|
Eburonian
The Eburonian (german: Eburon or ''Eburonium''), or, much less commonly, the Eburonian Stage, is a glacial complex in the Calabrian age of the Pleistocene epoch and lies between the Tegelen and the Waalian interglacial. The transition from the Tegelen to the Eburonian started about 1.78 million years ago, lasted 480,000 years (to 1.3 million years ago). In geologic strata, at its base, from its startpoint, the Neogene underlies different Gelasian deposits starkly in much of the Netherlands.Hey, R. W. ''The Plio-Pleistocene of England and Iceland'' in Van Couvering, John A. (editor), (1997) ''The Pleistocene Boundary and the Beginning of the Quaternary'', Cambridge, Cambridge University Press, p. 183. . Discovery As early as the 1920s, the names of the three well known glaciations - the Elster, the Saale and the Weichselian - had become established at the recommendation of Konrad Keilhack and Paul Woldstedt. After Penck & Brückner successfully identified a fourth glaciation in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menapian Glaciation
The Beestonian Stage is an early Pleistocene stage used in the British Isles. It is named after Beeston Cliffs near West Runton in Norfolk where deposits from this stage are preserved. The Beestonian precedes the Cromerian Stage and follows the Pastonian Stage. This stage consists of alternating glacial and interglacial phases instead of being a continuous glacial epoch. It is equivalent to Marine isotope stages 22 to (60?).Walker, M., 2005, ''Quaternary Dating Methods'', John Wiley & Son, Chichester, United Kingdom. Gibbard, P.L., S. Boreham, K.M. Cohen and A. Moscariello, 2007''Global chronostratigraphical correlation table for the last 2.7 million years v. 2007b'', jpg version 844 KB. Subcommission on Quaternary Stratigraphy, Department of Geography, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, England The Beestonian Stage and Marine Isotope Stage 22 ended about 866,000 years ago.Lisiecki, L.E., 2005Ages of MIS boundaries. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beestonian Stage
The Beestonian Stage is an early Pleistocene stage used in the British Isles. It is named after Beeston Cliffs near West Runton in Norfolk where deposits from this stage are preserved. The Beestonian precedes the Cromerian Stage and follows the Pastonian Stage. This stage consists of alternating glacial and interglacial phases instead of being a continuous glacial epoch. It is equivalent to Marine isotope stages 22 to (60?).Walker, M., 2005, ''Quaternary Dating Methods'', John Wiley & Son, Chichester, United Kingdom. Gibbard, P.L., S. Boreham, K.M. Cohen and A. Moscariello, 2007''Global chronostratigraphical correlation table for the last 2.7 million years v. 2007b'', jpg version 844 KB. Subcommission on Quaternary Stratigraphy, Department of Geography, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, England The Beestonian Stage and Marine Isotope Stage 22 ended about 866,000 years ago. Lisiecki, L.E., 2005Ages of MIS boundaries. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calabrian (stage)
Calabrian is a subdivision of the Pleistocene Epoch of the geologic time scale, defined as 1.8 Ma—774,000 years ago ± 5,000 years, a period of ~. The end of the stage is defined by the last magnetic pole reversal (781 ± 5 Ka) and plunge into an ice age and global drying possibly colder and drier than the late Miocene ( Messinian) through early Pliocene (Zanclean) cold period. Originally the Calabrian was a European faunal stage primarily based on mollusk fossils. It has become the second geologic age in the Early Pleistocene. Many of the mammalian faunal assemblages of the Early Pleistocene start in the Gelasian. For example, the Platygonus and other Blancan fauna appear first in the Gelasian. History of the definition of the Calabrian Because sea shells are much more abundant as fossils, 19th- and early-20th-century geo-scientists used the plentiful and well-differentiatable Mollusca (mollusks) and Brachiopods to identify stratigraphic boundaries. Thus the Calabrian was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek grc, label=none, πλεῖστος, pleīstos, most and grc, label=none, καινός, kainós (latinized as ), 'new'. At the end of the preceding Pliocene, the previously isolated North and South American continents were joined by the Isthmus of Panama, causing Great American Interchang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglian Stage
The Anglian Stage is the name used in the British Isles for a middle Pleistocene glaciation. It precedes the Hoxnian Stage and follows the Cromerian Stage in the British Isles. The Anglian Stage is correlated to Marine Isotope Stage 12 (MIS 12), which started about 478,000 years ago and ended about 424,000 years ago. Lisiecki, L.E. (2005Ages of MIS boundaries. Boston MA:Boston University Description The Anglian stage has often been correlated to the Elsterian Stage of northern Continental Europe and the in the |
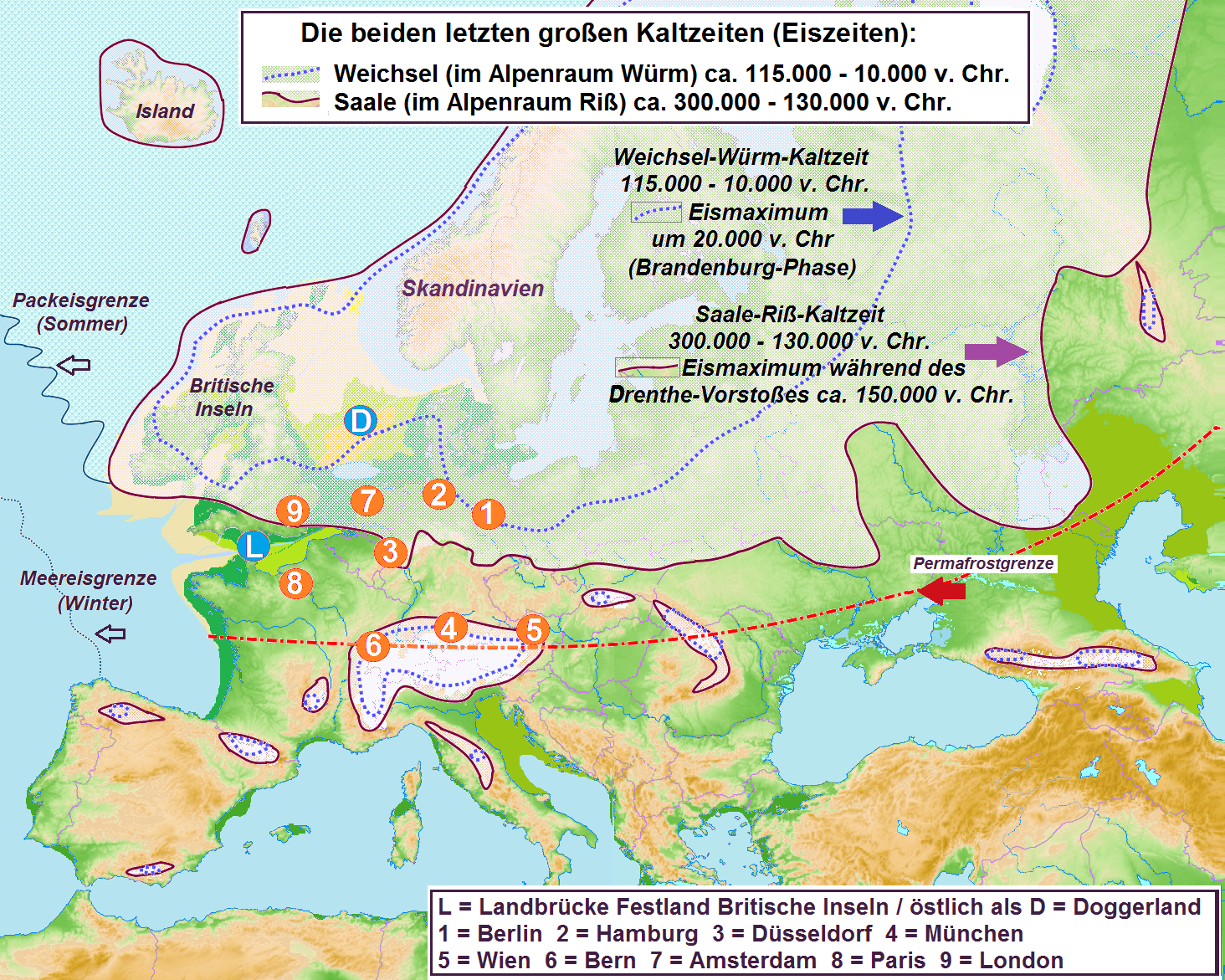
Saalian
The Saale glaciation or Saale Glaciation, sometimes referred to as the Saalian glaciation, Saale cold period (german: Saale-Kaltzeit), Saale complex (''Saale-Komplex'') or Saale glacial stage (''Saale-Glazial'', colloquially also the ''Saale-Eiszeit'' or ''Saale-Zeit''), covers the middle of the three large glaciations in Northern Europe and the northern parts of Eastern, Central and Western Europe by the Scandinavian Inland Ice Sheet between the older Elster glaciation and the younger Weichselian glaciation, also called the Last Glacial Period. Age and definitions It succeeded the Holstein interglacial and was followed by the Eemian interglacial. The Saale complex is currently estimated, depending on the source, as existing from around 300,000 to 130,000 years ago or 347,000 to 128,000 years ago (duration: around 219,000 years), roughly contemporaneous with the glaciation of the Riss Glacial in the Alpine region. The actual "ice age" includes only part of the Saale glaciation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elsterian
The Elster glaciation (german: Elster-Kaltzeit, ''Elster-Glazial'' or ''Elster-Zeit'') or, less commonly, the Elsterian glaciation, in the older and popular scientific literature also called the Elster Ice Age (''Elster-Eiszeit''), is the oldest known ice age that resulted in the large-scale glaciation of North Germany. It took place 500,000–300,000 years ago. It succeeded a long period of rather warmer average temperatures, the Cromerian Complex. The Elster was followed by the Holstein interglacial and the Saale glaciation. The glacial period is named after the White Elster, a right tributary of the Saale. Controversial correlations Traditionally, Elster was correlated with the Mindel glaciation of the Alps and the Anglian glaciation of Great Britain and Ireland. Analysis in the 1950s of oxygen isotopes in deep sea core samples introduced a global glacial history, with warm and cold phases identified by marine isotope stages (MIS). This identified two glacial stages in the ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elster Cold Period
The Elster glaciation (german: Elster-Kaltzeit, ''Elster-Glazial'' or ''Elster-Zeit'') or, less commonly, the Elsterian glaciation, in the older and popular scientific literature also called the Elster Ice Age (''Elster-Eiszeit''), is the oldest known ice age that resulted in the large-scale glaciation of North Germany. It took place 500,000–300,000 years ago. It succeeded a long period of rather warmer average temperatures, the Cromerian Complex. The Elster was followed by the Holstein interglacial and the Saale glaciation. The glacial period is named after the White Elster, a right tributary of the Saale. Controversial correlations Traditionally, Elster was correlated with the Mindel glaciation of the Alps and the Anglian glaciation of Great Britain and Ireland. Analysis in the 1950s of oxygen isotopes in deep sea core samples introduced a global glacial history, with warm and cold phases identified by marine isotope stages (MIS). This identified two glacial stages in the ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saale Complex
The Saale glaciation or Saale Glaciation, sometimes referred to as the Saalian glaciation, Saale cold period (german: Saale-Kaltzeit), Saale complex (''Saale-Komplex'') or Saale glacial stage (''Saale-Glazial'', colloquially also the ''Saale-Eiszeit'' or ''Saale-Zeit''), covers the middle of the three large glaciations in Northern Europe and the northern parts of Eastern, Central and Western Europe by the Scandinavian Inland Ice Sheet between the older Elster glaciation and the younger Weichselian glaciation, also called the Last Glacial Period. Age and definitions It succeeded the Holstein interglacial and was followed by the Eemian interglacial. The Saale complex is currently estimated, depending on the source, as existing from around 300,000 to 130,000 years ago or 347,000 to 128,000 years ago (duration: around 219,000 years), roughly contemporaneous with the glaciation of the Riss Glacial in the Alpine region. The actual "ice age" includes only part of the Saale glaciation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wolstonian Stage
The Wolstonian Stage is a middle Pleistocene stage of the geological history of Earth from approximately 374,000 until 130,000 years ago. It precedes the Eemian Stage in Europe and follows the Hoxnian Stage in the British Isles. It is also approximately analogous to the Warthe and Saalian stages in northern Europe; the Riss glaciation in the Alps; and the Illinoian Stage in North America. It is equivalent to Marine isotope stages (MIS) 10 through 6. MIS 10, 8 and 6 were glacial periods and 9 and 7 were interglacials. It is named after Wolston in the English county of Warwickshire. Description The Wolstonian Stage is a middle Pleistocene stage of the geological history of Earth that precedes the Ipswichian Stage (Eemian Stage in Europe) and follows the Hoxnian Stage in the British Isles. The Wolstonian Stage apparently includes three periods of glaciation. The Wolstonian Stage is temporally analogous to the Warthe Stage and Saalian Stage in northern Europe and the Riss glaci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiglian
The Tiglian, also referred to as the Tegelen, is a temperate complex stage in the glacial history of Northern Europe. It is preceded by the Praetiglian (stage). The stage was introduced by Zagwijn in 1957 based on geological formations in Tegelen in southern Netherlands. Originally, it was thought to be part of a sequence of glacials and interglacials, namely Praetiglian (cold), Tiglian (warm), Eburonian (cold), Waalian (warm), Menapian (cold), and Bavelian (warm). The Praetiglian and Tiglian are today regarded as corresponding to the Biber stage in the glacial history of the Alps and to the Gelasian (2.6-1.8 million years ago) in the global division of the Quaternary period. Deep sea core samples have identified approximately 40 marine isotope stages (MIS 103 – MIS 64) during the Gelasian. Thus, there have probably been about 20 glacial cycles of varying intensity during Praetiglian and Tiglian. The dominant trigger is believed to be the 41 000 year Milankovitch cycles of axia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waalian Interglacial
The Waalian interglacial (german: Waal-Warmzeit or ''Waal-Interglazial'') or Waalian Stage was an interglacial period of the Early Pleistocene in north-west Europe. It was preceded by the Eburonian Stage and succeeded by the Menapian Stage. It coincides with part of the much longer Beestonian stage in Britain. It is variously dated by different authorities. Oxford Reference gives 1.3 to 0.9 million years ago and the British Geological Survey 1.6 to 1.36 million years ago. However, the 2020 chart of the international authority on stratigraphic dating, the International Commission on Stratigraphy shows it as c. 1.6 to 1.4 million years ago. Its name is derived from a major branch of the Rhine delta, the Waal WAAL (99.1 FM "The Whale") is a commercial radio station licensed to Binghamton, New York. It airs a classic rock radio format and is owned by Townsquare Media. WAAL is the oldest FM radio station in the Binghamton metropolitan area. It is an .... References {{North ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |