital, land, or labor, is the new basis of wealth. The classes of a fully post-capitalist society are expected to be divided into knowledge workers or service workers, in contrast to the capitalists and proletarians of a capitalist society. In the book, Drucker estimated the transforma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tellus Institute
The Tellus Institute is an American non-profit organization established in 1976 with the aim of bringing scientific rigor and systemic vision to critical environmental and social issues. Tellus has conducted thousands of projects throughout the world, and now focuses on the global future and how to shape it. Background The Tellus Institute was founded as a non-profit research organization in 1976 by Paul Raskin and colleagues to conduct research on resource and environmental policy. Initially called Energy Systems Research Group (ESRG), the institute adopted its current name in 1990 to reflect its expanding focus on social-ecological systems from local to global levels (Tellus was the name of the Roman Earth Goddess). Tellus has partnered with hundreds of organizations, notably the Stockholm Environmental Institute, with which it coordinated programs from 1989 to 2006. The institute has conducted more than 3,500 studies worldwide. The methodology of Tellus projects has been the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
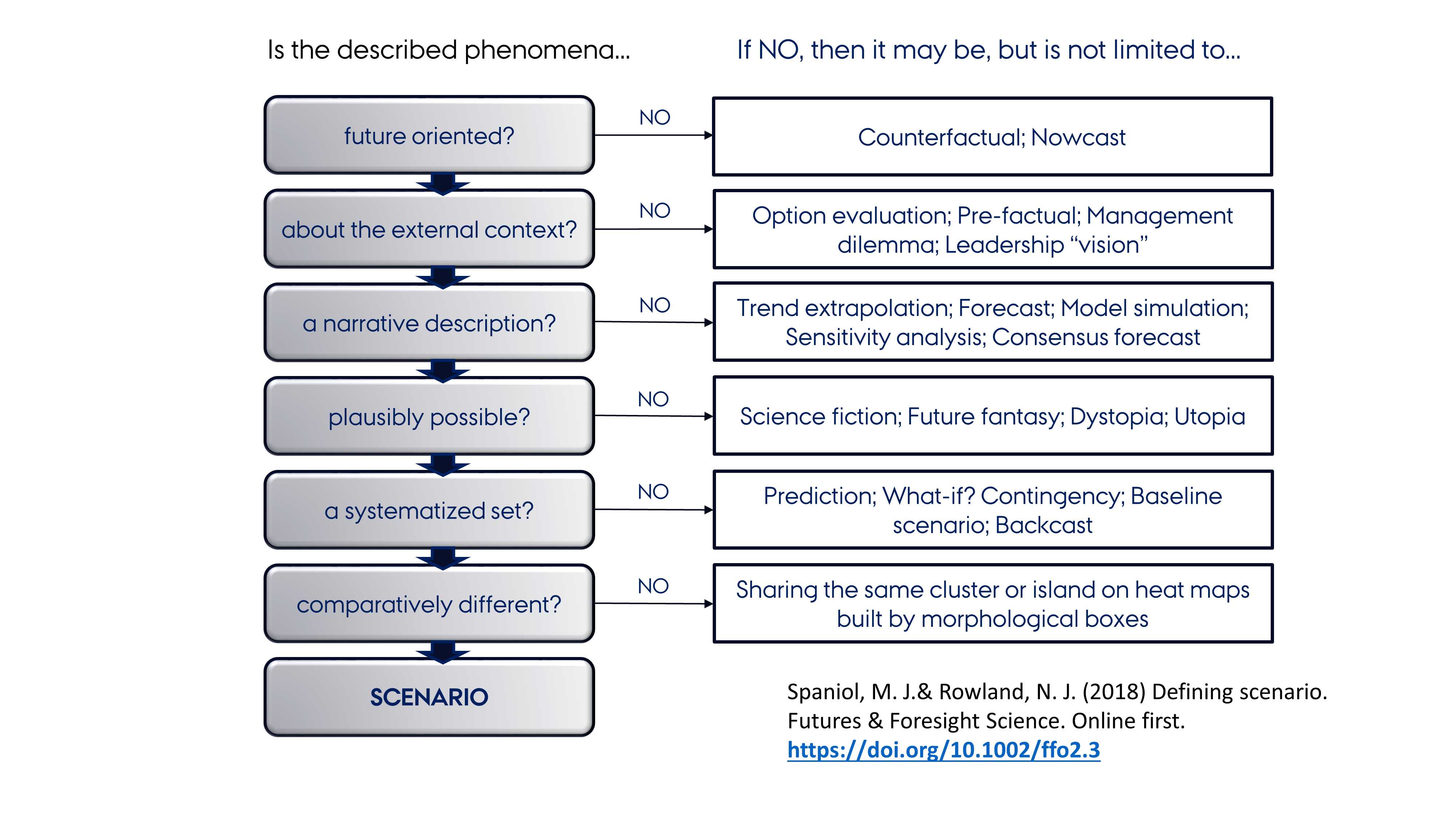
Scenario Analysis
Scenario planning, scenario thinking, scenario analysis, scenario prediction and the scenario method all describe a strategic planning method that some organizations use to make flexible long-term plans. It is in large part an adaptation and generalization of classic methods used by military intelligence. In the most common application of the method, analysts generate simulation games for policy makers. The method combines known facts, such as demographics, geography and mineral reserves, with military, political, and industrial information, and key driving forces identified by considering social, technical, economic, environmental, and political ("STEEP") trends. In business applications, the emphasis on understanding the behavior of opponents has been reduced while more attention is now paid to changes in the natural environment. At Royal Dutch Shell for example, scenario planning has been described as changing mindsets about the exogenous part of the world prior to formula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transition Scenario
Transition scenarios are descriptions of future states which combine a future image with an account of the changes that would need to occur to reach that future. These two elements are often created in a two-step process where the future image is created first (envisioning) followed by an exploration of the alternative pathways available to reach the future goal (backcasting). Both these processes can use participatory techniques (Raskin et al., 2002) where participants of varying backgrounds and interests are provided with an open and supportive group environment to discuss different contributing elements and actions. Transition scenarios are unique in type not only in terms of how they are created (process) but also their content. Their requirements are guided by transition management concepts and consider the "fundamental and irreversible change in the culture, structure and practices of a system" (Sondeijker, 2009:52,). Transition scenarios are emerging as a scenario type which i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Globalization
Globalization, or globalisation (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English; American and British English spelling differences#-ise, -ize (-isation, -ization), see spelling differences), is the process of foreign relations, interaction and integration among people, companies, and governments worldwide. The term ''globalization'' first appeared in the early 20th century (supplanting an earlier French term ''mondialization''), developed its current meaning some time in the second half of the 20th century, and came into popular use in the 1990s to describe the unprecedented international connectivity of the Post-Cold War era, post-Cold War world. Its origins can be traced back to 18th and 19th centuries due to advances in transportation and Information and communications technology, communications technology. This increase in global interactions has caused a growth in international trade and the exchange of ideas, beliefs, and culture. Globalization is primari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecological Footprint
The ecological footprint is a method promoted by the Global Footprint Network to measure human demand on natural capital, i.e. the quantity of nature it takes to support people or an economy. It tracks this demand through an ecological accounting system. The accounts contrast the biologically productive area people use for their consumption to the biologically productive area available within a region or the world ( biocapacity, the productive area that can regenerate what people demand from nature). In short, it is a measure of human impact on the environment. Footprint and biocapacity can be compared at the individual, regional, national or global scale. Both footprint and biocapacity change every year with number of people, per person consumption, efficiency of production, and productivity of ecosystems. At a global scale, footprint assessments show how big humanity's demand is compared to what Earth can renew. Global Footprint Network estimates that, as of 2014, humanity has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Global Citizens Movement
The global citizens movement is a constellation of organized and overlapping citizens' groups seeking to foster global solidarity in policy and consciousness. The term is often used synonymously with the anti-globalization movement or the global justice movement. Background The concept of global citizenship first emerged in the 4th Century BCE among the Greek Cynics, who coined the term “ cosmopolitan” – meaning ''citizen of the world''. The Stoics later elaborated on the concept, and contemporary philosophers and political theorists have further developed it in the concept of cosmopolitanism, which proposes that all individuals belong to a single moral community. The twenty-first century has seen increasing calls for global citizenship in light of how transportation and technology—are binding disparate parts of the world more closely together than ever before. Authors as Paul Raskin, Paul H. Ray, David Korten, and Gus Speth have argued for the existence of a latent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steady State
In systems theory, a system or a process is in a steady state if the variables (called state variables) which define the behavior of the system or the process are unchanging in time. In continuous time, this means that for those properties ''p'' of the system, the partial derivative with respect to time is zero and remains so: : \frac = 0 \quad \text t. In discrete time, it means that the first difference of each property is zero and remains so: :p_t-p_=0 \quad \text t. The concept of a steady state has relevance in many fields, in particular thermodynamics, economics, and engineering. If a system is in a steady state, then the recently observed behavior of the system will continue into the future. In stochastic systems, the probabilities that various states will be repeated will remain constant. See for example Linear difference equation#Conversion to homogeneous form for the derivation of the steady state. In many systems, a steady state is not achieved until some tim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Growth Imperative
Growth imperative is a term in economic theory regarding a possible necessity of economic growth. On the micro level, it describes mechanisms that force firms or consumers (households) to increase revenues or consumption to not endanger their income. On the macro level, a political growth imperative exists if economic growth is necessary to avoid economic and social instability or to retain democratic legitimacy, so that other political goals such as climate change mitigation or a reduction of inequality are subordinated to growth policies. Current neoclassical, Keynesian and endogenous growth theories do not consider a growth imperative or explicitly deny it, such as Robert Solow. In neoclassical economics, adherence to economic growth would be a question of maximizing utility, an intertemporal decision between current and future consumption (see Keynes–Ramsey rule). Other sociological and political theories consider several possible causes for pursuing economic growth, fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Millennium Ecosystem Assessment
The Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (MA) is a major assessment of the human impact on the environment, called for by the United Nations Secretary-General Kofi Annan in 2000, launched in 2001 and published in 2005 with more than $14 million of grants. It popularized the term ecosystem services, the benefits gained by humans from ecosystems. History During the 1990s, international conventions such as the UNEP Convention on Biological Diversity and the Convention to Combat Desertification identified the need for a global scientific ecosystem assessment. There had been advances in resource economics with little effect on environmental policy. In November 1998, UNEP, NASA, and the World Bank published a study called "Protecting our Planet, Securing our Future: Linkages Among Global Environmental Issues and Human Needs". In 2001, the Millennium Ecosystem Assessment was launched with work over a period of four years. Over 1300 contributors from 95 countries were involved as authors. F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |