|
Earth Gravitational Model
The Earth Gravitational Models (EGM) are a series of geopotential models of the Earth published by the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA). They are used as the geoid reference in the World Geodetic System. The NGA provides the models in two formats: as the series of numerical coefficients to the spherical harmonics which define the model, or a dataset giving the geoid height at each coordinate at a given resolution. Three model versions have been published: EGM84 with n=m=180, EGM96 with n=m=360, and EGM2008 with n=m=2160. n and m are the degree and orders of harmonic coefficients; the higher they are, the more parameters the models have, and the more precise they are. EGM2008 also contains expansions to n=2190. Developmental versions of the EGM are referred to as Preliminary Gravitational Models (PGMs). Each version of EGM has its own EPSG code as a vertical datum. History EGM84 The first EGM, EGM84, was defined as a part of WGS84. WGS84 combines the old GRS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
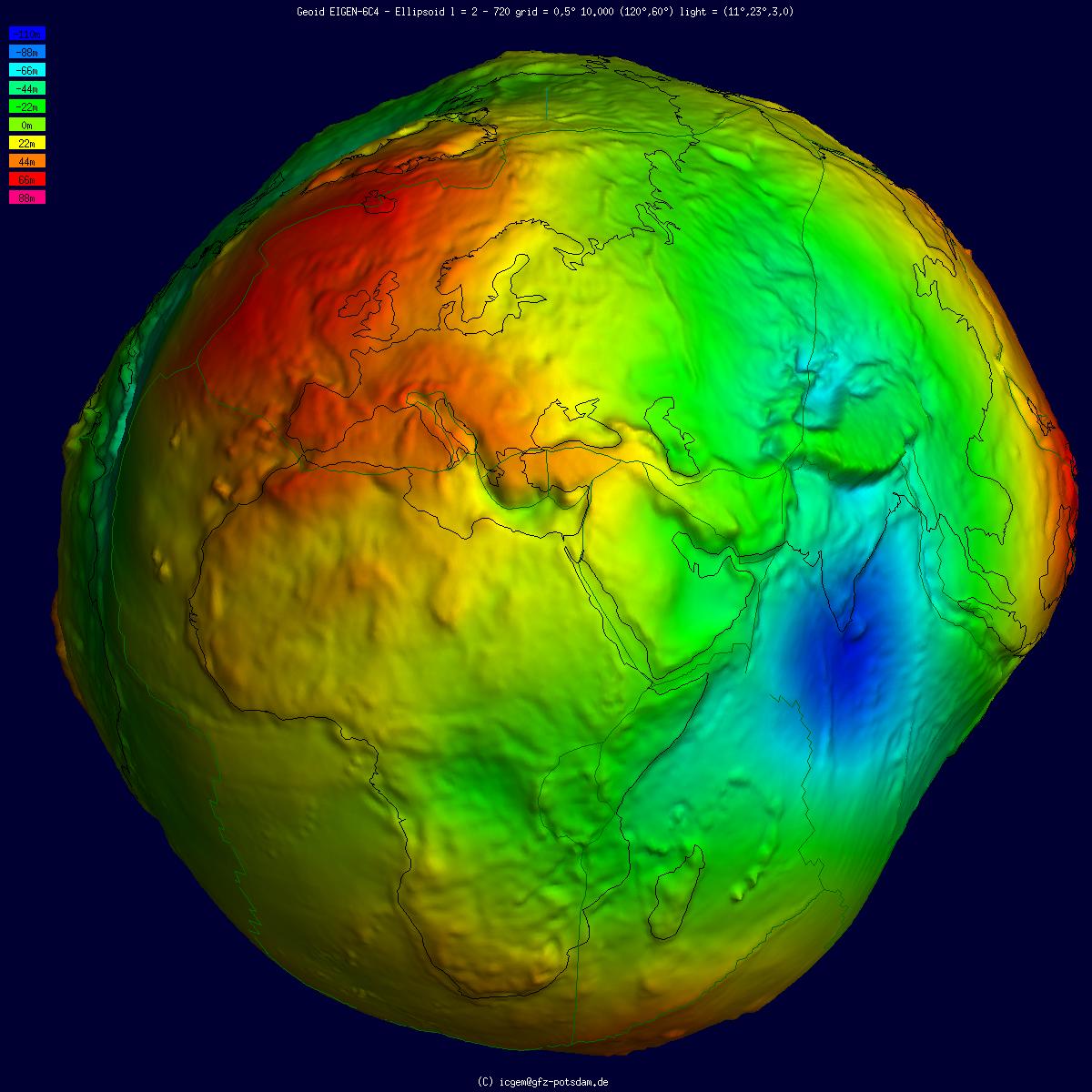
Geoid
The geoid () is the shape that the ocean surface would take under the influence of the gravity of Earth, including gravitational attraction and Earth's rotation, if other influences such as winds and tides were absent. This surface is extended through the continents (such as with very narrow hypothetical canals). According to Gauss, who first described it, it is the "mathematical figure of the Earth", a smooth but irregular surface whose shape results from the uneven distribution of mass within and on the surface of Earth. It can be known only through extensive gravitational measurements and calculations. Despite being an important concept for almost 200 years in the history of geodesy and geophysics, it has been defined to high precision only since advances in satellite geodesy in the late 20th century. All points on a geoid surface have the same geopotential (the sum of gravitational potential energy and centrifugal potential energy). The force of gravity acts everywher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth Gravitational Model 1996
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surface is made up of the ocean, dwarfing Earth's polar ice, lakes, and rivers. The remaining 29% of Earth's surface is land, consisting of continents and islands. Earth's surface layer is formed of several slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth's liquid outer core generates the magnetic field that shapes the magnetosphere of the Earth, deflecting destructive solar winds. The atmosphere of the Earth consists mostly of nitrogen and oxygen. Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere like carbon dioxide (CO2) trap a part of the energy from the Sun close to the surface. Water vapor is widely present in the atmosphere and forms clouds that cover most of the planet. More solar energy is rec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
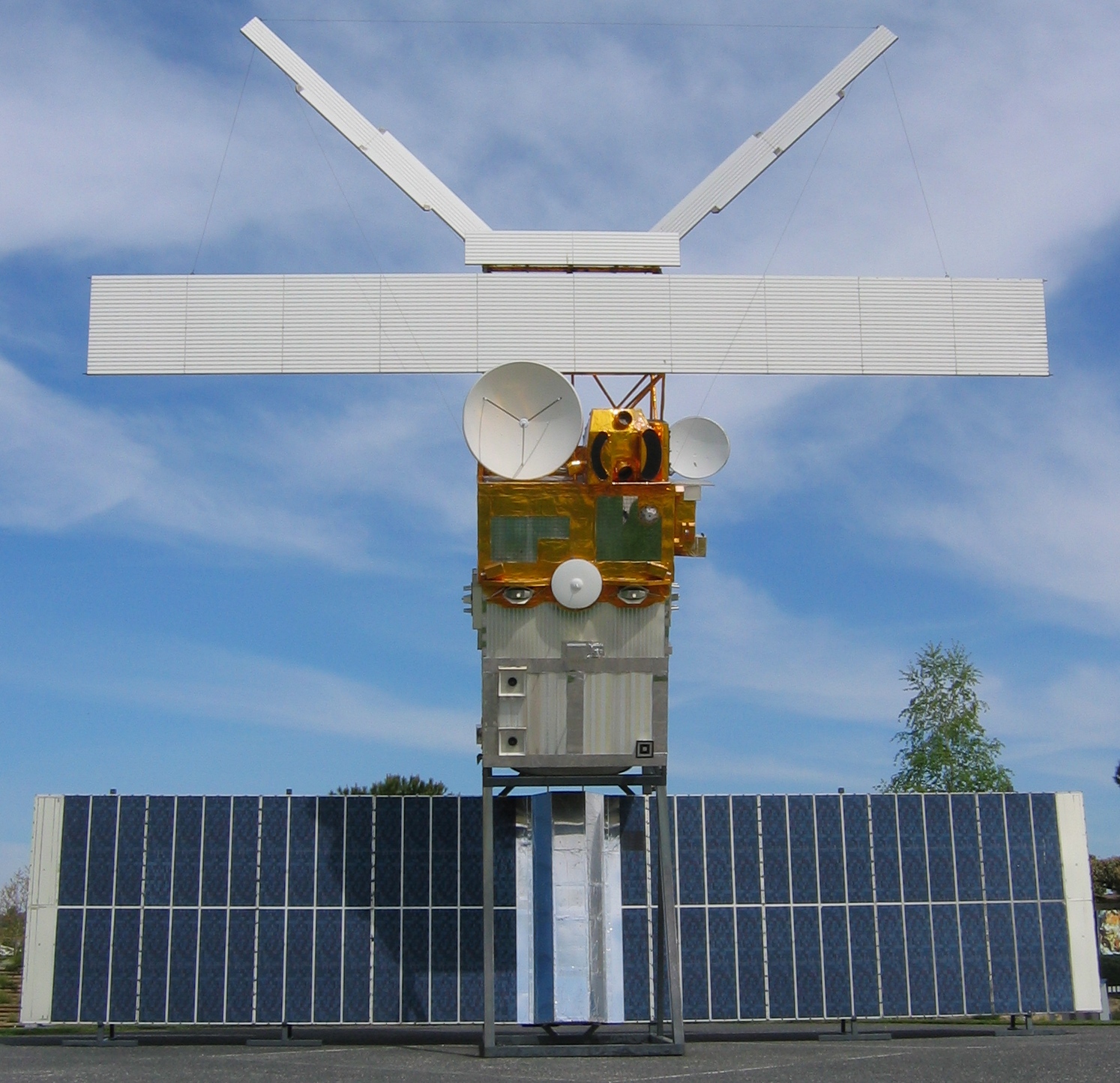
European Remote-Sensing Satellite
European Remote Sensing satellite (ERS) was the European Space Agency's first Earth-observing satellite programme using a polar orbit. It consisted of 2 satellites, ERS-1 and ERS-2. ERS-1 ERS-1 launched 17 July 1991 from Guiana Space Centre aboard an Ariane 4 rocket. The satellite was put into a Sun-synchronous polar orbit at an altitude of 782–785 km. ERS-1 failed on 10 March 2000 after nine years in orbit. Instruments ERS-1 carried an array of Earth-observation instruments that gathered information about the Earth (land, water, ice and atmosphere) using a variety of measurement principles. These included: * RA (Radar Altimeter) is a single frequency nadir-pointing radar altimeter operating in the Ku band. * ATSR-1 ( Along-Track Scanning Radiometer) is a 4 channel infrared radiometer and microwave sounder for measuring temperatures at the sea-surface and the top of clouds. * SAR ( synthetic-aperture radar) operating in C band can detect changes in surface h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Naval Research Laboratory
The United States Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) is the corporate research laboratory for the United States Navy and the United States Marine Corps. It was founded in 1923 and conducts basic scientific research, applied research, technological development and prototyping. The laboratory's specialties include plasma physics, space physics, materials science, and tactical electronic warfare. NRL is one of the first US government scientific R&D laboratories, having opened in 1923 at the instigation of Thomas Edison, and is currently under the Office of Naval Research. As of 2016, NRL was a Navy Working Capital Fund activity, which means it is not a line-item in the US Federal Budget. Instead of direct funding from Congress, all costs, including overhead, were recovered through sponsor-funded research projects. NRL's research expenditures were approximately $1 billion per year. Research The Naval Research Laboratory conducts a wide variety of basic research and applied r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WGS84
The World Geodetic System (WGS) is a standard used in cartography, geodesy, and satellite navigation including GPS. The current version, WGS 84, defines an Earth-centered, Earth-fixed coordinate system and a geodetic datum, and also describes the associated Earth Gravitational Model (EGM) and World Magnetic Model (WMM). The standard is published and maintained by the United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency. Definition The coordinate origin of WGS 84 is meant to be located at the Earth's center of mass; the uncertainty is believed to be less than . The WGS 84 meridian of zero longitude is the IERS Reference Meridian, European Organisation for the Safety of Air Navigation and IfEN: WGS 84 Implementation Manual, p. 13. 1998 5.3 arc seconds or east of the Greenwich meridian at the latitude of the Royal Observatory. (This is related to the fact that the local gravity field at Greenwich doesn't point exactly through the Earth's center of ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NAD83
The North American Datum (NAD) is the horizontal datum now used to define the geodetic network in North America. A datum is a formal description of the shape of the Earth along with an "anchor" point for the coordinate system. In surveying, cartography, and land-use planning, two North American Datums are in use for making lateral or "horizontal" measurements: the North American Datum of 1927 (NAD 27) and the North American Datum of 1983 (NAD 83). Both are geodetic reference systems based on slightly different assumptions and measurements. Vertical measurements, based on distances above or below Mean High Water (MHW), are calculated using the North American Vertical Datum of 1988 (NAVD 88). NAD 83, along with NAVD 88, is set to be replaced with a new GPS- and gravimetric geoid model-based geometric reference frame and geopotential datum in 2022. First North American Datum of 1901 In 1901 the United States Coast and Geodetic Survey adopted a national horizontal dat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ETRS89
The European Terrestrial Reference System 1989 (ETRS89) is an ECEF (Earth-Centered, Earth-Fixed) geodetic Cartesian reference frame, in which the Eurasian Plate as a whole is static. The coordinates and maps in Europe based on ETRS89 are not subject to change due to the continental drift. The development of ETRS89 is related to the global ITRS geodetic datum, in which the representation of the continental drift is balanced in such a way that the total apparent angular momentum of continental plates is about 0. ETRS89 was officially born at the 1990 Florence meeting of EUREF, following its Resolution 1, which recommends that the terrestrial reference system to be adopted by EUREF will be coincident with ITRS at the epoch 1989.0 and fixed to the stable part of the Eurasian Plate. According to the resolution, this system was named European Terrestrial Reference System 89 (ETRS89). Since then ETRS89 and ITRS diverge due to the continental drift at a speed about 2.5 cm per y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spheroidal Harmonic
Spheroidal wave functions are solutions of the Helmholtz equation that are found by writing the equation in spheroidal coordinates and applying the technique of separation of variables, just like the use of spherical coordinates lead to spherical harmonics. They are called ''oblate spheroidal wave functions'' if oblate spheroidal coordinates are used and ''prolate spheroidal wave functions'' if prolate spheroidal coordinates are used. If instead of the Helmholtz equation, the Laplace equation is solved in spheroidal coordinates using the method of separation of variables, the spheroidal wave functions reduce to the spheroidal harmonics. With oblate spheroidal coordinates, the solutions are called ''oblate harmonics'' and with prolate spheroidal coordinates, ''prolate harmonics''. Both type of spheroidal harmonics are expressible in terms of Legendre functions. See also * Oblate spheroidal coordinates, especially the section ''Oblate spheroidal harmonics'', for a more extensive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portable Graymap File Format
Netpbm (formerly Pbmplus) is an open-source package of graphics programs and a programming library. It is used mainly in the Unix world, where one can find it included in all major open-source operating system distributions, but also works on Microsoft Windows, macOS, and other operating systems. File formats Several graphics formats are used and defined by the Netpbm project. The portable pixmap format (PPM), the portable graymap format (PGM) and the portable bitmap format (PBM) are image file formats designed to be easily exchanged between platforms. They are also sometimes referred to collectively as the portable anymap format (PNM), not to be confused with the related portable arbitrary map format (PAM). The "magic number" (Px) at the beginning of a file determines the type, not the file extension, although it is best practice to use the right extension if possible. The PBM format was invented by Jef Poskanzer in the 1980s as a format that allowed monochrome bitmaps to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spherical Harmonics
In mathematics and physical science, spherical harmonics are special functions defined on the surface of a sphere. They are often employed in solving partial differential equations in many scientific fields. Since the spherical harmonics form a complete set of orthogonal functions and thus an orthonormal basis, each function defined on the surface of a sphere can be written as a sum of these spherical harmonics. This is similar to periodic functions defined on a circle that can be expressed as a sum of circular functions (sines and cosines) via Fourier series. Like the sines and cosines in Fourier series, the spherical harmonics may be organized by (spatial) angular frequency, as seen in the rows of functions in the illustration on the right. Further, spherical harmonics are basis functions for irreducible representations of SO(3), the group of rotations in three dimensions, and thus play a central role in the group theoretic discussion of SO(3). Spherical harmonics originate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GRACE And GRACE-FO
The Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) was a joint mission of NASA and the German Aerospace Center (DLR). Twin satellites took detailed measurements of Earth's gravity field anomalies from its launch in March 2002 to the end of its science mission in October 2017. The GRACE Follow-On (GRACE-FO) is a continuation of the mission on near-identical hardware, launched in May 2018. By measuring gravity anomalies, GRACE showed how mass is distributed around the planet and how it varies over time. Data from the GRACE satellites is an important tool for studying Earth's ocean, geology, and climate. GRACE was a collaborative endeavor involving the Center for Space Research at the University of Texas at Austin, NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, the German Aerospace Center and Germany's National Research Center for Geosciences, Potsdam. The Jet Propulsion Laboratory was responsible for the overall mission management under the NASA ESSP (Earth System Science Pathfinder) progra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |