|
Ebira People
The Ebira also known as Egbira people are an ethno-linguistic group of central Nigeria. Most Ebira people are from Kogi State, Nasarawa State. Until the separation of Kogi State from Kwara State, Okene was seen as the administrative centre of the Ebira-speaking people in Kogi state ,located not far from the Niger- Benue confluence. Since the formation of the state, the Ebira Ta'o people are found in four local governments namely: Adavi, Ajaokuta, Okehi and Okene each with their administration headquarters. Ebira Koto are found in Kogi and KotonKarfe LGA, Bassa LGA, Lokoja in Kogi and Abaji LGA in the Federal Capital Territory, and Nasarawa in Toto LGA. Another, the Eganyi are found in Ajaokuta LGA. And the Etuno can be found in Igarra town of Akoko-Edo LGA, Edo state. Geography In recent history, Ebira people inhabit a territory south-west of the confluence of the Niger and Benue Rivers though some Ebira communities also reside north-east of the confluence, the territory surround ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ebira Language
Ebira (pronounced as /eh 'be ra/; also known as Igbira, Egbura, or Okene) is a Niger-Congo language. It is spoken by around 2 million people in North central Nigeria Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf o .... It is the most divergent Nupoid language. Dialects Varieties of Ebira are:Blench, Roger. 2013. The Nupoid languages of west-central Nigeria: overview and comparative word list'. *Tao dialect, the more prominent dialect used in media and publishing. It is spoken to the west of the Niger-Benue confluence *Koto (Okpoto) dialect, spoken to the northeast of the Niger-Benue confluence. It is known only from a wordlist in Sterk (1978a). Blench (2019) lists Okene, Etuno (Tụnọ), and Koto. References Nupoid languages {{VoltaNiger-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
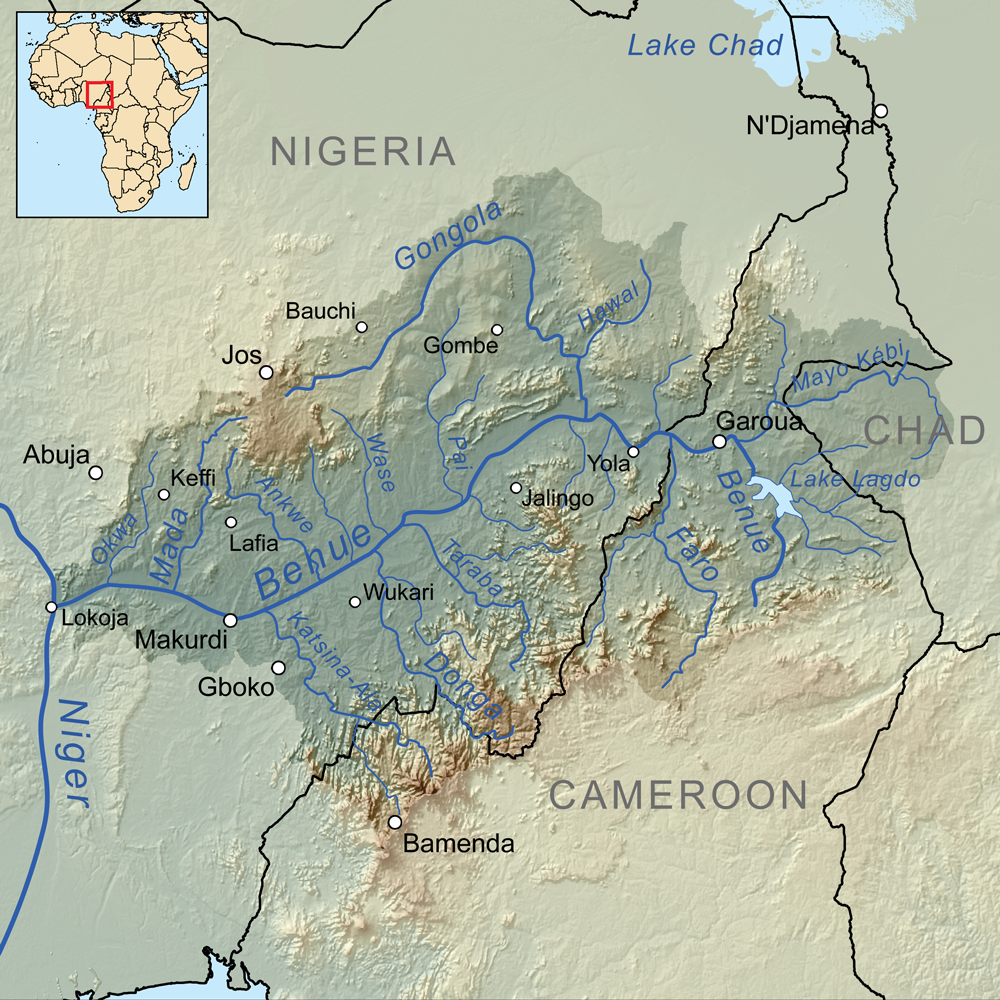
Lokoja
Lokoja is a city in Nigeria. It lies at the confluence of the Niger and Benue rivers and is the capital city of Kogi State. While the Yoruba (Oworo), Bassa Nge and Nupe are indigenous to the area, other ethnic groups of Nigeria, including the Kupa-Nupe, Hausa, Ebira, Igala, Igbo, Bini/Edo, and Tiv have recently established themselves. Projected to be the third fastest growing African continent city between 2020 and 2025, with a 5.93% growth. It was listed a second class township by the 1917 township ordinance of the colonial administration. This shows that Lokoja is an old city. Etymology Different ethnic groups lay claim to having named the city. * The Yoruba ( Oworo ) people believe the name comes from ''Ilu Oke Oja'' ("The settlement located on the hill did not fall"). * The Hausa believe the name comes from ''Loko Ja'' ("A red corner") and that the city was named by the emir of Zazzau. * The Nupe believe the name comes from ''Patti Lukongi'' ("The hill of doves"). * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hausa People
The Hausa ( autonyms for singular: Bahaushe ( m), Bahaushiya ( f); plural: Hausawa and general: Hausa; exonyms: Ausa; Ajami: ) are the largest native ethnic group in Africa. They speak the Hausa language, which is the second most spoken language after Arabic in the Afro-Asiatic language family. The Hausa are a diverse but culturally homogeneous people based primarily in the Sahelian and the sparse savanna areas of southern Niger and northern Nigeria respectively, numbering around 83 million people with significant indigenized populations in Benin, Cameroon, Ivory Coast, Chad, Sudan, Central African Republic, Republic of the Congo, Togo, Ghana, Eritrea, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Senegal and the Gambia. Predominantly Hausa-speaking communities are scattered throughout West Africa and on the traditional Hajj route north and east traversing the Sahara, with an especially large population in and around the town of Agadez. Other Hausa have also moved to large coastal cities in the re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerontocracy
A gerontocracy is a form of oligarchical rule in which an entity is ruled by leaders who are significantly older than most of the adult population. In many political structures, power within the ruling class accumulates with age, making the oldest the holders of the most power. Those holding the most power may not be in formal leadership positions, but often dominate those who are. In a simplified definition, a gerontocracy is a society where leadership is reserved for elders. Although the idea of the elderly holding power exists in many cultures, the gerontocracy has its western roots in ancient Greece. Plato famously stated that "it is for the elder man to rule and for the younger to submit". One example of the ancient Greek gerontocracy can be seen in the city state of Sparta, which was ruled by a ''Gerousia'', a council made up of members who were at least 60 years old and who served for life. In political systems Elders had leadership roles in many tribal societies. In the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
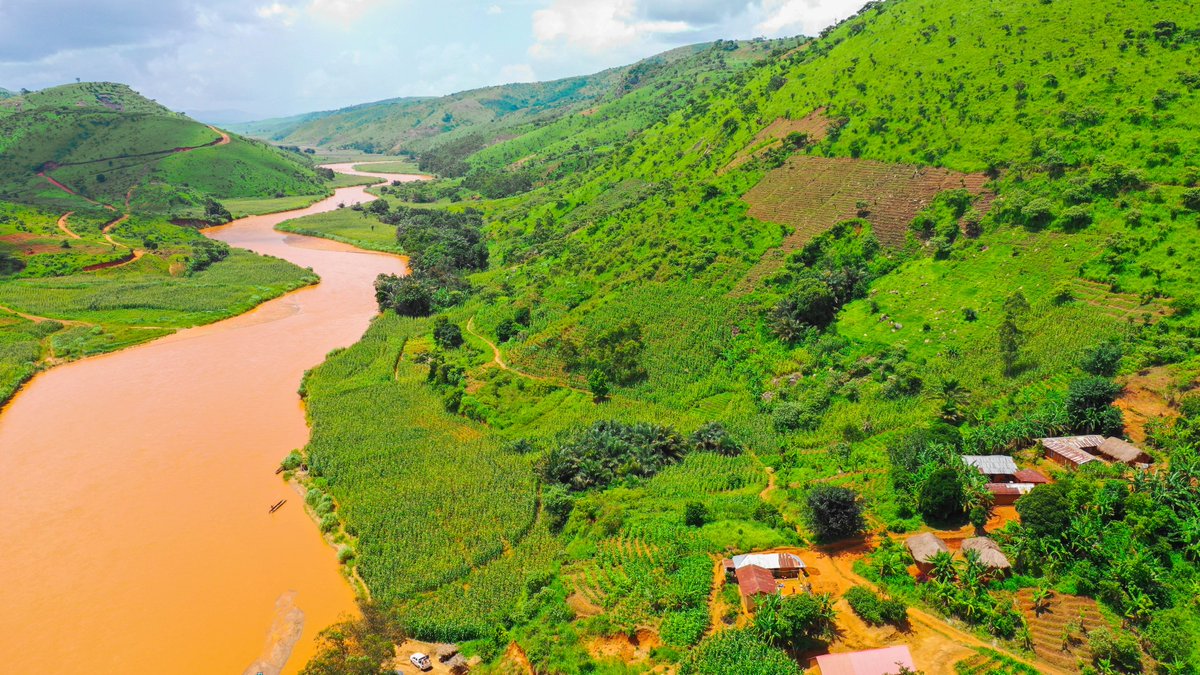
River Niger
The Niger River ( ; ) is the main river of West Africa, extending about . Its drainage basin is in area. Its source is in the Guinea Highlands in south-eastern Guinea near the Sierra Leone border. It runs in a crescent shape through Mali, Niger, on the border with Benin and then through Nigeria, discharging through a massive delta, known as the Niger Delta (or the Oil Rivers), into the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean. The Niger is the third-longest river in Africa, exceeded by the Nile and the Congo River. Its main tributary is the Benue River. Etymology The Niger has different names in the different languages of the region: * Fula: ''Maayo Jaaliba'' * Manding: ''Jeliba'' or ''Joliba'' "great river" * Tuareg: ''Egerew n-Igerewen'' "river of rivers" * Songhay: ''Isa'' "the river" * Zarma: ''Isa Beeri'' "great river" * Hausa: ''Kwara'' *Nupe: ''Èdù'' * Yoruba: ''Ọya'' "named after the Yoruba goddess Ọya, who is believed to embody the river" * Igbo: ''Ori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taraba State
) , image_map = Nigeria - Taraba.svg , map_alt = , map_caption = Location of Taraba State in Nigeria , coordinates = , coor_pinpoint = , coordinates_footnotes = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = , established_title = Date created , established_date = 27 August 1991 , seat_type = Capital , seat = Jalingo , government_footnotes = , governing_body = Government of Taraba State , leader_name = Darius Ishaku , leader_party = PDP , leader_title = Governor (List) , leader_title1 = , leader_name1 = Haruna Manu ( PDP) , leader_title2 = Legislature , leader_name2 = Taraba State House of Assembly , leader_title3 = Senators , leader_name3 = , leader_title4 = Representatives ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kwararafa
Kororofa (Kwararafa in Hausa) was a multiethnic state and/or confederacy centered along the Benue River valley in what is today central Nigeria. It was southwest of the Bornu Empire and south of the Hausa States. They rose to prominence before 1500, were in conflict with their more powerful neighbours in the 17th century, and reduced to a small tribute state by the 18th century.H. J. Fisher. The Sahara and Central Sudan. in The Cambridge History of Africa: From C 1600 to C 179. Richard Gray, J. D. Fage, Roland Anthony Oliver, eds. Cambridge University Press, (1975) pp. 134-136 It is believed that Kwararafa was either a confederacy conquest state, led by the modern Jukun people or perhaps a collective name given by their Muslim foes for a number of pagan peoples to their south. Regardless, a spiritually important pagan Jukun priest-kingship at Wukari appears to have been the centre of Kwararafa power, but in the 17th century, that may have spread much farther. Leo Africanus r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jukun People (West Africa)
Jukun (''Njikum'') are an ethno-linguistic group or ethnic nation in West Africa . The Jukun are traditionally located in Taraba, Benue, Nasarawa, Plateau, Adamawa, and Gombe States in Nigeria and parts of northwestern Cameroon . They are descendants of the people of Kwararafa . Most of the tribes in the north central of Nigeria trace their origin to the Jukun people and are related in one way or the other to the Jukuns . Until the coming of both Christianity and Islam, the Jukun people were followers of their own traditional religions. Most of the tribes, Alago, Agatu, Rendere, Goemai in Shendam, and others left Kwararafa when it disintegrated as a result of a power tussle . The Jukuns are divided into two major groups; the Jukun Wanu and Jukun Wapa . The Jukun Wanu are fishermen residing along the banks of the river Benue and Niger where they run through Taraba State, Benue State and Nasarawa State. The Wukari Federation, headed by the Aku Uka of Wukari, is now the main cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colonialism
Colonialism is a practice or policy of control by one people or power over other people or areas, often by establishing colonies and generally with the aim of economic dominance. In the process of colonisation, colonisers may impose their religion, language, economics, and other cultural practices. The foreign administrators rule the territory in pursuit of their interests, seeking to benefit from the colonised region's people and resources. It is associated with but distinct from imperialism. Though colonialism has existed since ancient times, the concept is most strongly associated with the European colonial period starting with the 15th century when some European states established colonising empires. At first, European colonising countries followed policies of mercantilism, aiming to strengthen the home-country economy, so agreements usually restricted the colony to trading only with the metropole (mother country). By the mid-19th century, the British Empire gave up me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deciduous
In the fields of horticulture and Botany, the term ''deciduous'' () means "falling off at maturity" and "tending to fall off", in reference to trees and shrubs that seasonally shed leaves, usually in the autumn; to the shedding of petals, after flowering; and to the shedding of ripe fruit. The antonym of ''deciduous'' in the botanical sense is evergreen. Generally, the term "deciduous" means "the dropping of a part that is no longer needed or useful" and the "falling away after its purpose is finished". In plants, it is the result of natural processes. "Deciduous" has a similar meaning when referring to animal parts, such as deciduous antlers in deer, deciduous teeth (baby teeth) in some mammals (including humans); or decidua, the uterine lining that sheds off after birth. Botany In botany and horticulture, deciduous plants, including trees, shrubs and herbaceous perennials, are those that lose all of their leaves for part of the year. This process is called abscissio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kabba
Kabba is a city in Kogi State in mid west Nigeria. It lies near the Osse River, at the intersection of roads from Lokoja, Okene, Ogidi, Ado-Ekiti, and Egbe. The town is about 295 kilometers away from Abuja. It is 511 kilometers from Lagos. Archbishop John Olorunfemi Onaiyekan, of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Abuja, based in Abuja, Nigeria, was born there, according to his Wikipedia article. Description Kabba was the administrative headquarters of the Kabba province of the defunct Northern Region of Nigeria, which includes all of the current Kogi State. Kabba is a trade centre for coffee, cocoa, yams, cassava, maize, sorghum, shea nuts, peanuts (groundnuts), beans, cotton, and woven cloth produced by the Yoruba, Ebira, and other peoples of the surrounding area. Kabba people speak a dialect of the Yoruba Language called Owe. Kabba is the headquarters of the Kabba/Bunnu local government area of Kogi state and the current Chairman of Kabba/Bunu Local Government is Hon.E. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etsakọ People
The Etsakọ people are the majority ethnic group in the northern region of Edo State, Nigeria. They are historically linked to the ancient Benin kingdom. Administratively, they presently occupy three local government areas of Edo State these are; Etsako East, Etsako West and Etsako Central, with Agenebode, Auchi, and Fugar as their administrative headquarters respectively The people of Owan are also known as Etsako. The Etsako,Owan, and Akoko-Edo people are often referred to as the Afenmai (Edo North), a land of warriors occupying the sprawling hills and valleys of Northern Edo state, that were derogatorily tagged Kukuruku people by the invading colonialist, in memory of the rallying "battle cry" code-sound of the people. Afenmai people have close linguistic and historical relationships. The local tradition of origin often traces their migration from Benin, which many oral traditionalists attribute probably to have happened around the 14th century BC. It is believed thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


%2C_scene_at_the_river_front.jpg)