|
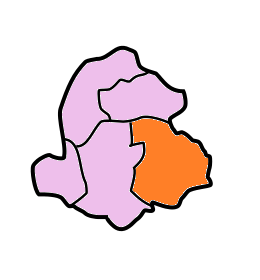
East Jaintia Hills District
East Jaintia Hills district is a district with its headquarters at Khliehriat in Meghalaya state of India. The district was carved out of Jaintia Hills district on 31 July 2012. Khliehriat and Saipung are the two community and rural development blocks of the district. History East Jaintia Hills District was carved out of the erstwhile Jaintia Hills District on 31 July 2012. Khliehriat, the district headquarters, was created as an administrative unit on August 14, 1976 and was upgraded to a civil sub division on May 27, 1982 before finally becoming the district headquarters. Geography The total area of the district is . The district comprises 2 community and rural development blocks viz. Khliehriat C&RD Block, and Saipung C&RD Block with the following boundaries: * North - Assam and West Jaintia Hills District * South - Bangladesh and Assam * East - Assam * West - West Jaintia Hills District Divisions East Jaintia Hills district is divided into two blocks, namely: Demographic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Districts Of Meghalaya ...
The Indian state of Meghalaya is divided into 12 districts. Districts Meghalaya currently has 12 districts: References {{Districts of India Districts Meghalaya Meghalaya (, or , meaning "abode of clouds"; from Sanskrit , "cloud" + , "abode") is a states and union territories of India, state in northeastern India. Meghalaya was formed on 21 January 1972 by carving out two districts from the state of As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaintia Hills Subdivisions Saipung
Jaintia may refer to: * Jaintia people, also known as Synteng or Pnar, a tribe of Meghalaya, India * Jaintia language, spoken by the Jaintia people * Jaintia Kingdom, a former kingdom in present-day North-East India * Jaintia Hills district Jaintia Hills District was a district in Meghalaya, India that was established in 1972 with headquarters at Jowai which was taken from the United Khasi Jaintia Hills District Council. It was once part of the ancient Jaintia Kingdom. The present i ..., an administrative district in Meghalaya, India See also * Jaintiapur Upazila, an administrative division of Bangladesh * Jaintia Rajbari, residence of Kings of Jaintia Kingdom {{disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Districts Of Meghalaya ...
The Indian state of Meghalaya is divided into 12 districts. Districts Meghalaya currently has 12 districts: References {{Districts of India Districts Meghalaya Meghalaya (, or , meaning "abode of clouds"; from Sanskrit , "cloud" + , "abode") is a states and union territories of India, state in northeastern India. Meghalaya was formed on 21 January 1972 by carving out two districts from the state of As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Jaintia Hills District
East Jaintia Hills district is a district with its headquarters at Khliehriat in Meghalaya state of India. The district was carved out of Jaintia Hills district on 31 July 2012. Khliehriat and Saipung are the two community and rural development blocks of the district. History East Jaintia Hills District was carved out of the erstwhile Jaintia Hills District on 31 July 2012. Khliehriat, the district headquarters, was created as an administrative unit on August 14, 1976 and was upgraded to a civil sub division on May 27, 1982 before finally becoming the district headquarters. Geography The total area of the district is . The district comprises 2 community and rural development blocks viz. Khliehriat C&RD Block, and Saipung C&RD Block with the following boundaries: * North - Assam and West Jaintia Hills District * South - Bangladesh and Assam * East - Assam * West - West Jaintia Hills District Divisions East Jaintia Hills district is divided into two blocks, namely: Demographic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Language
War (also spelled Waar), also known as War-Jaintia, is an Austroasiatic language spoken by about 16,000 people in Bangladesh and 51,000 people in India.Sidwell, Paul. 2018. ''The Khasian Languages: Classification, Reconstruction, and Comparative Lexicon''. Languages of the World 58. Munich: Lincom Europa. The language is spoken by the ''War Khasi tribe'', i.e. ''War'' sub-tribe of Khasi people. See also * Languages of India Languages spoken in India belong to several language families, the major ones being the Indo-European languages spoken by 78.05% of Indians and the Dravidian languages spoken by 19.64% of Indians, both families together are sometimes known ... References Khasian languages Languages of Bangladesh Languages of India Languages of Meghalaya {{AustroAsiatic-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khasi Language
Khasi () is an Austroasiatic language with just over a million speakers in north-east India, primarily the Khasi people in the state of Meghalaya. It has associate official status in some districts of this state. The closest relatives of Khasi are the other languages of the Khasic group; these include Pnar, Lyngngam and War. Khasi is written using the Latin and Bengali-Assamese scripts. Geographic distribution and status Khasi is natively spoken by people in India (as of 2011). It is the first language of one third of the population of Meghalaya, or , and its speakers are mostly found in the Khasi Hills and Jaintia Hills regions. There are also small Khasi-speaking communities in neighouring states of India, the largest of which is in Assam: people. There is also a very small number of speakers in Bangladesh. Khasi has been an associate official language of some districts within Meghalaya since 2005, and as of 2012, was no longer considered endangered by UNESCO. There ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biate Language
Biate is a Sino-Tibetan language spoken by the Biate people in several parts of Northeast India: in Meghalaya, Assam, Mizoram, Manipur and Tripura. Biate is pronounced as Bia-te (the e in te pronounced as "a"). Geographical distribution Biate is spoken in the following locations ('' Ethnologue''). *Assam: Dima Hasao (formerly North Cachar) and Cachar districts. *Meghalaya: East Jaintia Hills, West Jaintia Hills and East Khasi Hills districts. *Manipur *Mizoram *Tripura Tripura (, Bengali: ) is a state in Northeast India. The third-smallest state in the country, it covers ; and the seventh-least populous state with a population of 36.71 lakh ( 3.67 million). It is bordered by Assam and Mizoram to the ea ... Basic vocabulary Numbers Biate calendar Names of months Names of weeks References Languages of Assam Languages of Manipur Languages of Meghalaya Languages of Mizoram Endangered languages of India {{st-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pnar Language
Pnar (), also known as Jaiñtia is an Austroasiatic language spoken in India and Bangladesh Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the mos .... Phonology Pnar has 30 phonemes: 7 vowels and 23 consonants. Other sounds listed below are phonetic realizations. Vowels There is also one diphthong: /ia/. Consonants Syllable structure Syllables in Pnar can consist of a single nucleic vowel. Maximally, they can include a complex onset of two consonants, a diphthong nucleus, and a coda consonant. A second type of syllable contains a syllabic nasal/trill/lateral immediately following the onset consonant. This syllabic consonant behaves as the rhyme. (Ring, 2012: 141–2) References * * External links * http://projekt.ht.lu.se/rwaai RWAAI (Repository and Workspace for Aus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biate People
The Biates are one of the hill tribes of Assam, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Tripura and Manipur. Their language belongs to the Tibeto-Burman family. Spread over many parts of North-East India, they have a unique identity with a rich and distinctive history, culture, dialect and religious heritages. They are one of the oldest hill tribes of North East India especially among the Chin-Kuki-Mizo family. The term Biate comes from the word Bia-te. The word ‘Bia’ or ‘Biak’ means ‘speak’ or ‘worship’. ‘Te’ is a suffix denoting plurality. Hence, the two words combine to form the word ''Biate'', which means ''worshipper''. According to legends, while they were in Saitual, a group of people known as the Koilam or Kawilam from Rulchawm village of Mizoram (India) used to sacrifice human to appease a large python called Rulpui, believing that the snake had supernatural power. Thus, some writers are of the opinion that the word Biate originates from the term ''Rul-Bia-Te'' or ''Rul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pnar People
The Pnar, also known as Jaiñtia, are a sub-tribal group of the Khasi people in Meghalaya, India. The Pnar people are matrilineal. They speak the Pnar Language, which belongs to the Austro-Asiatic language family and is very similar to the Khasi language. The Pnar people are natives of West Jaintia Hills and East Jaintia Hills District of Meghalaya, India. They call themselves as "Ki Khun Hynñiew Trep" (Children of 7-hut). Their main festivals are Behdeinkhlam, Chad Sukra, Chad Pastieh and Laho Dance. Etymology The name "Pnar" is an endonym, while "Jaiñtia" and "Synteng" are exonyms. The word "Jaiñtia" is derived from the name of a former kingdom, the Jaintia Kingdom, whose rulers were Syntengs. One theory says that the word "Jaiñtia" is ultimately derived from the name of the shrine of Jayanti Devi or Jainteswari, an incarnation of the Hindu goddess Durga. Another theory says that the name is derived via Synteng from ''Sutnga'', a former settlement; the myth of Jayanti D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribal Religions In India
Roughly 8.6 per cent of India's population is made up of so-called "Scheduled Tribes" (STs), traditional tribal communities. Whilst most members of these tribes have adopted variants of Hinduism, Islam, or Christianity, a considerable number still adhere to their traditional tribal religions, with varying degrees of syncretism. Numbers According to the 2011 census of India, about 7.9 million out of 1,210 million people did not adhere to any of the subcontinent's main religious communities of Hinduism, Islam, Christianity, Sikhism, Buddhism, or Jainism. The census listed atheists, Zoroastrians, Jews, and various specified and unspecified tribal religions separately under the header "Other Religions and Persuasions". Of these religious census groupings, the most numerous are Sarnaism, listed variously in the census as ''Sarna'' (4.9 million respondents), '' Saridharma'' (506,000), and ''Santal'' (6,500); Koyapunem (1 million respondents); Donyi-Poloism (331,000); and Khasi (139,00 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
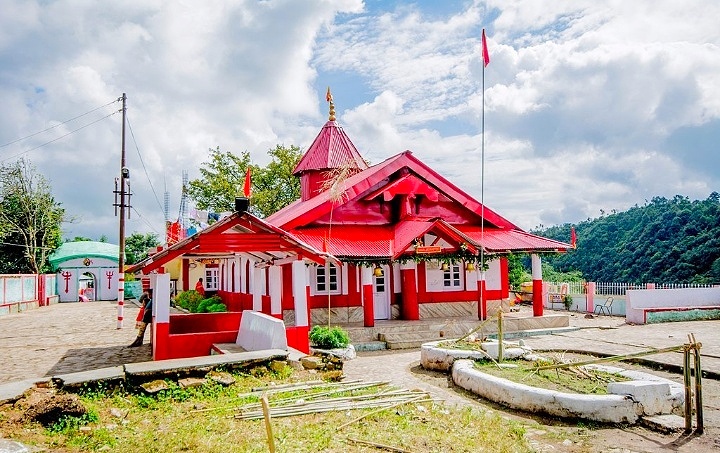
Hinduism In Meghalaya
Hinduism is a minority religion in the Meghalaya state of India constituting 12% of the state's population. The Nartiang Durga Temple in Meghalaya is one of the 51 Shakti peethas on Earth and is considered by Hindus of Meghalaya as the permanent abode of Goddess Durga. Hinduism is a popular religion practice by Rabhas, Hajongs, Kochs, Rajbongshis, Mikirs, Bengalis, Nepalis, Biharis etc. Tradition Festivals Hinduism is practiced by different groups of Meghalaya. Hindus celebrate many festivals in Meghalya. Diwali, Behdienkhlam, Navaratri, etc. are celebrated by people. Navaratri and other Goddess Pujas are celebrated mainly by Bengali people. Diwali is celebrated by almost all Hindus. Behdienkhlam is celebrated by Pnar/Jaintia Hindus with Niamatre believers. In Jowai, Behdienkhlam is a harvest festival celebrate by Hindus and Niamatre believers. This festival is popular among non-Christian Pnar people(Jaintia). Many other Hindu festivals celebrate Hindus like Makar Sankran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |